* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polygon
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
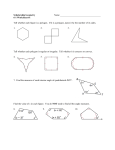
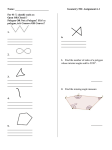
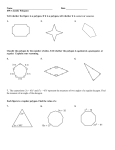
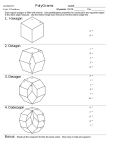
Teacher Notes Polygons Objective: To identify and name polygons; to find the sum of the measures of interior and exterior angles of convex and regular polygons; to solve problems involving angle measures of polygons. Terms of Importance Polygon – A closed figure formed by a finite number of coplanar segments such that the sides that have a common endpoint are noncollinear and each side intersects exactly two other sides, but only at their endpoints. Convex Polygon – A polygon such that no line containing a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon. Examples of convex polygons are Concave Polygon – A polygon such that lines containing a side of the polygon that contains a point in the interior of the polygon. Examples of concave polygons are n-gon – A polygon with n sides. Number of Sides 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 N Polygon Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon Heptagon Octagon Nonagon Decagon Hendecagon Dodecagon n-gon For other names of polygons go to … http://www.gomath.com/htdocs/ToGoSheet/Geometry/polygon_name.html Regular Polygon – A convex polygon with all sides and all angles congruent. Theorems Interior Angle Sum Theorem – If a convex polygon has n sides and S is the sum of the measures of its interior angles, then S = 180(n – 2). Examples Find the sum of a convex polygon that has 3 sides. S = 180(3 – 2) S = 180 Find the measure of each interior angle of a regular hexagon. First find the sum of all of the angles in a hexagon S = 180(6 – 2) S = 720 To find the measure of each interior angle, divide the sum of the angles by the number of angles in the hexagon 720/6 or 120 Exterior Angle Sum Theorem – If a polygon is convex, then the sum of the measures of the exterior angles, one at each vertex, is 360. Example Use the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem to find the measure of an interior angle and an exterior angle of a regular pentagon. A regular pentagon has 5 congruent interior angles. So the measure of each exterior angle is 360/5 or 72 Because each exterior angle is supplementary to each interior angle, the measure of each interior angle is 180 – 72 or 108