* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 Section 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
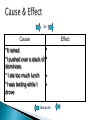
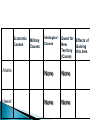
As the age of industrialization comes to a close, the United States begins to look beyond its shores toward expansionism. Why??? Imperialism Ideology Lilioukalani Stanford Dole Cause Effect So Cause Effect *It rained *I pushed over a stack of dominoes * I ate too much lunch *I was texting while I drove * * * * Because Examine the emergence of the United States as a World Power Understand the 4 causes of Imperialism as they relate to the expansion into Alaska and Hawaii Understand what cause and effect mean Be able to discuss the causes and effects of Imperialism Alaska had been settled by Russian fur traders in the late 1700’s, but by 1867 fur sources were becoming scarce. In addition, Russia was struggling to recover from the Crimean War. As a result, Russia offered to sell Alaska to the United States. Overcoming strong opposition from Congress, Secretary of State, William Seward bought Alaska for $7.2 million in 1867. Critics scoffed at “Seward’s folly” thinking that the territory was a frozen wasteland. But after gold and oil were discovered, Americans appreciated the bargain. Seward also acquired the Midway islands that same year. Why was Russian interested in selling Alaska? Why did many people think Secretary of State Seward had made a big mistake? Were they right? Explain. Main Idea: The United States extended its power and influence in the Pacific Expansion of a country’s control over other lands By the late 1800’s Great Britain, Germany, France, Belgium, and Japan had all begun imperialist activity. Economic interests: ◦ Looking for new markets (places to sell the goods they were mass producing) ◦ Looking for new places to invest their money ◦ Looking for new sources of raw materials Military Needs ◦ Strong navies and militaries needed places to stop and refuel or repair their ships Ideology ◦ Nationalism: strong love of one’s country ◦ Cultural Superiority: Social Darwinism This works in 2 ways: superiority and the right to conquer foreign lands, the ethical duty to help uncivilized inhabitants of other countries Scramble for Territory ◦ By 1800’s Great Britain controlled 25% of the world’s land and population ◦ Americans began to believe that it was their turn to expand the country What 4 main ideas inspired imperialist activity of the late 1800’s? ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ The quest for new markets The search for new raw materials Military and refueling bases The desire for more territory The ideology of nationalism and Social Darwinism Russia offered to sell Alaska to the United States for $7.2 million Secretary of State William Seward was eager to buy it for its resources of fur, timber, and metals Congress thought it was a “frozen wasteland” and opposed the purchase Seward proceeded with the purchase and was ridiculed by the public. After gold and oil were discovered, they appreciated the bargain they had gotten. Currently, Alaska produces approximately 363,000 ounces of gold each year. The current price of pure gold is approximately $900 per ounce. About how much money is Alaska gaining from its gold mining alone? Answer: $326 million Crude oil Forestry and Lumber Seafood Natural defense from Russia Great position for military or commercial shipping http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gIq8x9vnL f4 In the late 1800’s the United States became interested in Hawaii Decided it was an ideal spot for fueling stations and military bases Hawaii’s 8 islands were united under Chief Kamehameha in a monarchy. It operated a successful trade in sandalwood Soon missionaries (Social Darwinists) and families began to settle and raise crops, especially sugarcane Foreigners also brought diseases which killed great numbers of Hawaiians. Changing the native population from 300,000 to 40,000 Sugar planters grew very rich Early on, King Kamehameha allied himself with landowners and negotiated a treat to allow free trade of sugar into the United States. Landowners wanted more and more power over Hawaii Groups of American landowners and businessmen created a secret society called the “Hawaiian League” to overthrow the King The United States wanted Pearl Harbor in exchange for renewing the sugar treaty, but King Kamehameha refused to give up any part of Hawaiian lands. The Hawaiian League forced King Kamehameha to sign a new constitution under gunpoint giving Pearl Harbor to the United States. This constitution was called the “Bayonet Constitution” When King Kamehameha died in 1891 his sister, Liliuokalani became queen. She wanted to do away with the bayonet constitution John L Stevens, the U.S. Minister to Hawaii, ordered 4 boatloads of U.S. Marines ashore . They surrounded the palace with machine guns and cannons and forced Liliuokalani to surrender the monarchy He proclaimed Hawaii a republic with Sanford B Dole as president, under the protection of the United States while Congress decided on Annexation President Grover Cleveland was troubled by the events and put everything on hold pending an investigation The investigation condemned what occurred and proposed reinstating the monarchy. President Cleveland agreed but Dole refused to step down Historically, the Hawaiian Pineapple Company had a hand in the hostile overthrow of Hawaii's last queen, Liliuokalani, and the establishment of Hawaii as a U.S. territory. Sanford Dole, the cousin of James Dole, was briefly president of the Republic of Hawaii in the years immediately following the overthrow of the Hawaiian monarchy, in 1893 When William McKinnley became president, he supported annexation, which occurred in 1898 In 1959 it became the 50th state of the United States In 1993 President Clinton and Congress signed and apology to the Hawaiian people. How did the United States take control of Hawaii? ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Took over the land and the economy Forced chief to sign the bayonet constitution Forced the queen to surrender Annexed the territory Why was Hawaii an ideal location acquisition for the United States? ◦ It was in an ideal spot for refueling and military bases ◦ It had a profitable sugar industry ◦ Hawaii’s current crops include sugar, pineapple, orchids, macadamia nuts, coffee, and papaya Ideological Causes Quest for Effects of New Gaining Territory this area (Cause) Alaska None None Hawaii None None Economic Causes Military Causes What is a cause? What is an effect? What is Imperialism? Who was Queen Lilioukalani? Who was Stanford Dole? What were the 4 major causes of Imperialism? In retrospect, was Hawaii a good investment/purchase for the U.S.? Why was Hawaii a good addition for the United States? What role did the sugar trade play in the annexation of Hawaii? W Write a 1-3 paragraph essay explaining the causes and effects of Imperialism in Alaska and Hawaii Adapted Homework: (With permission only) Prepare a list of causes and effects and present it orally to me tomorrow during tutorial period. China remained isolated and was not even industrialized In 1842 Great Britain forced China to open 5 ports for trade Russia, France, Germany, and Great Britain controlled “Spheres of Influence”, an area that they had special economic or political control over. U.S. became concerned that they did not have a sphere of influence, so they proposed the Open Door Policy Yellow: France Orange: Britain Green: Germany Purple: Japan Red: Russia Open Door Policy was deigned to give all countries equal trading rights in China Sent notes to other countries supporting the open door policy No one else accepted it Back in China…. Chinese nationalists formed a secret society called the Society of Rightous and Harmonious fists They began attacking Chinese Christians, and missionaries In June 1900, the boxers attacked Bejing Western Nations sent 20,000 troops, (2,000 were Americans) who stopped the rebellion Proposed the Open Door Policy Sent troops to put down the boxer rebellion Forced China to sign a settlement treaty How did the Boxer rebellion actually help the United States? Provided increased support for the Open Door Policy What motivated the Boxers to attack foreigners in Bejing? Resentment & anger toward foreign influences Desire to push foreigners out What affect did the open door policy have of China? Allowed foreign influence Exploited the resources of China Allowed missionaries into the country Since the 1600’s Japan was relatively cut off from the rest of the world (on purpose) U.S. began pressuring Japan to open up for trade In 1854 it agreed to open for trade, then went through a rapid period of modernization and industrialization. It began to want to expand into Manchuria (which Russia also wanted) In 1904 Russo-Japanese war broke out. After about 1 ½ years Japan asked the U.S. to help negotiate a peace treaty. President Theodore Roosevelt received a Nobel Peace Prize for negotiating the treaty. Japan emerged as the victor and as a major world power. President Roosevelt was concerned about Japan’s intentions for expansion and sent a military expedition of 4 squadrons of battleships around the world, stopping in Japan to impress upon them not to threaten the U.S. How did the United States exert influence in Japan? ◦ By displaying military power ◦ Negotiating a treaty to end the Russo-Japanese war What large territory did the United States purchase from Russia in 1867? What did Queen Liliuokalani surrender to the United States in 1893? In 1854 what Asian country was pressured to open itself to United States trade? Draw a timeline Add important events that occurred from 1850-the mid 1900’s that affected the United States’ policy of expansionism. There should be at least 10 events on the timeline