* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Notes from Mr. Martin
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
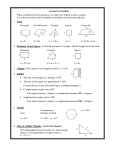
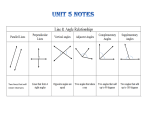
Types of quadrilaterals rhombus Geometry Notes NAME of Shape triangle quadrilateral pentagon hexagon heptagon octagon decagon # of sides 3 sides 4 sides 5 sides 6 sides 7 sides 8 sides 10 sides Type of Triangle Equilateral Isosceles Scalene Right Triangle Has 2 sets of parallel lines and all lines are of equal length. Has one set of parallel lines and 2 lines are of equal length. Has 2 sets of parallel lines Has 2 sets of parallel lines and all 4 sides are equal. Has 2 sets of parallel lines and 2 sets of equal length lines. trapezoid Paralleogram square rectangle Description All 3 sides are of equal length 2 sides of equal length no sides equal length has a right angle Name of Angle Acute angle Obtuse angle Right angle Straight angle Complimentary angles Supplementary angles Description Less than 90° Greater than 90°and less than 180° Equal to 90° Equal to 180° 2 angles that equal 90° 2 angles that equal 180° This is a compass. It is used to draw circles. d Diameter: A line which passes through the center, from side to side. Radius: A line from the center to a point on the circumference r π is the symbol “pi” We will use the number 3.14 for π Circle Formulas Cicumference: the line around the outside of a circle. It is the perimeter of the circle. The radius is always ½ of the diameter. This means that the diameter is always 2x (twice) the radius. Circumference of a circle = of the circumference. Area of a circle = πr² πd This means you multiply 3.14 x the length of the diameter to find the length This means you multiply 3.14 x the radius x the radius Rectangles: Are quadrilaterals and parallelograms. They have 2 sets of parallel lines and four 90º angles. To find the perimeter of a rectangle, simply add up all four sides. Remember to add up 4 sides. If I label only 2 sides, you must figure out the length of the unlabelled sides. This is easy because the 2 long sides are equal and the 2 shorts sides are equal. Find the perimeter of this rectangle: The perimeter of this rectangle will be 12+12+5+5= 34 cm. Perimeter: Just add up all the sides. Length 12 cm Width 5 cm Area: Length x width Now find the area. The formula for the area of a rectangle is A= l x w (length x width) So 12 cm x 5 cm = 60 cm² The area is 60 cm² Finding the missing angle: To find the missing angle in any triangle or quadrilateral you need to remember this: All the angles in a triangle add up to 180º and all the angles in any quadrilateral add up to 360º Since all the angles of a triangle must equal 180º, I know that 60º + 40º + X = 180º. 60º 40º 180º X must be 80º , because 60º+40º+80º=180º Xº Try another: Find the missing angle in this quadrilateral. 110º 80º 80º Xº WJM VIII Mr. Martin said that all the angles in any quadrilateral must equal 360º, so that means 110º + 80º + 80º + Xº = 360º. X must be 90º, because 110º + 80º + 80º + 90º = 360º Triangles Side 15cm A= ½bh This is a right triangle because it has a right (90°) angle. height 10cm Triangle formula: To find the area of a triangle: A= ½bh means you multiply ½ of the base x the height. Example: Find the area of this triangle. base 6cm In this case ½ of the base = 3cm (½ of 6 is 3) and the height is 10 cm. So 3 x 10 = 30 cm² The area of this triangle is 30 cm The height must be a line perpendicular (can’t be slanted or diagonal) to the base. Height 10cm Side 12cm The area of this triangle (A= ½bh ) will be 6 X 10=60cm² The base is 12cm, so half of 12cm is 6cm. The height is 10cm so 6 X 10 = 60 Side 12cm Base 12cm Two triangles make a quadrilateral: Height or width base or length The area of a rectangle is A= l x w which is the same as saying A= b X h. A triangle is half of this. or A = b x h Why is a triangle ½ of the rectangle? Look at the two triangles making a rectangle. Notice how they make half of a rectangle? That’s why the formula for a triangle is ½ b x h because a triangle is half the rectangle. Geometry of Cubes. Cubes have: 6 faces (sides) 8 vertices (corners) Vertices is the plural of vertex 12 edges. (edges) This is a pattern (aka jacket) which can be folded into a cube. It is made of six congruent squares. (I tried anyways) It is a solid figure, or a 3D shape. Face Edge Vertex FORMULAS To calculate the area of each face simply multiply the length by the width. A = l x w To calculate the surface area of a cube: find the area of one face and then multiply by 6. To calculate the volume of a cube multiply length by width by height V=l xwxh Length width WJM VIII Formulas: Remember that two letters beside each other means Multiply them together. l= length; w = width; b = base; h = height; r = radius; c=circumference Area of a Rectangle A=lw Area of a Parallelogram A= bh Area of a Triangle A = ½bh Area of a Circle A = r2 (=3.14) Circumference of a Circle C = 2r Volume of a Cube V = lwh Volume of a Sphere V = (4/3)r3 Volume of a Cone V = (1/3)r2h Volume of a Cylinder V = r2h Surface Area of a Sphere A = 4r2