* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
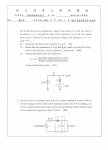
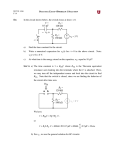
AL-Essay-A.C. / p.1 1. (89-IIA-6) (a) Derive, from first principles, expressions for the energies stored by (i) a pure capacitor of capacitance C charged by a voltage V0 , and (ii) (b) a pure inductor of inductance L through which a current (5 marks) The charged capacitor in (a)(i) is isolated and then connected across the inductor in (a)(ii). Show that the charge on the capacitor varies with subsequent time t as Q Q0 cos 0 t , and obtain a value for (c) I 0 flows. 0 . (4 marks) Draw a phasor diagram for a series LCR circuit connected across a signal generator of voltage V V0 cos t . Derive the condition for the maximum stored energies of the inductor and the capacitor to be the same. (d) (5 marks) With reference to the stored energies, compare the two physical situations described in parts (b) and (c). (2 marks) 2. (91-IIA-4b,c) (b) A series circuit is formed from a coil of inductance 500 H, a 2 V light bulb, an open switch and a 2 V battery. Explain your expected observations when (i) the switch is closed and (ii) after connecting a neon lamp across the coil, the switch is opened. (4 marks) (c) Draw a circuit which can be used to observe the periodic variations of current I together with those of an applied a.c. voltage V for the coil of (b). Explain mathematically the phase difference you would expect between I and V. (6 marks) 3. (93-IIA-5) (a) (i) Briefly describe an experiment to investigate the r.m.s. current in an LRC series circuit for different frequencies of an a.c. supply. (No mathematical derivation is expected.) (ii) Sketch a graph showing how the r.m.s. current in the circuit varies with the applied frequency. Account for the shape of the curve with the aid of phasor diagrams. (i) Sketch, on the same graph in (ii), the curves for (I) smaller resistance; (II) larger resistance. (11 marks) (b) The figure shows a simplified tuning circuit for radio receivers. (i) (ii) 4. Explain its operation. Suggest a method to improve the reception performance of the circuit. Explain briefly. (5 marks) (95-IIB-4b,c) (b) What is the physical meaning of the reactance of a capacitor? On what factor does the reactance of a capacitor depend? (2 marks) AL-Essay-A.C. / p.2 (c) 5. Briefly explain the actions of the two capacitors and the inductor in the following smoothing circuit. (6 marks) (00-IIB-4) (a) (i) (ii) (b) Explain the meaning of the marking ’50 V 470 F’ on a capacitor. Explain qualitatively the meaning of self induction by referring to a coil with a decreasing current. (3 marks) A charged ideal capacitor is connected across an ideal inductor. d 2Q 1 Q The charges Q oscillating in the circuit satisfies LC dt 2 (i) 6. Sketch a graph to show the time variation of the energies in the capacitor and the inductor within a period. (ii) Through energy considerations, make an analogy between this capacitor-inductor circuit and the mass-spring system. State the quantities in the mass-spring system that ‘correspond’ to the charge, the current, the capacitance and the inductance. (Assume no energy loss in both cases.) (iii) Explain why it would be difficult to sustain such an electromagnetic oscillation in practice. With the aid of a graph, describe how the current in the circuit actually varies with time. (10 marks) (c) When each of the components, a resistor, a capacitor and an inductor, is connected to a sinusoidal a.c. supply of variable frequencies, describe how its impedance varies with the applied frequency. Hence explain, with the aid of a circuit diagram, how two of them can be employed to obtain the low frequency component(s) from a multi-frequency a.c. signal. (3 marks) (03-IIB-4b,c) (b) A source of sinusoidal a.c. voltage is applied across a coil of resistance R and inductance L./ (i) Sketch the graphs of current and voltage V=Vosin(2ft) of the coil against time for 2fL>>Rand explain their phase relationship. (ii) Illustrate the difference between resistance and reactance by stating their physical meaning. Explain why the size of the current depends on the frequency f of the source. (5 marks) (c) The figure shows the circuit for a power pack. (i) (ii) Briefly explain how the rectification unit ABCE works. Sketch and explain the output voltage if capacitor and inductor L are absent. Sketch the voltage across L as well as the output voltage. Account for their shapes by explaining the respective functions of C2 and L. (6 marks)