* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Upper Merion Area High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
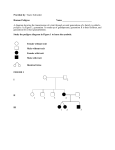
Upper Merion Area High School Biology I Pedigree Lab Name______________________________________ Background: 1. What is a pedigree? 2. Why is a pedigree done (two purposes)? 3. What is a carrier? 4. How is a dominant trait inherited, human example? 5. How is a recessive trait inherited, human example? 6. Describe how a co-dominant trait can be identified, give a human example? 7. Describe how a sex-linked trait can be identified, give a human example? Purpose (why are we doing this pedigree?) Hypothesis: (Write an if/then statement considering the trait of an individual what their parents traits would have to be). Materials: Method: Using a fictious family description you are going to create their family pedigree. The family will then be assigned a trait. You as a genetic councilor will identify how the trait was inherited. 1. Using the family description draw the family pedigree. Members of the same generation should be on the same horizontal line All individuals must be labeled with their name. 2. Using the list of affected individuals identify (shade in) all the individuals with the trait Carriers or Heterozygous should be half shaded 3. Create a key that shows the normal, affected, and heterozygous individuals. Data: Attach the pedigree chart, with the trait labeled, and key included. Generations in line, neat Individuals named Pedigree is correct Key and Trait on Pedigree Individuals with trait identified Carriers/Heterozygous identified Analysis: 1. How many generations are there on your pedigree? 2. Who was: Rowena to AnnetteCharles to TamiPenelope to MikeEthel to BernitoStu to FifiNancy to Luanne3. Name the trait, and describe how was the trait inherited (dominant, recessive, sex linked, or co-dominance)? 4. Why do you think it was inherited by this method (three reasons)? 5. What was your hypothesis is it supported?