* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arteries
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Large intestine wikipedia , lookup
Lymphatic system wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Vascular remodelling in the embryo wikipedia , lookup
William Harvey wikipedia , lookup
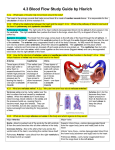
The Blood Vessels ~The Vascular System Ch 20 Leonardo Da Vinci Human Anatomy Sonya Schuh-Huerta, Ph.D. Types of Blood Vessels • Arteries carry blood Away from the heart • Capillaries smallest blood vessels – The site of exchange of molecules between blood & tissue fluid • Veins carry blood toward the heart Structure of Blood Vessels • Composed of 3 layers (= tunics) – Tunica intima endothelium; composed of simple squamous epithelium – Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle • Contraction = vasoconstriction • Relaxation = vasodilation – Tunica externa composed of C.T. • Lumen – Central blood-filled space of a vessel Structure of Blood Vessels Tunica intima Endothelium Subendothelial layer Internal elastic membrane Tunica media (smooth muscle and elastic fibers) Valve External elastic membrane Tunica externa (collagen fibers) Lumen Artery Capillary network Lumen Vein Basement membrane Endothelial cells (b) Capillary Structure of Arteries, Veins, & Capillaries Vein Artery (a) Structure of Arteries, Veins, & Capillaries Lab iScopy Pix Types of Arteries • Elastic arteries the largest arteries – – – – Diameters range from 2.5 cm to 1 cm Includes the aorta and its major branches Sometimes called conducting arteries High elastin content dampens surge of BP Vasa vasorum Elastin Lumen Tunica Tunica Tunica externa media intima (a) Elastic artery (aorta, 12) Types of Arteries • Muscular (“distributing”) arteries – Lie distal to elastic arteries – Diameters range from 1 cm to 0.3 mm – Includes most named arteries – Tunica media is thick – Unique feature • Internal & external elastic laminae External Internal Lumen elastic elastic membrane membrane Tunica Tunica externa media (b) Muscular artery (40) Types of Arteries • Arterioles – Smallest arteries – Diameters range from 0.3 mm to 10 µm – Larger arterioles possess all three tunics – Diameter of arterioles controlled by • Local factors in the tissues • Sympathetic nervous system Lumen Endothelium Tunica media (c) Small arteriole (285) Capillaries • Smallest blood vessels – Diameter from 8–10 µm • RBCs pass through single file!!! – Site-specific functions of capillaries • Lungs oxygen enters blood, carbon dioxide leaves • Small intestines receive digested nutrients • Endocrine glands pick up/release hormones • Kidneys removal of nitrogenous wastes RBCs in a Capillary – Single File Capillary Beds • Network of capillaries running through tissues • Precapillary sphincters – Regulate the flow of blood to tissues • Tendons & ligaments poorly vascularized • Epithelia & cartilage avascular – Receive nutrients from nearby CT Capillary Beds Vascular shunt Precapillary sphincters Metarteriole Thoroughfare channel True capillaries Terminal arteriole Postcapillary venule (a) Sphincters open—blood flows through true capillaries. Capillary Beds Terminal arteriole Postcapillary venule (b) Sphincters closed—blood flows through metarteriole—thoroughfare channel & bypasses true capillaries (no blood/O2 to tissue) Capillary Permeability • Endothelial cells held together by tight junctions & desmosomes • Intercellular clefts gaps of unjoined membrane – Small molecules can enter & exit • 2 types of capillary – Continuous most common – Fenestrated have pores; least common Continuous Capillary Pericyte Red blood cell in lumen Intercellular cleft Endothelial cell Basement membrane Tight junction Endothelial nucleus Pinocytotic vesicles (a) Continuous capillary. Least permeable and most common (e.g., skin, muscle). Fenestrated Capillary Pinocytotic vesicles Red blood cell in lumen Fenestrations (pores) Endothelial nucleus Basement membrane Tight junction Intercellular cleft Endothelial cell (b) Fenestrated capillary. Large fenestrations (pores) increase permeability. Occurs in special locations (e.g., kidney, small intestine). Routes of Capillary Permeability • 4 routes into & out of capillaries – Direct diffusion – Through intercellular clefts – Through cytoplasmic vesicles – Through fenestrations (= pores) Low Permeability Capillaries • Blood-Brain Barrier – Capillaries have complete tight junctions – No intercellular clefts present – Vital molecules pass through • Highly selective transport mechanisms – Not a barrier against: • Oxygen, carbon dioxide, & some anesthetics (ie. many drugs) Sinusoids • Wide, leaky capillaries found in some organs – Usually fenestrated – Intercellular clefts are wide open • Occur in bone marrow, spleen, & liver – Sinusoids have large diameter & twisted course Sinusoids Endothelial cell Red blood cell in lumen Large intercellular cleft Tight junction Incomplete basement membrane Nucleus of endothelial cell (c) Sinusoidal capillary. Most permeable. Occurs in special locations (e.g., liver, bone marrow, spleen). Veins • Conduct blood from capillaries toward the heart • Blood pressure is much lower than in arteries • Smallest veins called venules – Diameters from 8–100 m – Smallest venules called postcapillary venules • Venules join to form veins • Tunica externa is the thickest tunic in veins (not the tunica media) Mechanisms to Counteract Low Venous Pressure Valve (open) • Valves in some veins! – Particularly in limbs • Skeletal muscle pump – Muscles press against thin-walled veins – Helps return blood to heart & prevent pooling Contracted skeletal muscle Valve (closed) Vein Direction of blood flow Summary of Blood Vessel Anatomy Vascular Anastomoses • Vessels interconnect to form vascular anastomoses – Organs receive blood from more than one arterial source • Neighboring arteries form arterial anastomoses – Provide collateral channels • Veins anastomose more frequently than arteries Vasa Vasorum • Tunica externa of large vessels have – Tiny arteries, capillaries, & veins • Vasa vasorum “vessels of vessels” – Nourish outer region of large vessels • Inner half of large vessels receive nutrients from luminal blood Pulmonary Circulation • Pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle – Divides into right & left pulmonary arteries • Superior & inferior pulmonary veins – Carry oxygenated blood into the left atrium Pulmonary Circulation Left pulmonary artery Air-filled alveolus of lung Aortic arch Pulmonary trunk Right pulmonary artery O2 Three lobar arteries to right lung CO2 Gas exchange Pulmonary capillary Two lobar arteries to left lung Pulmonary veins Right atrium Pulmonary veins Left atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle Blood Vessels Throughout Life • Fetal circulation – All major vessels in place by month 3 of development – Differences between fetal & postnatal circulation • Fetus must supply blood to the placenta • Very little blood is sent through the pulmonary circuit (lungs not doing gas exchange yet; no breathing until born) Shunts Away from the Pulmonary Circuit • Foramen ovale • Ductus arteriosus Vessels to & from the Placenta • Umbilical vessels run in the umbilical cord – Paired umbilical arteries – Unpaired umbilical vein • Fetal vessels & structures – Ductus venosus – Ligamentum teres – Ligamentum venosum Fetal & Newborn Circulation Compared Fetus Aortic arch Superior vena cava Ductus arteriosus Ligamentum arteriosum Pulmonary artery Pulmonary veins Heart Lung Foramen ovale Fossa ovalis Liver Ductus venosus Ligamentum venosum Hepatic portal vein Umbilical vein Ligamentum teres Inferior vena cava Umbilicus Abdominal aorta Common iliac artery Umbilical arteries Medial umbilical ligaments Urinary bladder Umbilical cord Placenta (a) High oxygenation Moderate oxygenation Low oxygenation Very low oxygenation Disorders of the Blood Vessels • • • • • • Aneurysm Deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb Venous disease Microangiopathy of diabetes Arteriovenous malformation Varicose veins Abdominal Aneurysm Aortic aneurysm Disorders of the Blood Vessels • Atherosclerosis begins in youth • Often related to fatty diet, little exercise, etc. – Consequences evident in middle – old age – Males (ages 45–65) • More common than in females – Females • Experience heart disease & atherosclerosis later in life than males Atherosclerosis What is one of the best ways to maintain vascular health…? Lab Guide to the Vessels Systemic Circulation • Systemic arteries – Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart – Aorta largest artery in the body!!! Major Arteries Arteries of the head and trunk Internal carotid artery External carotid artery Common carotid arteries Vertebral artery Subclavian artery Brachiocephalic trunk Aortic arch Ascending aorta Coronary artery Thoracic aorta (above diaphragm) Celiac trunk Abdominal aorta Superior mesenteric artery Renal artery Gonadal artery Inferior mesenteric artery Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery Arteries that supply the upper limb Subclavian artery Axillary artery Brachial artery Radial artery Ulnar artery Deep palmar arch Superficial palmar arch Digital arteries Arteries that supply the lower limb External iliac artery Femoral artery Popliteal artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Arcuate artery (a) Anterior view Major Arteries – Pulse Points Superficial temporal artery Facial artery Common carotid artery Brachial artery Radial artery Femoral artery Popliteal artery Posterior tibial artery Dorsalis pedis artery The Aorta • Ascending aorta arises from the left ventricle – Branches coronary arteries • Aortic arch lies posterior to the manubrium – Branches • Brachiocephalic trunk • Left common carotid • Left subclavian arteries The Aorta Right common carotid artery Right subclavian artery Right internal jugular vein Right subclavian vein Right brachiocephalic vein Brachiocephalic trunk Right pulmonary artery Left internal jugular vein Left subclavian artery Left subclavian vein Left brachiocephalic vein Left common carotid artery Aortic arch Left pulmonary artery Ligamentum arteriosum Superior vena cava Thoracic aorta Ascending aorta Pulmonary trunk Right atrium Left atrium Right ventricle Inferior vena cava Left ventricle The Aorta • Descending aorta continues from the aortic arch – Thoracic aorta in the region of ~T5–T12 – Abdominal aorta ends at L4 • Divides into right & left common iliac arteries Common Carotid Arteries • Located in the anterior triangle of the neck • 2 branches of the common carotid artery: – External carotid artery – Internal carotid artery Common Carotid Arteries • External carotid artery branches: – Superior thyroid artery – Lingual artery – Facial artery – Occipital artery – Posterior auricular artery – Superficial temporal artery – Maxillary artery Common Carotid Arteries • Internal carotid artery branches: – Optithalmic artery – Anterior cerebral artery – Anterior communicating artery • Forms part of the cerebral arterial circle – Middle cerebral artery Arteries of the Head & Neck Ophthalmic artery Basilar artery Vertebral artery Internal carotid artery External carotid artery Common carotid artery Thyrocervical trunk Costocervical trunk Subclavian artery Axillary artery (a) Arteries of the head and neck, right aspect Branches of the external carotid artery Superficial temporal artery Maxillary artery Occipital artery Facial artery Lingual artery Superior thyroid artery Larynx Thyroid gland (overlying trachea) Clavicle (cut) Brachiocephalic trunk Internal thoracic artery Vertebral Arteries • Supply the posterior brain • Join to form the basilar artery – Basilar artery divides into 2 posterior cerebral arteries • Posterior cerebral arteries connect to the posterior communicating arteries Cerebral Arterial Circle • 2 posterior communicating arteries join the anterior communicating artery Anterior Cerebral arterial circle (circle of Willis) Frontal lobe Optic chiasma Anterior communicating artery Anterior cerebral artery Middle cerebral artery Internal carotid artery Posterior communicating artery Mammillary body Posterior cerebral artery Basilar artery Temporal lobe Vertebral artery Pons Occipital lobe Cerebellum Posterior (c) Major arteries serving the brain (inferior view, right side of cerebellum and part of right temporal lobe removed) Arteries of the Upper Limb • Subclavian artery enters the axilla as the axillary artery • Axillary artery becomes the brachial artery at the inferior border of teres major • Brachial artery divides into Radial artery & ulnar artery Arteries of the Upper Limb & Thorax Vertebral artery Thyrocervical trunk Costocervical trunk Common carotid arteries Right subclavian artery Suprascapular artery Thoracoacromial artery Axillary artery Left subclavian artery Brachiocephalic trunk Posterior intercostal arteries Subscapular artery Anterior intercostal artery Posterior circumflex humeral artery Internal thoracic artery Anterior circumflex humeral artery Lateral thoracic artery Brachial artery Deep artery of arm Descending aorta Common interosseous artery Radial artery Ulnar artery Deep palmar arch Superficial palmar arch Digital arteries Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta • • • • • • • • Inferior phrenic arteries Celiac trunk Superior mesenteric artery Suprarenal arteries Renal arteries Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) arteries Inferior mesenteric artery Common iliac arteries Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta Hiatus (opening) for inferior vena cava Hiatus (opening) for esophagus Adrenal (suprarenal) gland Celiac trunk Kidney Abdominal aorta Diaphragm Inferior phrenic artery Middle suprarenal artery Renal artery Superior mesenteric artery Lumbar arteries Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) artery Ureter Inferior mesenteric artery Median sacral artery Common iliac artery The Celiac Trunk & Main Branches Liver (cut) Diaphragm Inferior vena cava Celiac trunk Common hepatic artery Hepatic artery proper Gastroduodenal artery Right gastric artery Gallbladder Pancreas (major portion lies posterior to stomach) Duodenum Abdominal aorta Esophagus Left gastric artery Stomach Splenic artery Left gastroepiploic artery Spleen Right gastroepiploic artery Superior mesenteric artery (a) The celiac trunk and its major branches. The left half of the liver has been removed. Arteries of Pelvis & Lower Limbs • • • • • • Internal iliac arteries External iliac artery Femoral artery Popliteal artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Arteries of the Pelvis Aorta Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery External iliac artery (a) Anterior view Arteries of the Pelvis & Lower Limbs Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery Superior gluteal artery External iliac artery Deep artery of thigh Lateral circumflex femoral artery Descending branch Medial circumflex femoral artery Obturator artery Femoral artery Adductor hiatus Popliteal artery Genicular artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Fibular artery Dorsalis pedis artery Arcuate artery Dorsal metatarsal arteries (a) Anterior view Arteries of the Pelvis & Lower Limbs Popliteal artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Lateral plantar artery Medial plantar artery (b) Posterior view of leg Fibular artery Dorsalis pedis artery (from top of foot) Plantar arch Systemic Veins • • • • 3 major veins enter the right atrium Superficial veins lie just beneath the skin Multivein bundles venous plexuses Unusual patterns of venous drainage – Dural sinuses – Hepatic portal system Venae Cavae & Tributaries • Superior vena cava – Returns blood from body regions superior to the diaphragm • Inferior vena cava – Returns blood from body regions inferior to the diaphragm • Superior and inferior vena cava – Join the right atrium Major Veins of the Systemic Circulation Veins of the head and trunk Dural venous sinuses External jugular vein Vertebral vein Internal jugular vein Right and left brachiocephalic veins Superior vena cava Great cardiac vein Hepatic veins Splenic vein Hepatic portal vein Renal vein Superior mesenteric vein Inferior mesenteric vein Inferior vena cava Common iliac vein Internal iliac vein Veins that drain the upper limb Subclavian vein Axillary vein Cephalic vein Brachial vein Basilic vein Median cubital vein Ulnar vein Radial vein Digital veins Veins that drain the lower limb External iliac vein Femoral vein Great saphenous vein Popliteal vein Posterior tibial vein Anterior tibial vein Small saphenous vein Dorsal venous arch Dorsal metatarsal veins Veins of the Head & Neck • Venous drainage – Internal jugular veins – External jugular veins – Vertebral veins Ophthalmic vein Superficial temporal vein Facial vein Occipital vein Posterior auricular vein External jugular vein Vertebral vein Internal jugular vein Superior and middle thyroid veins Brachiocephalic vein Subclavian vein Superior vena cava (a) Veins of the head and neck, right superficial aspect Veins of the Head & Neck • Dural sinuses – Superior & inferior sagittal sinuses – Straight sinus – Transverse sinuses – Sigmoid sinus Superior sagittal sinus Falx cerebri Inferior sagittal sinus Straight sinus Cavernous sinus Confluence of sinuses Transverse sinuses Sigmoid sinus Jugular foramen Right internal jugular vein (b) Dural venous sinuses of the brain Veins of the Thorax • Azygos vein • Hemiazygos vein • Accessory hemiazygos vein Veins of the Upper Limbs • Deep veins – Follow the paths of companion arteries – Have the same names as the companion arteries • Superficial veins – Visible beneath the skin • • • • Cephalic vein Basilic vein Median cubital vein Median vein of the forearm Veins of the Thorax & Right Upper Limb Brachiocephalic veins Right subclavian vein Axillary vein Brachial vein Cephalic vein Basilic vein Internal jugular vein External jugular vein Left subclavian vein Superior vena cava Azygos vein Accessory hemiazygos vein Hemiazygos vein Posterior intercostals Inferior vena cava Ascending lumbar vein Median cubital vein Median antebrachial vein Cephalic vein Radial vein Basilic vein Ulnar vein Deep palmar venous arch Superficial palmar venous arch Digital veins Veins of the Abdomen • • • • • Lumbar veins Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) veins Renal veins Suprarenal veins Hepatic veins Tributaries of the Inferior Vena Cava Hepatic veins Inferior vena cava Right suprarenal vein Right gonadal vein External iliac vein Inferior phrenic vein Left suprarenal vein Renal veins Left ascending lumbar vein Lumbar veins Left gonadal vein Common iliac vein Internal iliac vein (a) Tributaries of the inferior vena cava; venous drainage of the paired abdominal organs. Tributaries of the Inferior Vena Cava Right Left Diaphragm Hepatic veins Inferior vena cava Renal veins Abdominal aorta Common iliac veins (b) Dissection of the posterior abdominal wall illustrating abdominal vessels. The Hepatic Portal System • A specialized part of the vascular circuit • Picks up digested nutrients • Delivers nutrients to the liver for processing The Basic Scheme of the Hepatic Portal System Hepatic veins Inferior vena cava (not part of hepatic portal system) Gastric veins Liver Hepatic portal vein Spleen Inferior vena cava Splenic vein Right gastroepiploic vein Inferior mesenteric vein Superior mesenteric vein Small intestine Large intestine Rectum (b) The veins of the hepatic portal system Veins of the Pelvis & Lower Limbs • Deep veins – Share the name of the accompanying artery • Superficial veins – Great saphenous vein empties into the femoral vein Veins of the Right Lower Limb & Pelvis Common iliac vein Internal iliac vein External iliac vein Inguinal ligament Femoral vein Great saphenous vein (superficial) Popliteal vein Small saphenous vein Fibular vein Anterior tibial vein Dorsalis pedis vein Dorsal venous arch Dorsal metatarsal veins (a) Anterior view Questions…? What’s Next? Lab: Blood & Blood Vessels Mon Lecture: Finish material & Rev Mon Lab: Lab Exam 4! Wed Lecture: Lecture Exam 4!