* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SAT Math Power Point Week 3
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
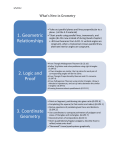
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Definitions Segments and Lines Triangles Polygons and Circles 2D Perimeter/Area and 3D Volume/Surface Area Lines extends indefinitely Segments are portions of lines that starts at a point and end at another points. These are called Endpoints Rays starts at a point and extends indefinitely in one direction Things that are “Congruent” are equaled in measurement Angles are the space in-between two connected rays that is usually measured in Degrees Vertical Angles are two opposite angles formed by two intersecting lines. Vertical angles are also congruent Complementary Angles are two angles whose sum is 900 Supplementary Angles are two angles whose sum is 1800 A Linear Pair are pairs of connected angles that form a straight line and are also supplementary angles The Segment Addition Postulate proposed that if two segments are put together, they form a bigger segment Example: The measure of AB is 2 and the measure of AC is 5. What is the measure of BC? Midpoint formula: Given points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) 𝑥1 + 𝑥2 𝑦1 + 𝑦2 , 2 2 Distance Formula 𝑑= 𝑥22 − 𝑥12 + 𝑦22 − 𝑦12 Example: Given (5, 3) , (-4, y) and a distance of 5. Find the midpoint Slopes in Geometry is the same as in Algebra Parallel lines have the same slope a b e f i j m n c d g h k l o p Triangle Sum Theorem: The sum of all the angles within a triangle is equal to 1800 Types of Triangles by Sides Equilateral – All sides of a triangle have the same length Isosceles – Exactly two sides of a triangle have the same length Scalene – All sides of the triangle have different length Types of Triangles by Angle Acute – All angles in the triangle have a measure of less than 900 Obtuse – Exactly one angle in a triangle has a measure of more than 900 Right – Exactly one angle in a triangle has a measure of 900 Triangle Inequality states that the sum of any two sides must always be greater than the third side Pythagorean Theorem If a triangle is a right triangle, the sum of the squared length of two the sides is equaled to the length of the third side squared. If a right triangle is labeled as followed a c b Then we have the equation 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 = 𝑐 2 Special Right Triangles 45-45-90 30-60-90 Two Triangles are congruent if they satisfy the conditions in one of the following: SSS, SAS, AAS, ASA, Leg-Hypotenuse Two Triangle are similar if all the ratios between corresponding parts of the triangles are the same Polygons are shapes with 3 or more straight sides and angles Interior Angle Sum on a polygon is defined by 180(n-2) Where n is the number of sides A couple of Polygons includes Triangle, Quadrilaterals, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Nonagon, and Decagon Examples of Quadrilaterals include Parallelograms, Rhombus, Rectangle, Square, Kite Keep in mind that all regular polygons can be broken up into triangles Circles are perfectly round shapes Diameter is any line drawn from one end of a circle to the other end that must pass through the center Radius is the any line drawn from the center to one end of a circle Chords are any line drawn from one end of a circle to another end that doesn’t pass through the center Circumference of a circle is the distance around the circle defined as C = 2πr Arc length is a portion of the circumference Perimeter is the distance around a shape In particular for a quadrilateral, the formula is 2l + 2w Area is the flat space a shape can hold Volume is the space a solid can hold Surface area is the sum of all the areas of a solid Solids include Prisms, Cylinders, Pyramids and Spheres All formulas for area, volume, and surface area are on the first page of each section