* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 10 test 04-05
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
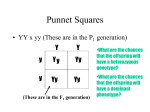
Lab Biology Name _____________________________ Mendelian Genetics Exam: Chapter 10 Mutiple Choice. Choose the best answer for each question. 2 pts each. _____1. A variation of a gene is called a(n): a. allele b. chromosome c. mutation d. trait _____ 2. A student crosses wrinkled-seeded (rr) pea plants with round-seeded (RR) pea plants. Only round seeds were produced in the resulting plants. This illustrates the principle of a. dominance & recessiveness b. pollination c. segregation d. independent assortment _____3. Uppercase letters represent ______________ alleles. a. independent b. genetic c. recessive d. dominant _____ 4. Mendel obtained his P1 generation by allowing the pea plants to: a. segregate b. independently assort c. self-pollinate d. cross-pollinate _____ 5. Which genetic principle states that genes are distributed to gametes in a random fashion? a. mutation b. dominance c. independent assortment d. segregation _____ 6. The appearance of a recessive trait in offspring of animals most probably indicates: a. one parent was homozygous dominant and the other parent was homozygous recessive for that trait b. both parents carried at least one recessive gene for that trait c. neither parent carried recessive genes for that trait d. one parent was homozygous dominant and the other parent was heterozygous for that trait Create a punnett square to solve the following problems. Show the parental genotypes, and phenotypic/genotypic results of the offspring for every problem. Unless otherwise indicated, you will receive 2 points for showing the correct parental genotypes, 2 points for showing the correct offspring genotypes based on your parents, and 2 points for each correct ratio and answer to additional questions based on your offspring genotypes. 7. In pigs, a curly tail is dominant over a straight tail. Show the cross between two straight-tailed pigs. (8 pts) a) Offspring genotypic ratio: ________________________ _______________________________________________ b) Offspring phenotypic ratio:________________________ _____________________________________________ 8. In pea plants, tallness is due to a dominant allele and shortness to the recessive allele. Show the cross between a homozygous dominant plant and a heterozygous plant. (8 pts) a) Offspring genotypic ratio: ___________________________ __________________________________________________ b) Offspring phenotypic ratio:___________________________ _________________________________________________ 9. In humans, dimples are a dominant trait. Having no dimples is recessive. Show the cross between two people who are both heterozygous for dimples. (10 pts) a) Offspring genotypic ratio: _________________________ _______________________________________________ b) Offspring phenotypic ratio: ________________________ _______________________________________________ c) What are the chances that they will have a child without dimples?____________________ 10. In the Munster family, green skin is dominant to white skin. Herman Munster and his wife have four children. Two of the children are heterozygous for green skin and the other two have white skin. What are the phenotypes and genotypes of the parents? (8 pts = 4 points for offspring genotypes, 2 points for parental genotypes, 2 points for parental phenotypes) a) Genotypes of Parents:________________________ b) Phenotypes of Parents: _______________________ 11. In the human population, brown eyes are dominant to blue eyes. Show a cross between a man with blue eyes and a woman who is pure for brown eyes. (10 pts) a) Offspring genotypic ratio: ___________________________ _____________________________________________ b) Offspring phenotypic ratio: __________________________ ________________________________________________ c) What are the chances that they will have a child who has blue eyes?________________ 12. Japanese four o’ clocks are flowers that exhibit incomplete dominance. Neither red flowers (R) nor white flowers (W) are dominant. Show a cross between a red flower and pink flower. (8 pts) a) Offspring genotypic ratio: _________________________ _______________________________________________ b) Offspring phenotypic ratio: ________________________ _______________________________________________ 13. In rabbits, black coat color is dominant to white coat color. A breeder of rabbits has just received some black rabbits whose parents are unknown. He wants to make sure that the rabbits are pure for black coat color. The breeder performs a testcross and gets the following results: 2 black bunnies and 2 white bunnies. Show the testcross that would yield these results. (10 pts) a) What is the known genotype of the rabbit used to perform the testcross? ________________ b) What is the genotype of the black rabbit? __________ c) Is the rabbit pure for black coat color? ____________ 14. In pea plants, green pods are dominant to yellow pods. Show a cross between a plant that is pure for green pods and a pure yellow pod plant. (8 pts) a) Offspring genotypic ratio: _________________________ ________________________________________________ b) Offspring phenotypic ratio:_________________________ 15. In humans, unattached earlobes are dominant over attached earlobes. Determine the phenotypic and genotypic percentages of a cross between a heterozygous woman and a man with attached earlobes. (8 pts) a) Offspring genotypic ratio: _________________________ ________________________________________________ b) Offspring phenotypic ratio:_________________________ ________________________________________________ Use the dihybrid punnett square below to answer questions 16-20. Remember: Round seeds are dominant to wrinkled, and yellow seeds are dominant to green. 2 pts each RY RY X Ry Ry rY 2 rY 6 ry 1 3 5 4 ry _____ 16. The phenotype represented by the box labeled 1 is: a. round, yellow b. round, green c. wrinkled, yellow d. wrinkled, green _____ 17. The genotype represented by the box labeled 2 is: a. RRYY b. RrYY c. RrYy d. rrYy _____ 18. Which of the following boxes represents the same phenotype as the box labeled X? a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 _____19. The genotypes of the parents are: a. RRYy x Rryy b. RrYy x RRYY _____20. The phenotypes of the parents are: a. round, yellow x round, green b. wrinkled, yellow x round, green c. round, yellow x round, yellow d. wrinkled, green x round, green c. RrYy x RrYy d. rrYy x Rryy d. 6