* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 5–2) CCSS Then/Now Key
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Systolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
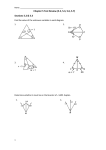
12/1/2015 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 5–2) CCSS Then/Now Key Concept: Definition of Inequality Key Concept: Properties of Inequality for Real Numbers Theorem 5.8: Exterior Angle Inequality Example 1: Use the Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem Theorems: Angle-Side Relationships in Triangles Example 2: Order Triangle Angle Measures Example 3: Order Triangle Side Lengths Example 4: Real-World Example: Angle-Side Relationships 1 12/1/2015 Over Lesson 5–2 Find the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle with vertices D(–2, 9), E(3, 6), and F(–7, 0). Find the coordinates of the orthocenter of the triangle with vertices F(–1, 5), G(4, 4), and H(1, 1). ___ (3-4)___ In ∆RST, RU is an altitude and SV is a median. Find y if m∠ ∠RUS = 7y + 27. Find RV if RV = 6a + 3 and RT = 10a + 14. What is the center of gravity of a triangle named? Over Lesson 5–2 Find the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle with vertices D(–2, 9), E(3, 6), and F(–7, 0). A. (–4, 5) B. (–3, 4) C. (–2, 5) D. (–1, 4) 2 12/1/2015 Over Lesson 5–2 Find the coordinates of the orthocenter of the triangle with vertices F(–1, 5), G(4, 4), and H(1, 1). A. B. C. (2, 3) D. Over Lesson 5–2 ___ ___ In ∆RST, RU is an altitude and SV is a median. Find y if m∠ ∠RUS = 7y + 27. A. 5 B. 7 C. 9 D. 11 3 12/1/2015 Over Lesson 5–2 ___ ___ In ∆RST, RU is an altitude and SV is a median. Find RV if RV = 6a + 3 and RT = 10a + 14. A. 3 B. 4 C. 21 D. 27 Over Lesson 5–2 Which of the following points is the center of gravity of a triangle? A. centroid B. circumcenter C. incenter D. orthocenter 4 12/1/2015 Content Standards G.CO.10 Prove theorems about triangles. Mathematical Practices 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. You found the relationship between the angle measures of a triangle. • Recognize and apply properties of inequalities to the measures of the angles of a triangle. • Recognize and apply properties of inequalities to the relationships between the angles and sides of a triangle. 5 12/1/2015 6 12/1/2015 Use the Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem Exterior Angle Inequality ∠14 > ∠4 ∠9 > ∠6 ∠14 > ∠11 ∠9 > ∠7 ∠14 > ∠2 ∠14 > ∠3 + ∠4 Vertical Angles ∠14 > ∠11 = ∠9 Definition of Inequality ∠14 > ∠3 Answer: Thus m∠14 is greater than m∠2, m∠3, m∠4, m∠6, m∠7, m∠9, and m∠11 Use the Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem Exterior Angle Inequality Vertical Angles ∠10 > ∠5 ∠16 > ∠10 > ∠5 ∠15 > ∠12 > ∠5 ∠17 > ∠5 + ∠6 ∠12 = ∠10 > ∠5 Definition of Inequality ∠17 > ∠5 Answer: Thus m∠5 is less than than m ∠ 10, m∠12, m∠15, m∠16, and m∠17 7 12/1/2015 A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. 8 12/1/2015 Summary: 1. The longest side is across from the largest angle. 2. The largest angle is across from the longest side. Order Triangle Angle Measures List the angles of ∆ABC in order from smallest to largest. Recall: The largest angle is across from the longest side. Answer: ∠C, ∠A, ∠B 9 12/1/2015 List the angles of ∆TVX in order from smallest to largest. A. ∠X, ∠T, ∠V B. ∠X, ∠V, ∠T C. ∠V, ∠T, ∠X D. ∠T, ∠V, ∠X Order Triangle Side Lengths List the sides of ∆ABC in order from shortest to longest. Recall: The longest side is across from the largest angle. Answer: AC, AB, BC 10 12/1/2015 List the sides of ∆RST in order from shortest to longest. A. RS, RT, ST B. RT, RS, ST C. ST, RS, RT D. RS, ST, RT Angle-Side Relationships HAIR ACCESSORIES Ebony is following directions for folding a handkerchief to make a bandana for her hair. After she folds the handkerchief in half, the directions tell her to tie the two smaller angles of the triangle under her hair. If she folds the handkerchief with the dimensions shown, which two ends should she tie? Recall: The largest angle is across from the longest side. Answer: So, Ebony should tie the ends marked Y and Z. 11 12/1/2015 KITE ASSEMBLY Tanya is following directions for making a kite. She has two congruent triangular pieces of fabric that need to be sewn together along their longest side. The directions say to begin sewing the two pieces of fabric together at their smallest angles. At which two angles should she begin sewing? A. ∠A and ∠D B. ∠B and ∠F C. ∠C and ∠E D. ∠A and ∠B 12