* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy.Practice.Quiz3
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
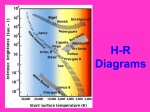
Astronomy Practice Quiz 3: Stars 1. The source of the Sun’s energy is ____. a. chemical burning b. nuclear division Name: _________________ c. nuclear fusion 2. About 90 percent of stars on the H-R diagram are ____. a. supergiants b. main-sequence stars c. white dwarfs 3. All stars, regardless of size, eventually ____. a. turn into black dwarfs b. explode d. photosynthesis d. black holes c. run out of fuel and collapse 4. The Sun is a ____. a. black hole b. black dwarf c. main-sequence star d. become black holes d. red giant 5. Massive stars terminate in a brilliant explosion called a ____. a. red giant b. protostar c. neutron star d. supernova 6. What is the next stage in the Sun’s life cycle? a. white dwarf b. red giant c. planetary nebula d. black dwarf 7. According to Figure 25-1, which main-sequence stars are brightest? a. the smallest b. the coolest c. the hottest d. none of the above 8. In the H-R diagram above, which letter represents the Sun? a. A b. B c. C d. D 9. According to Figure 25-1, the Sun has an absolute magnitude of ____. a. –5 b. 0 c. 5 d. 5000 10. A Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram shows the relationship between ____. a. absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude b. temperature and absolute magnitude c. parallax and temperature d. apparent magnitude and parallax 11. The source of the Sun’s energy is ____. a. chemical burning b. nuclear fusion 12. What determines the final stages of a star’s life cycle? a. size b. color c. temperature c. nuclear fission d. magnitude 13. After the red giant phase, the next phase for a medium mass star is: a. nova b. planetary nebula c. white dwarf 14. This is how bright a star appears on Earth. a. apparent magnitude b. absolute magnitude d. photosynthesis c. magnitude d. black dwarf d. luminosity 15. Another name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star is ______. a. red giant b. nebula c. supernova d. black hole Astronomy Practice Quiz 3: Stars 1. The source of the Sun’s energy is ____. a. chemical burning b. nuclear division Name: _________________ c. nuclear fusion 2. About 90 percent of stars on the H-R diagram are ____. a. supergiants b. main-sequence stars c. white dwarfs 3. All stars, regardless of size, eventually ____. a. turn into black dwarfs b. explode d. photosynthesis d. black holes c. run out of fuel and collapse 4. The Sun is a ____. a. black hole b. black dwarf c. main-sequence star d. become black holes d. red giant 5. Massive stars terminate in a brilliant explosion called a ____. a. red giant b. protostar c. neutron star d. supernova 6. What is the next stage in the Sun’s life cycle? a. white dwarf b. red giant c. planetary nebula d. black dwarf 7. According to Figure 25-1, which main-sequence stars are brightest? a. the smallest b. the coolest c. the hottest d. none of the above 8. In the H-R diagram above, which letter represents the Sun? a. A b. B c. C d. D 9. According to Figure 25-1, the Sun has an absolute magnitude of ____. a. –5 b. 0 c. 5 d. 5000 10. A Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram shows the relationship between ____. a. absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude b. temperature and absolute magnitude c. parallax and temperature d. apparent magnitude and parallax 11. The source of the Sun’s energy is ____. a. chemical burning b. nuclear fusion 12. What determines the final stages of a star’s life cycle? a. size b. color c. temperature c. nuclear fission d. magnitude 13. After the red giant phase, the next phase for a medium mass star is: a. nova b. planetary nebula c. white dwarf 14. This is how bright a star appears on Earth. a. apparent magnitude b. absolute magnitude d. photosynthesis c. magnitude d. black dwarf d. luminosity 15. Another name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star is ______. a. red giant b. nebula c. supernova d. black hole