* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notepacket - Human Physiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
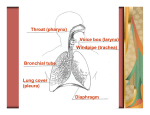
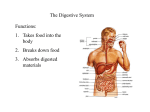
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY: Body Systems Digestive, Circulatory & Immune, Respiratory, Excretory (Urinary), Muscular & Skeletal, Nervous & Endocrine DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 6 Basic Nutrients --- Proteins, Carbohydrates, Fats, Vitamins, Minerals & H2O Energy Content of Food Energy comes from the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates, fats & proteins This energy is released by cell ______________ ***Fats contain _____________ as many calories as carbs. or protein Digestion & Absorption _______________ = process by which food molecules are broken down These molecules enter cells through cell membranes ______________ a) _______________ digestion – pieces of food are cut, crushed, or broken into smaller particles so _____ is increased b) _______________ digestion – carried out by ***______________*** (that act on the surface of food particles) Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum Anus MOUTH & PHARYNX (= back of throat) Mouth – mechanical & chemical digestion --- ___________ secreted by salivary glands ______________ – prevents food from entering the trachea (air passage) ESOPHAGUS Waves of muscular contraction & relaxation = ________________ (pushes food along toward stomach) STOMACH Thick-walled _____________ sac Mechanical digestion of food occurs by contractions of stomach wall ***Chemical digestion of ____________ begins here ___________ – when mucus layer is damaged, gastric juices eat away at cells & painful ulcers can form… Relation to _____________??? SMALL INTESTINE 3 parts (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) ***Most ________________ digestion takes place here*** ***Site of ________________*** a) CHEMICAL DIGESTION Pancreas – secretes MANY _____________ into small intestine Liver – secretes ___________ (stored in ______ bladder) --- Bile emulsifies fats (= breaks up fats/oils to increase ____) Intestinal juice – contains enzymes that COMPLETE the digestion of carbohydrates, fats & proteins amino acids simple sugars fatty acids (& glycerol) b) ABSORPTION Nutrients diffuse through _______________ cells and enter either capillaries OR ____________ To increase absorption, the small intestine: --- Is very LONG (6.5 meters) & has many FOLDS --- Is covered with millions of finger-like projections called __________ LARGE INTESTINE ***NO ______________ occurs here*** Undigested & unabsorbed materials come here ________________ – can become infected Appendicitis ________________ of water (3/4 reabsorbed) & minerals --- Diarrhea vs. Constipation ________________ of undigested & indigestible material Cellulose, bacteria, bile, mucus, etc... Becomes _________ (stool) Stored in ____________ Released/eliminated through __________ Absorption of _____________ (K, B) produced by _____________ CIRCULATORY & IMMUNE SYSTEMS Transport = process by which substances move ________ or ________ of cells, are distributed ______________ cells OR are circulated between parts of a multicellular organism Humans have a single heart & a network of blood vessels The heart pumps blood & the vessels carry it TO & FROM all ______ of the body BLOOD VESSELS a) Arteries = thick, muscular, elastic blood vessels that carry blood ___________ from the heart b) Veins = thin-walled blood vessels that ___________ blood to heart Most have _____________ that prevent the backflow of blood c) Capillaries = connect arterioles TO venules Very narrow blood vessels with walls only _______ cell thick ***Sites of _______________ between body cells & blood Arteries aterioles capillaries (sites of exchange) venules Veins THE HEART ___-chambered muscular organ The 2 upper chambers are called ____________ The 2 lower chambers are called ____________ The atria _____________ blood & the ventricles ___________ it out Made up of ______________ muscle ***CIRCULATION through the HEART*** Oxygen-poor blood (deoxygenated blood) returning from the body enters the _____ Passes through a valve & enters the _____ Pumps it through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs (exchange occurs) Pulmonary veins return the oxygenated blood to the _____ Passes through a valve & enters the _____ Pumps blood out (through the large ___________) to the rest of the body CONTROL of HEARTBEAT ____________ = pacemaker = specialized muscle cells in the walls of the _____ that send electrical impulses to the heart, causing the atria to contract ____________ triggers an impulse almost immediately after causing the ____________ to contract BLOOD PRESSURE = pressure the blood exerts on _____________ walls BP ____ to a maximum during ______________ (systolic pressure) BP ____ to a minimum during ______________ (diastolic pressure) Average BP is ____ / ____ (systolic pressure / diastolic pressure) ____________ can be felt when the ____ contracts & then relaxes CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES __________________ (high BP) – caused by stress, sodium (Na), smoking, aging, obesity, lack of exercise, etc… __________________ – narrowing of arteries due to deposits of __________________ & other fatty material Heart disease – narrowing OR blockage of ____________ arteries (which supply heart muscle with ____________ & _____) Ex. Heart Attack (complete blockage) BLOOD COMPONENTS Plasma Red Blood Cells (RBCs) White Blood Cells (WBCs) Platelets 1) Plasma = ____________ portion 55% of blood (90% of which is ____________) RBCs, WBCs & platelets make up 45% of blood (____________ portion) 2) Red Blood Cells – have NO ___________ when mature Contain ***_____*** (a RED, IRON containing pigment/protein that helps transports _____ & CO2) Made by the __________ ____________ Shape = biconcave disc About 30 trillion RBCs in avg. adult 3) White Blood Cells a) _______________ = defend against infection by surrounding, engulfing & destroying bacteria by phagocytosis b) _______________ = produce ***______________*** which attack ***_____________*** (= foreign substances) --- Involved in the ____________ response There are actually 5 types of WBCs… Produced by bone marrow & ___________ tissue (lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus gland, spleen) ______________ = a disease of the bone marrow in which there is an ________________ production of non-functional WBCs --- A form of ____________ 4) Platelets = cell fragments involved in ***_________ ___________*** Produced by the cytoplasm of bone marrow _______________ = a hereditary disease in which one or more of the clotting factors are _____________ in the blood IMMUNE SYSTEM _______________ = viruses, bacteria, fungi & other microorganisms that can cause DISEASE = a failure of ______________ --- The human body has a 3-Line Defense against infection: 1st Line Defense – physical & chemical barriers Ex. ____________ (Most pathogens cannot get by unbroken skin), sweat, tears, saliva, _____________ (traps pathogens), stomach acid 2nd Line Defense – the start of an infection triggers an ______________________ response Causes swelling, redness, warmth & pain in infected area --- The inflammation ATTRACTS _________________ which ingest the pathogens & the inflammation eventually dies down 3rd Line Defense – involves the IMMUNE SYSTEM --- Lymphocytes produce ________________ that attack pathogens OR "mark" them for killing Antibodies are ______________ for certain pathogens If an antigen enters the body a 2nd time, ______________ are produced MORE QUICKLY because of memory WBCs ---This is why we usually do not get chicken pox twice, the same cold twice, etc… TYPES of IMMUNITY a) ______________ = when the body produces its own ______________ to attack an antigen 1. Actually having the disease 2. ______________ (dead or weakened bacteria/virus is injected to trigger an antibody response) b) ______________ = antibodies from an "outside" source are introduced into an individual’s blood Only ____________ since body gradually destroys the antibodies ____________ immunity – protects infant for 1st few months of life BLOOD TYPES A, B, AB & O There are ______________ present on the surface of RBCs --- Ex. Type A blood will have antigen ____ on its RBC surfaces The plasma contains _______________ for the antigens NOT present on the RBC surface --- Ex. Type A blood will have ___________ antibodies in its plasma ALLERGIES An __________________ to an antigen that is NOT normally harmful Ex. Pollen, dust mites, peanuts, animal hair ________________ gets released & induces an ____________________ response Runny nose, swollen eyes, sneezing, coughing, rash, redness, pain RESPIRATORY SYSTEM _______________ surface = the surface through which gas exchange takes place The respiratory surface MUST BE: ____________ (so ______________ can occur rapidly) ____________ (because O2 & CO2 must be in solution) In _____________ with an O2 source ***Gas exchange takes place by ______________ (FROM an area of _____________ concentration TO an area of __________ concentration)*** ***The greater the _____, the MORE exchange that can take place*** O2 is taken in, transferred to the __________, then carried to the various cells/tissues of the body CO2 (waste product from cell ____________) is removed from the blood & transferred to the external environment ***_____________*** = principal respiratory organs of the human body Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchial tubes Bronchioles Alveoli (air sacs) NOSE Air enters through the ____________ (which have hairs that ___________ foreign particles) Nasal passages are lined with _____________ membranes that have _________ and secrete _____________ (moistens the air) Help trap bacteria, dust, pollen, etc… Air is _____________ by capillaries Therefore, air that enters the body via the nose gets ***filtered, moistened & warmed*** PHARYNX – passageway for air as it passes to the trachea LARYNX (Voice Box) – contains the ___________ ___________ TRACHEA (“________________”) – connects pharynx to bronchi Surrounded by ______________ rings that help keep it open Lined with _____________ _____________ membranes Cilia sweep inhaled foreign substances back up into the pharynx where they are usually swallowed BRONCHI – connect trachea with ______________ tubes (= tree-like branches of the bronchi) BRONCHIOLES – connect bronchial tubes with _____________ Walls are very ___________ ALVEOLI (_______ _________) = the fundamental units of gas exchange ***The _________ (only ______ cell thick) are the respiratory surface ***Surrounded by many ________________ ____ diffuses from alveoli into surrounding capillaries while ______ (and some _______) diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli HEMOGLOBIN (Hb) Most O2 is carried from the lungs to body cells/tissues by ____ LUNGS: Hb combines with O2 to form ____________________, which is ___________ RED TISSUES: Hb drops off O2 Blood turns ___________ RED (purple) since Hb now contains NO oxygen DISEASES of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Bronchitis = _________________ of the linings of the bronchial tubes, which become irritated, swollen & get clogged with __________ Asthma = severe ___________ reaction which constricts the bronchioles Emphysema = lung disorder in which the walls of the _____________ break down, making the respiratory surface ____________ --- Leads to shortness of breath & difficulty breathing Pneumonia = alveoli become filled with ___________ --- Prevents the exchange of ________ SMOKING Linked to COPD & lung ___________ Smoke contains carbon ______________ (CO) which has a greater attraction for _____ than O2 So _________ oxygen is in the blood ____ the amount of ___________ in air passages --- Constant coughing (smoker’s cough) Particles from smoke damage walls of alveoli ________________