* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 2
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Median graph wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
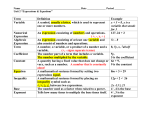
SOL Algebra 2 Properties Commutative (order), Associative (grouping), Additive Identity (+ 0), Additive Inverse, Multiplicative Identity (x 1), Distributive Property Reflexive, Symmetric, & Transitive Properties of Equality (Transitive – Inequality) If a > b and b > c, then a > c. Addition Property, Subtraction Property, Multiplication Prop. If a = b, then a + c = b + c. If x + 1 > y, then x + 1 + z > y + z. (for inequality) Simplifying Expressions Imaginary numbers: i, i2 = -1, i3 = -i, i4 = 1 pattern Factoring (top top, bottom bottom, cancel top & bottom) Basic Exponent Laws (add or subtract exponents, distribute) Factoring techniques: CMF: Factor out what is common among terms. DOTS: a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a - b) SOTC: a3 + b3 = (a + b)( - + ) DOTC: a3 – b3 = (a - b)( + + ) Easy T (factors of last term that add up to middle term) Perfect Square T: (x – 3)2 or (x + 5)2 not the same as (x2 + 52) Hard T (guess and check, or grouping) Convert: Rational Exponent to Radical (root) Expressions TI – 84: Dealing with imaginary numbers: Use (a + bi) MODE. Use the exponent (^) key and USE ( ) for fractions. Radical expressions (MATH menu: cube root, others) The STORE key may be helpful to check your answers. Parabola: y = a (x – h)2 + k Technique: Find the vertex (h, k) a > 0 (up) a < 0 (down) OR y – k = a (x – h)2 For horizontal parabolas: x = a (y – k)2 + h OR x – h = a (y – k)2 a > 0 (facing right) a < 0 (facing left) SOL Algebra 2 Polynomials x-intercepts zeros solutions (roots) Graph Function Equation If k is a zero, then f(k) = 0. When k is plugged into x, the answer is 0. If 5 is a zero, then (x – 5) is a factor. If (x + 3) is a factor, then –3 is a zero. Think opposite! If ½ is a zero, then (x – ½ ) is a factor. Using SLIDE, this becomes the factor (2x – 1). If -3/4 is a zero, then (x + ¾) is a factor. Using SLIDE, this becomes the factor (4x + 3). FOIL the factors to get the function: y = f(x) or equation: f(x) = 0. # of turns + 1 = degree of function (linear, quadratic, cubic, quartic) Double roots (graph merely touches the x-axis) no real zeros graph doesn’t touch or cross the x-axis a > 0 (upward) a < 0 (downward) TI-84: Y=…, Graph, 2nd Trace [Calculate] Use the STORE key to determine if a number is a zero or not. For easy input, try 2nd Enter [Entry]. Don’t Forget: Parentheses, Parentheses, Parentheses Functions Function value, domain & range, operations including composition TI-84: Y = …, GRAPH, TABLE, TABLESET (ASK)… Pick a point (x,y) from the graph. Plug in the x & y and see if the equation is true. Eliminate choices where equation is false. Pick another easy point (x,y) if necessary. The x- and y- intercepts are good choices. Transformations of Basic Graphs: effects of h & k Horizontal shift: h (left or right) Vertical shift: k (up or down) Example: y = /x/ (basic graph with vertex at origin) y = a /x – h/ + k (absolute value function) Or y – k = a /x – h/ Think opposite…(h,k) new vertex SOL Algebra 2 Solving Equations Use the STORE key. Check to see if there are 2 or more solutions. Use ( Type in the left side and/or right side of the equation carefully. ) with fractions, rational expressions, quantities inside a square root. If the discriminant b2 – 4ac for a quadratic equation is negative, then the solutions are imaginary (involves i). Rational Expressions: You can also use the LCD or crossmultiplication methods. Radical Expressions: You can square both sides of EQ at the right time (isolate radical first). Remember if the root is even, put + and -. Quadratic Expressions: You can factor the left side or use the quadratic formula. Get the standard form first: ax2 + bx + c = 0. Absolute Value Equations/Inequalities /2x + 1/ = 7 , , This branches out into two equations. 2x + 1 = 7 or 2x + 1 = -7. Solve for x. The graph consists usually of two points. endpoints have holes full endpoints (dots) /2x + 1/ > 7 (same with ) The graph consists of two separate parts. Solution has the word ‘or’. Try solving: 2x + 1 > 7. /2x + 1/ < 7 (same with ) The graph consists of one major part (sANDwich). Solution looks like: a x b. Solve: -7 < 2x + 1 < 7. TI-84 keys: Y= … MATH NUM ABS for absolute value symbol 2nd MATH [TEST] for inequality symbols GRAPH SOL Algebra 2 Scatterplots/Linear Regression/Best Fit Is there a correlation at all? Positive (rising line), Negative (falling line), None (scattered) Slope: m = rise / run Y-intercept b Is it a line that best fits the data points? Then think of y = mx + b. Also, draw a line that fits the data. Then read the coordinates. Is it a curve (parabola) that fits the data? Then think of y = ax2+bx+c Sometimes, you have to change the equation first. (Isolate y on the left.) a > 0 (parabola facing up) a < 0 (down) TI-84: Think of the right entries for L1 & L2. You may simplify entries for L1. (example: number of years since 1980) STAT EDIT …(input)… STAT CALC 4 [LinReg ax+b] y = ax + b gives the equation from which you can predict y Just plug number into x! L1 independent variable L2 variable to predict or find Systems of Equations/Inequalities Look for intersection points of 2 graphs. Or solve the system. (You usually solve for y first in terms of x.) Input: Y1= … Y2 = …. GRAPH. Look at the coordinates of intersection points. Or try 2nd TRACE [Calculate] Intersection Linear Programming: Get the objective function. Plug in x & y coordinates of vertices. Check what is asked for: maximum or minimum? solid line Use y = mx + b form instead of standard > or < dashed line > upper portion shaded < lower portion Sequences & Variation Sigma notation, arithmetic (d), geometric (r) patterns Problem solving, arithmetic & geometric means, rule for an Direct vs. Inverse Joint: z = kxy y = kx y=k/x (square, cube roots, etc.) x/y=x/y xy = xy Word Problems (direct: divide & inverse: product = product) REVIEW your Sequences Quiz and STATISTICS QUIZ!