* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forensic Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
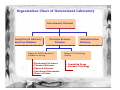
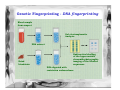
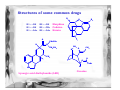
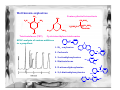
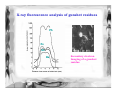
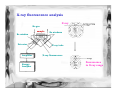
Forensic Science Prof. Dominic T.W. Chan Department of Chemistry, CUHK Rm. SC 163 (South Wing) Tel: 2609-6260 Email: [email protected] Definition of “Forensic Science” • The term “forensic” comes from the Latin word forum, which means “the market-place”. In Roman society, justice was administered in the market-place. • Forensic Science is the study of objects (or evidence) that relate to a crime. • Forensic Scientists observe, classify, compare, use numbers, measure, predict, interpret data, and draw inferences, or reasonable conclusions based on evidence. Objectives • This presentation will introduce some of the experimental methods used by forensic scientists for inspecting common evidence, such as fingerprint, suspected drugs, explosives and bloodstains. Organization Chart of Government Laboratory Government Chemist Analytical & Advisory Services Division Forensic Science Division Physical & Biochemical Evidence Group • • • • • Biochemical Sciences Chemical Sciences Physical Sciences Questioned Documents Scene of Crime Administration Division Drugs & Toxicology Group • Controlled Drugs • Forensic Toxicology Fingerprints • A freshly formed fingerprint contains approximately 1 µg of materials and consists mainly of sweat (99% water, sodium and potassium chloride). There are trace amounts of amino acids and urea plus fatty substances transferred from other parts of the body to the fingers. H2N Amino acid C COOH H R O Urea H3N C NH3 Fatty substances e.g. Undecan-2,6-dienoic acid COOH Common Fingerprint Patterns Plain Arch Tented Arch Loop Central Pocket Loop Plain Whorl Double Loop Developing Latent Fingerprints A. Dusting for fingerprint • for firm smooth surfaces, e.g. drinking glass or window • two common powders (i) vegetable black, a fine carbon powder, for lightcolored surfaces (ii) aluminum powder, a fine white powder, for darkcolored surfaces Developing Latent Fingerprints B. Cyanoacrylate (Superglue) Fuming method • • Superglue vapor polymerizes on latent fingerprints to produce a white deposit. For flexible and rough surface, e.g. aluminum foil, paper, wood and plastics. A- CN H2C C COOR H2C + C - CN A- CN COOR C - A COOR CN H2C POLYMER C COOR CN Further Reaction A C COOR CN C - COOR • Ninhydrin spray is also used on crime scenes to visualize fingerprints, which contain trace amount of amino acids. O O OH OH NH2 + H R OH H COOH O Ninhydrin Amino acid RCHO + + CO2 + O NH3 Hydrindantin (partially reduced ninhydrin) O O OH OH N O + NH3 O OH H O Condensation reaction O OH O Ruhemann’s purple (a blue-purple pigment) Advanced techniques for developing fingerprints C. Laser luminscence Principle of Laser-induced fluorescence Blood spatter analysis 90° 70° 50° 30° 20° 10° Medium velocity impact blood spatter on vertical surface Medium-velocity impact blood spatter on horizontal surface Genetic Fingerprinting - DNA fingerprinting Blood sample from suspect Gel electrosphoretic Analysis DNA extract Dried bloodstain Radioactive labelling of the hypervariable element& photographic imaging of the labelled sequences DNA digested with restriction endonuclease A DNA fingerprint testing for paternity Father Mother Child 3 - the one in question Child 2 Child 1 From father From mother From neither the father nor the mother Mystery Powder and substances • Abused drugs • Suspicious fire • Drunken driving • Explosive & gunshot residues Dangerous Drugs Ordinance in Hong Kong “… over 930 drugs are subject to more regulatory control than other over-the-counter drugs” “… over 140 drugs ... are deemed to need more stringent control owing to their propensity to being abused, which may not only induce dependence in the abusers but could be very detrimental to their health” “… drugs with similar chemical structures are categorised and controlled as a group, e.g. the “Phenethylamines” group to which “Ecstasy” belongs” Common abused drugs in Hong Kong • Heroin (> 60%) • Opium • Cannabis •Ice (methamphetamine hydrochloride) • Phenethylamine or Ecstasy group (Rave Party drugs) - MDMA, MDA, MDEA, MBDB • Benzodiazepines - Midazolam maleate, estazolam and diazepam • Ketamine • Alcohol (uncontrolled drug except for drivers) Structures of some common drugs R1 R1 = -OH R1 = -OH R1 = -OAc R2 = -OH R2 = -CH3 R2 = -OAc O R2 Morphine Codeine Heroin N O H CH2CH3 N CH2CH3 N N CH3 CH3 O O CH3 O HN Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) O H Cocaine C6H5 Methamphetamine • Central nervous system stimulants, appetite suppressants and dependence-forming R = NH2 R = NHCH3 R = NH3CH3Cl R Amphetamine Methamphetamine (MA) Ice “Ecstasy” or “rave party” drugs • Central nervous system stimulants and a hallucinogen • have evidence of permanent damage to the brain on prolonged use O O R R = NH2 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) R = NHCH3 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) R = NHCH2CH3 3,4-methylenedioxyethamphetamine (MDEA) Common Benzodiazepines • Some are used as sedatives or hypnotics, others used as anxiolytics, muscle relaxants or anti-convulsants. • Dependence, drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, depression & loss of memory O N HN N N F F O2N Cl Midazolam maleate (Dormicum or Blue gremlin) NHCH3 Cl Cl Cl Flunitrazepam (Rohypnol or Cross) O N N N N Ketamine N Triazolam (Halicon or Blue gremlin) • Cause hallucinogens, visual distortion, a loss of sense of time, sense & identity, out-ofbody feeling. Characterization and identification of drugs Screening Tests • Solubility tests • pH test • Spot or color tests More Sophisticated Tests • Immunoassays • Chromatographic analysis Immunoassays • large proteins, called antibodies, can recognize and lock on to specific smaller molecules, called antigens, to form a complex Attachment of known antibody to support Addition of sample with unknown amount of drug Addition of excess radiolabelled drug (antigen) Incubation to establish equilibrium Wash to remove unbound radiolabelled drugs Wash to remove unbound drugs Measure the radioactivity of the bound drugs Chromatography Gas chromatography Screening of urine drugs using gas chromatography 1. Amphetamine 2. Methamphetamine 3. Meperidine 4. Phencyclidine 5. Methadone 6. Proposyphene 7. Amitriptyline 8. Cocaine 9. Imipramine 10. Cyheptamide 11. Codeine 12. Diazepam 13. Flunitrazepam Other applications of chromatography in forensic science: • Identify drunken drivers • Suspicious fire Explosives and gunshot residues A photograph of a bullet speeding towards its target Explosives and gunshot residues • A bullet Cartridge case Lead-Antimony core Flash holes Percussion Cap Anvil Propellant (explosive) Guilding metal jacket Well known explosives CH3 O2N NO2 No2 Trinitrotoluene (TNT) Pentacrythritol tetranitrate NO2 CH2ONO2 N No2 N N O2NOH2C NO2 CH2ONO2 CH2ONO2 Cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine HPLC analysis of various additives in a propellent H N H N 1. Diphenylamine O2N H N 2. Carbazole 3. 2-nitrodiphenylamine 4. Dinitrotoluene No2 CH3 NO2 5. N-nitrosodiphenylamine O N N 6. 2,4-dinitrodiphenylamine O2N H N NO2 X-ray fluorescence analysis of gunshot residues Pb Fe Sb Ba Secondary electron Imaging of a gunshot residue X-ray fluorescence analysis X-ray He gas sample Be window Detector Amplifier Energy Analyzer Be windows X-ray tube X-ray fluorescence fluorescence in X-ray range Physical Examination • Checking up on Suspicious Signatures & Documents • Accident reconstruction • Contact evidence examination • Precious metals/Gems analysis in deception and theft cases Analysis of questioned handwriting and signatures Top-of-letter handwriting analysis Botton-of-letter handwriting analysis Space analysis Slant analysis THE END Assignment Write an essay on the portable alcohol detector for use in the field detection of drunken drivers