* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rock Cycle - Valhalla High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
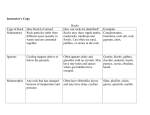
The Rock Cycle- its story Formation of Rocks in More Detail See p6 ESRT C Rock Cycle in Earth’s Crust Depo s and B ition uria l /or and n o cti tation a p en m o em C SEDIMENTARY ROCK M e lt in g athe r ( U pl ift) ing & E ro s i on Pressure t and/or a e H orphism Metam n l i f t) r o s i o p (U &E g n i r the Wea lting Me at io METAMORPHIC ROCK IGNEOUS ROCK n re ss u H e r e a P t r a o / n d is m M e ta m or p h We ( U p l if t ) n Weathering & Erosio SEDIMENTS E r o s ion • To Read the Rock Cycle, follow the arrows around Me ltin g MAGMA S di o li fi c Start with Magma, these are types of Igneous Intrusions which will become Igneous Rock Sometimes pieces of the surrounding rock remain unmelted and become part of the igneous rock (xenolith) Igneous Intrusions-cut through the parent rock Making Sediments and Sedimentary Rock… • • • • • • • Uplift Weathering Erosion Deposition Burial Compaction And Cementation (natural glue- silica, calcite or iron oxides) Sediment Sorting in Land Derived Sedimentary Rocks Sorting of sediments produces separation of the particle sizes(p6) • Pebbles/gravels are dropped first (form conglomerate) • Sands (form sandstone) • Silts, clays are dropped last (form shale) Chemical Origin in Chemically formed Sedimentary Rock • Water contains dissolved minerals, which can fall out of solution (precipitate) due to evaporation or chemical action • Limestone can be formed from tiny grains of calcite deposited from sea or lake waters • Other examples are rock salt (halite) and rock gypsum Organic Origin • Calcite is dissolved out of rocks on land, carried to an ocean or lake, and taken out of the water by shell-producing organisms (eg. Clams, oysters, sea snails) • When these organisms die, their shells pile up and are broken down into fragments, and can form organic limestone Metamorphism… • Metamorphic rocks are not formed from magma or sediment • Metamorphic rocks “morph” (change) from existing rock, due to heat, pressure and chemicals • Pressure squeezes grains closer together (more dense, less porous) • Heat and chemicals may rearrange the particles (new minerals may be formed) Types of Metamorphism Regional Metamorphism: large areas of rock are under intense heat/pressure, which occurs during mountain-building • Heat comes from friction of rocks, and pressure from overlying weight and the squeezing of moving rocks Contact Metamorphism: when hot magma forces itself into overlying rock (intrusions) and bakes the rock Contact Metamorphism Results in Folations if more then one mineral makes up rock • Occurs when the pressure on the rocks squeezes minerals into parallel layers • The rocks tend to split easily along these layers What is the Rock Cycle? • Is the repeated series of events by which rock gradually and continually changes from one type to another • Theses events are geological events-meaning they happen in the Earth’s crust or on it • Another word to describe this is geologic process • Can you name some of these processes? Reading the Rock Cycle Chart • See page 6-7 in the ESRT • First Classify your Rock Samples-work together with your partner • Place them on the Rock Cycle diagram enlarged copy-work together to complete Part II of Lab Complete Understanding the Rock Cycle 1. When granite changes into schist, what geologic processes does it have to undergo? 2. Change gneiss into conglomerate, which geologic processes are involved? 3. Which type of rock can change into the same kind of rock without going through the entire rock cycle? Sum Up: • What are 3 great “truths” about the Rock Cycle? Think about everything we talked about today and see if you can list them below: Sum Up: (well maybe 5 truths…) 1. The Rock Cycle is a model of the natural changes that occur in rocks and rock material 2. Shows all Rocks are made from other rocks or rock remains 3. Shows Rocks are classified upon basis of formation 4. Shows that there are a variety of ways that rocks can change at the surface or within the Earth 5. It keeps on going and going….and has been since the Earth’s Spheres formed Food for thought… • Do we have any influence on the Rock Cycle? If so, what? • What force is driving the Rock Cycle?