* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes 9-4 Sea Floor Spreading Name p. 331
Survey
Document related concepts
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
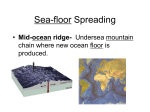
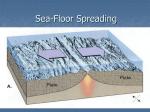
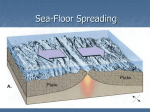
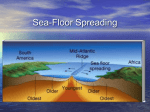
Notes 9-4 Sea Floor Spreading Name _____________________________ p. 331-337 Period _____ Date __________ Even though there is no light and freezing temperatures at the depths of the ocean, the ocean floor is still teeming with _____________. At the East Pacific Rise, ocean water sinks through ________________, or ______________ in the crust. The water is heated by contact with hot material from the _____________________. Bizarre creatures have been discovered at the hot-water _________________. This has provided scientists with ______________________ that supports Wegener’s hypothesis of _________________ __________________. Mapping the Mid-Ocean Ridge The longest chain of mountains in the world is the _________________________________. Scientists started mapping this mountain range in the mid-1900s using ____________________. (a device that bounces __________________ waves off underwater objects & records the echoes) Parts of the mid-ocean ridge poke above the surface. For example, the island of _______________________. A valley, almost twice as deep as the Grand Canyon splits the ___________ of the mid-ocean ridge. Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading ___________________ _______________, an American geologist began studying maps of the mid-ocean ridge & reconsidered Wegener’s idea. In 1960, Hess suggested that at the mid-ocean ridge, molten material _____________ from the ________________ and erupts. The molten material then _____________________ out, pushing _________________ rock to both sides of the ridge. Hess called the process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor _________-______________ _____________________. Three types of evidence support Hess’ theory 1. Evidence from ________________ ____________________: in the 1960s, scientists explored the ocean floor in Alvin and found that new material is ___________________ along the mid-ocean ridge. Rocks shaped like pillows or toothpaste can only form when molten material hardens _________________ after erupting under water. 2. Evidence from _________________ _______________________: Earth’s magnetic poles reverse themselves over time. The rock that makes up the ocean floor lies in a pattern of magnetized “stripes”. These hold a record of _____________________ in the magnetic field. Molten material contains _____________, which lined up in the direction of Earth’s magnetic poles when it cooled. This locked in a “magnetic memory” in the rocks on the ocean floor. 3. Evidence from _______________ _______________________: The Glomar Challenger sent drilling pipes through water ____ km deep in 1968. Samples from the sea floor allowed scientist to determine the ages of rocks. Scientists found that the __________________ away from the M-OR, the ____________________ the rocks. The youngest rocks were always in the __________________ of the ridge. Subduction at Deep-Ocean Trenches Ocean floor does not continue to get wider due to underwater canyons called ________________________________ ________________________. A deep ocean trench forms where the oceanic crust bends _________________________. ____________________________ takes place at the deep-ocean trenches. This is the process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the _____________________. ________________________ _______________________ under the lithosphere push new crust that forms at the MOR ____________________ from the ridge and toward a DOT (deep-ocean trench). New oceanic crust is _____________. But as it moves away from the MOR, it cools & becomes more __________________. Eventually, ____________________ pulls the older, denser crust down the trench. At DOTs, subduction allows part of the ocean floor to sink back into the mantle in a process that takes tens of _____________________ of years. Subduction & Earth’s Oceans Subduction & sea-floor spreading can change the ______________ & __________________ of the oceans. Pacific Ocean: it is ___________________. How? A deep ocean trench __________________more crust than the MOR can _____________________! Atlantic Ocean: it is _______________________. It only has a ___________ short trenches. The spreading ocean floor has nowhere to go! So the continents move also & the whole ocean gets ________________.