* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alabama COS Standards
Survey
Document related concepts
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Principia Mathematica wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
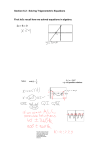
Algebra II with Trigonometry Pacing Guide Suggested Book List 1st Grade All Sorts of Numbers – counting * Henry the Fourth – ordinal numbers * 3 Little Firefighters – sorting * It’s About Time! * Bug Dance * The Best Vacation Ever – data collecting, problem solving skills * Count on Clifford 2nd Grade Amanda Bean’s Amazing Dream – multiplication * Clocks and More Clocks - time * Much Bigger than Martin – size “Slowly, Slowly, Slowly” said the Sloth * Lemonade for Sale - money * 100 Days of School – counting to 100 * Biggest Bed in the World – size * Give Me Half – halves 3rd Grade Sir Cumference and the Dragon Pi * Grandfather’s Tang Story - changing shape * Chicken Soup with Rice – months * Counting on Frank – size comparison, math facts, counting * Hershey’s Milk Chocolate Bar Fraction * How Much is a Million Mummy Math: An Adventure in Geometry * Millions of Cats * Three Days on a River in a Red Canoe 4th Grade Carry On, Mr. Bowditch Sir Cumference and the Great Knight of Angle Land – acute, obtuse, straight angles Sir Cumference and the Sword in the Cone – cubes, pyramids, prisms Sir Cumference and the First Round Table – measurement * A Million Fish…More or Less Dear Mr. Henshaw A Higher Geometry * The Village of Round and Square Houses - shape 5th Grade * How the Second Grade Got $8205.50 to Visit the Statue of Liberty – money Hannah, Divided The Secret Life of Amanda K. Woods – probability Tuck Everlasting – calculate population Gulliver’s Travel – geometry Jayden’s Rescue – problem solving The Curious Incident of the Dog in the Night – time, probability The Heroic of Hercules Amsterdam – counting 6th Grade The Da Vinci Code – Fibonacci Sequence The Twenty-one Balloons – mathematical reasoning Journey to Topaz – measurement 7th Grade The Sand-Reckoner – problem solving The Pearl – currency calculation Middle – High School Imaginary Numbers Mathematics in the Time of Pharaohs Medieval Chinese Innovations Math Talk: Mathematical Ideas in Poems for Two Voices High School Against the Odds – number theory Five Equations that Changed the World The Man Who Loved Only Numbers Math Equals: Biographies of Women Mathematical Scandels Archimede’s Revenge – application of math Calculus and Pizza * denotes AR books Algebra II with Trig Grade Math Pacing Guide Textbook Correlation Pacing Guide AMSTI Big Ideas / Essential Question Essential Vocabulary AHSGE & NAEP Correlations / ARMT Blueprint Alabama COS Standards 1ST Nine Weeks 7. Solve equations, inequalities, and applied problems involving absolute values, radicals, and quadratics over the complex numbers, as well as simple trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Example: solving x2- 8x > -12, 3x = 81, 2 2 sin x + sin x = 0, or logx 2 = 5 1.1-1.6 2 Weeks Compound inequality, absolute value, extraneous solution Solving equations using laws of exponents, including rational and irrational exponents Expressing the solution of an equation, inequality, or applied problem as a graph on a number line or by using set or interval notation 13. Use different forms of representation to compare characteristics of data gathered from two populations. Evaluating the appropriateness of the design of an experimental study Describing how sample statistics reflect values of population parameters Experimental probability, simulation, sample space, theoretical probability 15. Calculate probabilities of events using the laws of probability. Using permutations and combinations to calculate probabilities Calculating conditional probability Calculating probabilities of mutually exclusive events, independent events, and dependent events Page 2 of 13 NAEPA3a, b, A4a, c, N1g, j, N5e Technology Based Lessons / Links 13. Use different forms of representation to compare characteristics of data gathered from two populations. Evaluating the appropriateness of the design of an experimental study Describing how sample statistics reflect values of population parameters 2.1-2.7, 9.1, 9.2 2½ Weeks NAEPA1h, A2a, b, d, e, f, A3a, A4c, A1e Relation, domain, range, mapping diagram, vertical- line test, function, vertex, translation, parent function, branch, scatter trend line 3. Analyze families of functions, including shifts, reflections, and dilations of y = k x (inverse variation), y = kx (direct variation/linear), y = [x] (greatest integer), y = x2 (quadratic), y = ax (exponential), and y = logax (logarithmic). Example: comparing the graphs of y = 2x, y = 2x + 1, y = 2x + 1, and y = -2x Identifying the domain and range of a relation given its graph, a table of values, or its equation, including those with restricted domains Example: finding the domain of y = 1 x3 or y = x2 Identifying real-world situations corresponding to families of functions Linear inequality 7. Solve equations, inequalities, and applied problems involving absolute values, radicals, and quadratics over the complex numbers, as well as simple trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Example: solving x2- 8x > -12, 3x = 81, 2 sin2x + sin x = 0, or logx 2 = 5 Solving equations using laws of exponents, including rational and irrational exponents Expressing the solution of an equation, inequality, or applied problem as a graph on a number line or by using set or interval notation Page 3 of 13 8. Solve systems of linear equations or inequalities in two or three variables using algebraic techniques, including those involving matrices. Example: solving a system of linear equations using augmented matrices and row operations, matrix operations of a graphing calculator, or substitution Evaluating the determinant of a 2x2 or 3x3 matrix Solving word problems involving real-life situations 3.1-3.6 8. Solve systems of linear equations or inequalities in two or three variables using algebraic techniques, including those involving matrices. Example: solving a system of linear equations using augmented matrices and row operations, matrix operations of a graphing calculator, or substitution 2½ Weeks NAEPA2a, A2c, A4a, A4g Evaluating the determinant of a 2x2 or 3x3 matrix Solving word problems involving real-life situations Page 4 of 13 Algebra II with Trig Grade Math Pacing Guide Textbook Correlation Pacing Guide 13.1-13.8 1 Week Big Ideas / Essential Question AMSTI Essential Vocabulary AHSGE & NAEP Correlations / ARMT Blueprint Alabama COS Standards 2ND Nine Weeks 9. Graph trigonometric functions of the form y=a sin(bx), y=a cos(bx), and y=a tan(bx). Determining period and amplitude of sine, cosine, and tangent functions from graphs or basic equations Example: solving problems involving harmonic motion Problem” Chapter 13 and some 14 Periodic function, cycle, period, amplitude, standard position, initial side, terminal side, coterminal angles, unit circle 1 Week ACT Review 11. Define the six trigonometric functions using ratios of the sides of a right triangle, coordinates on the unit circle, and the reciprocal of other functions. “High Drive” “Ferris Wheel 13.1-13.8 1 Week “High Drive” “Ferris Wheel Problem” Chapter 13 and some 14 Page 5 of 13 standard position, initial side, terminal side, coterminal angles, unit circle , central angle, intercepted arc, radian, trigonometric ratios for a right triangle NAEPM1m, G2c Technology Based Lessons / Links 7. Solve equations, inequalities, and applied problems involving absolute values, radicals, and quadratics over the complex numbers, as well as simple trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Example: solving x2- 8x > -12, 3x = 81, 2 2 sin x + sin x = 0, or logx 2 = 5 14.1-14.6 4 Weeks NAEPA3c, A4a, A4e, M1m Solving equations using laws of exponents, including rational and irrational exponents Expressing the solution of an equation, inequality, or applied problem as a graph on a number line or by using set or interval notation Trigonometric ratios for a right triangle 10. Solve general triangles, mathematical problems, and real-world applications using the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines. Deriving formulas for Law of Sines and Law of Cosines Determining area of oblique triangles 11. Define the six trigonometric functions using ratios of the sides of a right triangle, coordinates on the unit circle, and the reciprocal of other functions. Trigonometric identity 12. Verify simple trigonometric identities using Pythagorean and/or reciprocal identities. Example: verifying cos2 + tan2 cos2 = 1 Page 6 of 13 Algebra II with Trig Grade Math Pacing Guide Textbook Correlation Pacing Guide AMSTI Big Ideas / Essential Question Essential Vocabulary AHSGE & NAEP Correlations / ARMT Blueprint Alabama COS Standards 3RD Nine Weeks 8. Solve systems of linear equations or inequalities in two or three variables using algebraic techniques, including those involving matrices. Example: solving a system of linear equations using augmented matrices and row operations, matrix operations of a graphing calculator, or substitution 4.1-4.8 3 Weeks Evaluating the determinant of a 2x2 or 3x3 matrix Solving word problems involving real-life situations 1. Determine the relationships of subsets of complex numbers. Example: using Venn diagrams or tree diagrams to show how subsets of complex numbers are related 5.1-5.8 5 Weeks “Fireworks” “High Dive” Day 23 (Chapter 5) 2. Simplify expressions involving complex numbers, using order of operations and including conjugate and absolute value. Examples: simplifying 3i and 3i 8 , (4-2i)2, Page 7 of 13 Matrix, matrix element, zero matrix, scalar, square matrix, coefficient matrix, variable matrix, constant matrix, augmented matrix NAEPA4a, A4g, N3a, A4d, G2c Imaginary#, i, complex #, Complex # plane NAEPA1e, A2a, A2c, A2g, A4a, A3b, A3c, A4c, G2c Technology Based Lessons / Links Quadratic function, vertex, axis zero, of symmetry, parabola, zero of a function, discriminant 3. Analyze families of functions, including shifts, reflections, and dilations of y = k (inverse x variation), y = kx (direct variation/linear), y = [x] (greatest integer), y = x2 (quadratic), y = ax (exponential), and y = logax (logarithmic). Example: comparing the graphs of y = 2x, y = 2x + 1, y = 2x + 1, and y = -2x Identifying the domain and range of a relation given its graph, a table of values, or its equation, including those with restricted domains Example: finding the domain of y = 1 x3 or y = x2 Identifying real-world situations corresponding to families of functions Factoring, GCF, perfect square trinomial, difference of two squares, completing the square Parabola, axis of symmetry, vertex 4. Determine approximate real zeros of functions graphically and numerically and exact real zeros of polynomial functions. Using the zero product property, completing the square, and the quadratic formula Deriving the quadratic formula 5. Identify the characteristics of quadratic functions from their roots, graphs, or equations. Generating an equation when given its roots or graph Graphing a function when given its equation Examples: graphing equations of the form y = a(x-h)2 + k; graphing equations of the form y = ax2 + bx + c Determining the maximum or minimum values of quadratic functions both graphically and algebraically Applying functions to real-world problems Page 8 of 13 6. Perform operations on functions, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition. Determining the inverse of a function or a relation Performing operations on polynomial and rational expressions containing variables Example: simplifying 3 x5 + 5 2 x 6x 5 Constructing graphs by analyzing their functions as sums, differences, or products 14. Determine an equation of linear regression from a set of data. Examining data to determine if a linear, quadratic, or exponential relationship exists and to predict outcomes Page 9 of 13 Algebra II with Trig Grade Math Pacing Guide Textbook Correlation Pacing Guide AMSTI Big Ideas / Essential Question Essential Vocabulary AHSGE & NAEP Correlations / ARMT Blueprint Alabama COS Standards 4TH Nine Weeks 4. Determine approximate real zeros of functions graphically and numerically and exact real zeros of polynomial functions. Using the zero product property, completing the square, and the quadratic formula Deriving the quadratic formula 6.1-6.6 2 Weeks Relative maximum, relative minimum, multiple zero, multiplicity, sum of cubes, difference of cubes, conjugates Synthetic division, remainder theorem 6. Perform operations on functions, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition. Determining the inverse of a function or a relation Performing operations on polynomial and rational expressions containing variables Example: simplifying 3 x5 + 5 x2 6x 5 Constructing graphs by analyzing their functions as sums, differences, or products Page 10 of 13 NAEPA2g, A3b, A3c, A4a Technology Based Lessons / Links 3. Analyze families of functions, including shifts, reflections, and dilations of y = k x (inverse variation), y = kx (direct variation/linear), y = [x] (greatest integer), y = x2 (quadratic), y = ax (exponential), and y = logax (logarithmic). Example: comparing the graphs of y = 2x, y = 2x + 1, y = 2x + 1, and y = -2x 7.1-7.8 3 Weeks Radical function Identifying the domain and range of a relation given its graph, a table of values, or its equation, including those with restricted domains Example: finding the domain of y = 1 x3 or y = x2 Identifying real-world situations corresponding to families of functions Composite function, inverse relation, inverse function 6. Perform operations on functions, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition. Determining the inverse of a function or a relation Performing operations on polynomial and rational expressions containing variables Example: simplifying 3 x5 + 5 2 x 6x 5 Constructing graphs by analyzing their functions as sums, differences, or products Radical equation 7. Solve equations, inequalities, and applied problems involving absolute values, radicals, and quadratics over the complex numbers, as well as simple trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Example: solving x2- 8x > -12, 3x = 81, 2 2 sin x + sin x = 0, or logx 2 = 5 Page 11 of 13 NAEPA1e, A1g, A2a, A3b, A4a, N1d, N5f Solving equations using laws of exponents, including rational and irrational exponents Expressing the solution of an equation, inequality, or applied problem as a graph on a number line or by using set or interval notation 3. Analyze families of functions, including shifts, reflections, and dilations of y = k (inverse x variation), y = kx (direct variation/linear), y = [x] (greatest integer), y = x2 (quadratic), y = ax (exponential), and y = logax (logarithmic). Example: comparing the graphs of y = 2x, y = 2x + 1, y = 2x + 1, and y = -2x 8.1-8.6 3 Weeks Exponential function, growth factor, decay factor, asymptote, logarithm, common logarithm, logarithmic function Identifying the domain and range of a relation given its graph, a table of values, or its equation, including those with restricted domains Example: = finding the domain of y = 1 x3 or y x2 Identifying real-world situations corresponding to families of functions 6. Perform operations on functions, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition. Determining the inverse of a function or a relation Performing operations on polynomial and rational expressions containing variables Example: simplifying 3 x5 + 5 x2 6x 5 Constructing graphs by analyzing their functions as sums, differences, or products Page 12 of 13 NAEPA13, A1h, A2a, A2b, A2e, A2h, A3a, A3b Exponential equation, change of base formula, logarithmic equation, natural logarithmic function 7. Solve equations, inequalities, and applied problems involving absolute values, radicals, and quadratics over the complex numbers, as well as simple trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Example: solving x2- 8x > -12, 3x = 81, 2 2 sin x + sin x = 0, or logx 2 = 5 Solving equations using laws of exponents, including rational and irrational exponents Expressing the solution of an equation, inequality, or applied problem as a graph on a number line or by using set or interval notation 13. Use different forms of representation to compare characteristics of data gathered from two populations. Evaluating the appropriateness of the design of an experimental study Describing how sample statistics reflect values of population parameters 6.7, 9.7 12.1-12.5 1 Week Sample, sample proportion, random sample, margin of error 14. Determine an equation of linear regression from a set of data. Examining data to determine if a linear, quadratic, or exponential relationship exists and to predict outcomes 15. Calculate probabilities of events using the laws of probability. Using permutations and combinations to calculate probabilities Calculating conditional probability Calculating probabilities of mutually exclusive events, independent events, and dependent events Page 13 of 13 NAEPD1b, D1d, D2a, D2d, D4c, D4e, D4i