* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes Notes 1) Three Conditions Magma Forms Under a
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
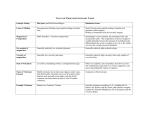
Volcanoes Notes 1) Three Conditions Magma Forms Under a) Temperature i) If the temperature of a rock rises above the melting point of the minerals it is composed of, the rock will melt. b) Pressure i) If a certain amount of pressure is relieved from the rock, its melting point will decrease, thus melting the rock. c) Fluids i) If fluids like water, are added to the rock, it may decrease the melting point of its minerals. This causes the rock to melt. 2) Tectonic Settings Where Volcanoes Form a) Subduction Zones i) At subduction zones, when two plates collide and one sinks, a trench is formed. ii) As the oceanic plate subducts, fluids (water) combine with the crust and mantle material. iii) The fluids decrease the melting points of the rock, causing it to melt. This creates magma. A-3 b) Mid-Ocean Ridge i) When magma comes up at a rift valley, it adds material to the mid-ocean ridge. ii) The magma is formed because it comes closer to the crust, creating less pressure. A-2 c) Hot Spots i) A hotspot is a volcanically active area of Earth’s surface, usually far from a plate boundary. ii) When there is a mantle plume (solid, hot material column,) and the lithosphere moves over it, islands form over the hotspot. iii) This magma is formed from a rise in temperature. 3) Types of Lava a) Mafic i) Mafic is rich in magnesium and iron, and is usually dark in color. ii) Mafic rock is commonly in the oceanic and continental crust. b) Felsic i) Felsic is rich in light-colored silicate materials. ii) Felsic is in continental crust. 4) Volcanic Eruptions a) Quiet Eruptions i) Quiet eruptions usually form from mafic magma. Gases can escape due to its low viscosity. b) Explosive Eruptions i) Explosive eruptions have Felsic lava. It is cooler and stickier than mafic. Due to the lava type, gases, and vapors, Felsic lava throws pyroclastic (rock fragments,) into the air. 5) Types of Volcanoes a) Shield Volcanoes i) Shield volcanoes are cones that are broad at the bottom and slowly slope. ii) Usually have quiet eruptions. Layers of hot lava flow out near the vent, harden, and slowly build up. b) Cinder Cones i) Cinder cones have very steep slopes. The angle of the slope can be close to 40 degrees and rarely more than a few hundred meters high. ii) Cinder cones form from explosive eruptions and are made of pyroclastic material. c) Composite Volcanoes i) Composites have alternating layers of hardened lava and pyroclastic material. ii) Lava flows on the side of the cone during a quiet eruption. iii) During an explosive eruptions, large amounts of pyroclastic material are thrown near the vent.