* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circle Geometry
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
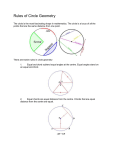
Circle Geometry Terms: 1. Circle - 2. Radius 3. Diameter 4. Arc 5. Chord 6. Perpendicular Lines 7. Parallel Lines 8. Congruent 9. Converse 10. Concentric Circles – 11. Perpendicular Bisector – 12. Midpoint – 13. Tangent – 14. Secant – 15. Isosceles – 16. Scalene – 17. Transversal – 18. Altitude – Page 1 Page 2 19. Parallelogram – 20. Rhombus – 21. Trapazoid – 22. Subtends – 23. Minor Arc – 24. Major Arc – 25. Central Angle – 26. Inscribed Angle – 27. Cyclic Quadrilateral – 28. Sector – 29. Segment – 30. Supplementary Angles – Chord Properties Page 3 Do Investigation 1, page 206-207 – D-J, Investigation 2, page 210,211 – I-N, # 12 1. The __________________ _______________ of a chord goes through the _________________ of a circle. 2. The ________________________ to a chord through the centre of a circle ________________ the chord. 3. Two ____________________ chords of a circle are ______________ from the centre of a circle. 4. The longest chord of a circle is the _____________ . Assign pp. 208, 211 - #4, 5, 6, 7, 14, 15 Converse Statements: Original – If it is raining, then the grass will be wet. Converse – If the grass is wet, then it is raining. The converse is not a true statement. Original – If 2 lines on the same plane are perpendicular, then they form right angles. Converse – If 2 lines on the same plane form right angles, then they are perpendicular. Both the converse and original are true, therefore the statement can be written with iff. 2 lines on the same plane are perpendicular iff they form right angles. Original – If 2 angles have a sum of 180, then they are supplememtary. Converse – Page 4 iff statement – Assign p. 209 - # 10, p. 212 - #17,19,20,21 Problems Involving Chords: 1. A chord is 8.0 cm from the centre of a circle which has a diameter of 20.0 cm. How long is the chord? 2. A chord 10.0 cm long is 12.0 cm from the centre of a circle. What is the radius? Assign p. 221, # 36,37,38 Proofs Congruence Postulates (page 212): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. SSS SAS ASA SAA HL Reasons for angles and sides being equal: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Vertically opposite angles Shared or common side Definition of a midpoint Definition of a bisector Definition of a radius Definition of a right angle Tips for doing proofs: 1. Begin with the ___________ statement 2. Prove triangles are congruent by a _____________ 3. Reason following a postulate will be “_____________ of ______________ triangles” Examples: 1. Given: E bisects AB and CD Prove: AC = BD 2. Given: ΔABC is isosceles D is the midpoint of BC Prove: BAD = CAD 3. Given: O is the centre of a circle Prove: CBO = ADO 4. Given: TP is the bisector of AC Prove: ΔTAC is isosceles Page 5 Page 6 Note p. 218 – Ex. 4 Assign p 216 - #22,23,24,26 Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Slope (m) = = = Do Investigation 3, page 222 (A,B,C,3) Conjectures about slope: 1. Slopes of parallel lines are ___________________. 2. Slopes of perpendicular lines are ______________ ______________. 3. Slopes of horizontal lines are ________________. 4. Slopes of vertical lines are __________________. A figure is a parallelogram if the __________________ sides have ________________ that are _______________. A figure is a rectangle if the _________________ sides are __________ in length and have ____________________ sides with slopes that are ____________________ __________________. Length or distance = Midpoint = Pythagorean Triples – Discuss page 227, #19 (only a,b,c,d with 112A) Assign pp. 226-228 - #10, 16, 18, 20, 21a-e, 26 Page 7 Discuss p. 229, Ex. 8 Assign p. 230, #29, 31 Angles and Arcs 1. A ________________ angle is equal to the measure of the ________ that __________________ it. 2. If an _________________ angle and a _________________ angle are ____________________ by the same _________, then the measure of the ___________________ angle is ________________ the measure of the ____________________ angle. 3. An __________________ angle that is ___________________ by a diameter is equal to ______________. 4. For 2 __________________ lines that are cut by a _______________, the following are true: a. _____________________ angles are equal ( ____ pattern) b. _____________________ interior angles are equal ( _____ pattern) 5. In a ___________ ______________________, the opposite angles are _________________________. Page 8 6. When 2 lines ___________________, the vertically ______________ angles are equal. 7. Note page 238, #18. Discuss page 235, #5 Assign p. 234 – 237, #1,2,6,12(2 of each),13, 14, 15 Handout on angles. Problems on Sectors and Segments Equations : Area of a circle = πr2 Circumference of a circle = πd or 2πr Assign 239-242, #19,20,21,22,25,26,28ac,31,34,42,43a Handout on Problems on Sectors Tangent Properties handouts (Notes and Problems) Example: Superman is flying 3500 m above the earth, which has a radius of 6400 km. How far on the earth can he see? Transformations of Circles Page 9 Equation of a Circle in Standard Form: Discuss Investigation 6, page 252 Equation: x2 + y 2 = r 2 Mapping: (x,y) → (rx, ry) Example: A circle has a radius of 5 cm and the centre is at (0,0). a. What is the equation of the circle? b. What is the mapping rule as a transformation of x2 + y2 = 1 c. Where do each of the following points lie in connection to the circle? a. (2,-6) b. (-3,4) c. (2.5,4.2) Do questions 1-2, page 253 Example: A circle has its centre at the origin and contains a chord with endpoints A(4,8) and B(-8,4). Determine the equation of the circle. Assign page 253- #3-6 Transformations: Page 10 A circle with a centre at a point other than the origin has an equation of: (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2, where (h,k) is the centre. Example: An equation of a circle is defined by (x – 2)2 + (y + 4)2 = 16 a. What is the mapping rule? b. Where is the centre? y c. What is the radius? d. Where do points A(3,-1) and x B(6,-4) lie in relation to the circle? e. Graph. Example: Identify the equation of the following circle: y x Page 11 Example: A circle whose equation is (x + 4)2 + (y – 1)2 = 9 is translated 3 units left and 2 units up. The radius is doubled. What is the new equation and mapping? Assign: Pages 255-257, #7-12abc,20 Changing from Standard to General Form: Steps: 1. Multiply the brackets by using FOIL. 2. Group all terms on the left side and zero on the right side. 3. Combine like terms and arrange in the following form: Ax2 + Ay2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 Example: Change (x – 3)2 + (y + 1)2 = 6 into general form. Page 12 Changing General to Standard Form: (Complete the Square) Steps: 1. Group the x and y terms together. 2. Complete the square for both variables a. Take half of the term in front of the x and square it. b. Add this # to both sides of the equation to balance. c. Do the same for the y term. 3. Factor the perfect square trinomials. 4. Combine the terms on the right side. Example: Rewrite the following into standard from: 1. x2 + y2 + 2x – 6y + 3 = 0 2. x2 + y2 – 3x + 5y – 1 = 0 Transformational Form Page 13 To change from standard form to transformational form, consider (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2 1. Transformational form must equal 1, as does the unit circle. 2. This is done by dividing the equation by r2. 3. The left side is then all enclosed by square brackets. 4. The final outcome is the radius and the centre point is enclosed. Examples: a. (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2 b. (x – 3)2 + (y + 4)2 = 25 c. What is the equation in transformational form of a circle whose centre is (1,-5) having a radius of 7? Assign Page 263- #37-41abc Ellipses Page 15 Definition – a closed plane curve generated by a point moving in such a way that the sum of its distances from 2 fixed points(foci) is a constant. An ellipse does not have a radius. It has a centre and a major and minor axis. The equation of an ellipse has the form: 1 2 a ( x h) + 1 2 b ( y k ) = 1 where 2a is the length of the horizontal axis and 2b is the length of the vertical axis. The longer axis is called the major axis and the shorter is called the minor axis. Example: What is the equation in transformational form of an ellipse with a centre at (2,-1) and a horizontal axis of 12 units and a vertical axis of 8 units? Example: Rewrite the following in transformational form. State the centre, and the length of the major and minor axes. Graph. 9x2 + 4y2 = 36 Assign pp. 265-267, #42,43,44,49,50,51