* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Personal encylopedia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
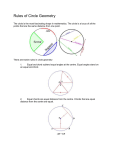
Personal encylopedia Alternate segment theorem: the angle between the tangent and chord at the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. Arc of a circle: a connected section of the circumference. Calculating its length. Associative law: it doesn't matter how you group the numbers (i.e. which you calculate first) when you add or multiply. Chord: a line joining two points on a circle. Circle theorems: e.g. proving the angle subtended by an arc at the centre of a circle is double that at any point on the circumference. Commutative law: you can swap numbers over and still get the same answer when you add or multiply. Constructing polygons within a circle: hexagons and pentagons. Convert a recurring decimal to a fraction. Cosine rule: a squared = b squared + c squared - 2bc cosA Difference between 'equation', 'formula', 'identity' and 'expression': an equation contains unknown quantities and can be solved for x e.g. 3x + 2 = 11; a formula links one unknown quantities to others e.g. A = 2r; an identity is true whatever the value of the unknown quantities e.g. 2(x + y) = 2x + 2y; an expression contains unknown quantities but no equals sign. Distributive law: you get the same answer when you (a) mutliply a number by a group of numbers added together or (b) do each multiplication separately and then add them. Frequency density: the frequency of values divided by the class width of values. Frustrum of a cone: a truncated cone or pyramid where the plane cutting off the apex is parrallel to the base. Instrumental and relational understanding: the former is the application of rules without knowing why, the latter the understanding of what to do and why to do it (Skemp, 1976) Lines and line segments: Lines are a collection of points that stretch to infinity - a line segment exists between two points. Mean from grouped data Mixed numbers consist of an integer and a fraction. Perpendicular from the centre to a chord bisects the chord Prime factor decomposition: Breaking numbers down into their prime factors and writing numbers as a product of their prime factors, including the use of index form. (download) Proof that the angles in a quadrilaterial add up to 360 degrees: using proof of the angles in a triangle. Proof that the angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees: using properties of parrallel lines Properties of angles (download) Properties of parrallelograms Quadratic equations: and how to factorise them. Quadrilaterals: types and properties. Quartiles and interquartile range: Quartiles are the boundaries between four quarters of numbers, and the interquartile range is the range between the first and third quartile. SAS etc. triangles and why SSA triangles aren't unique. Scalar multiple of a vector Sector and segment: sector is a pizza slice, a segment is the area contained between a chord and a circumference. Includes how to measure the area of a sector. Short division: Much like long division, but quicker and emphasises the spoken method more. Take as many digits of the dividend from the LHS such that the divisor is contained at least once, then write the remainder next to the next digit. Sine rule: a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C Surds: square roots that cannot be reduced to a whole number. Tangent: a line that touches a circle at just one point. Tangents from an external point: and how to use this fact. Tessellations: shapes that fit together but aren't square. The unitary method involves altering an equation so that one variable equals 1, to make the equation easier to solve e.g. a man walks 15 miles in 10 hours, how fast does he walk? If you divide both sides by 10, you find he walks 1.5 miles in 1 hour, so his speed is 1.5 miles per hour. Triangular numbers: numbers the objects forming an equilateral triangle i.e. 1, 3, 6, 10, 15... Vector notation Vector operations