* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5. Power supplies requirements
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
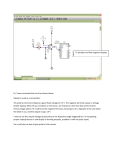
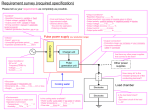
CTF3 Technical Specifications Modulator for a 50 MW – 12 GHz Klystron G.McMonagle AB-RF CONTENTS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction....................................................................................................................................... 3 General description .......................................................................................................................... 3 Characteristics of the klystron .......................................................................................................... 4 Oil tank ............................................................................................................................................. 4 Power supplies requirements ........................................................................................................... 5 5.1 High voltage pulsed power supply ........................................................................................... 5 5.2 Filament power supply ............................................................................................................. 5 5.3 Ion pump power supplies ......................................................................................................... 6 6. Fast protective network .................................................................................................................... 6 7. Cooling ............................................................................................................................................. 6 8. Electrical network ............................................................................................................................. 6 9. X-ray shielding, HV protection.......................................................................................................... 7 10. Local control, status and interlocking ........................................................................................... 7 10.1 Status ....................................................................................................................................... 7 10.2 Measurements.......................................................................................................................... 7 10.3 Interlocks .................................................................................................................................. 8 11. Remote control ............................................................................................................................. 8 12. Mechanical specifications for the installation ............................................................................... 9 13. Transport .................................................................................................................................... 10 14. Acceptance tests ........................................................................................................................ 10 15. Guarantee of operation .............................................................................................................. 10 16. Maintenance ............................................................................................................................... 10 17. Management .............................................................................................................................. 10 18. Deliverable documents ............................................................................................................... 10 19. Schedule .................................................................................................................................... 11 2/11 1. Introduction CLIC, an acronym for “Compact Linear Collider”, is a study of a linear electron / positron collider for the 1 to 5 TeV energy range. A conceptual feature of CLIC is the two beam scheme, where a lower energy, high current drive beam runs in parallel to the high energy beam. The drive beam produces the RF power required to accelerate the main beam. CLIC is recognized as a potential project after the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) The CLIC Test Facility CTF has already in the past served as a test bench for CLIC technology. In its 3rd stage, CTF3, it can be considered as a CLIC module, designed to demonstrate the RF power generation scheme. In addition to the CTF3 facility a stand alone test stand is required for 12GHz high gradient testing is required . This document describes the technical specifications of a high voltage modulator. The modulator will provide power for the 50 MW – 12 GHz klystron for the test stand. 2. General description The modulator is composed of: - a permanent magnet focussed klystron Toshiba or SLAC model (provided by CERN). - a high voltage pulsed power supply (negative polarity) - a filament heater power supply - an ion pump power supply - a hydraulic network - a X-ray shielding - a control-command system - racks containing the materiel The supply include the design and manufacture of the elements, the integration of the klystron(s) provided by CERN, the control – command and interlocks system, the testing and measurements, the delivery and the on-site installation. The modulator will be installed at CERN in Geneva. The general layout of the modulator is presented in Figure 1. Figure 1 : General layout of the modulator 3/11 3. Characteristics of the klystron The klystron will be supplied by CERN. The reference is Toshiba or SLAC. The klystron will be manipulated and installed by CERN. The general characteristics of the klystron can be found in Table 1. Parameters Specifications units RF Frequency 12 (11.4) GHz Peak RF power RF gain 50 MW dB Efficiency RF pulse length Observations 1 % µs 100 Hz Duty cycle Klystron voltage 470 (Toshiba) % kV Nominal voltage: kV Klystron current Inverse klystron voltage 250 (Toshiba) max A kV Nominal current: A Heater voltage max V Nominal value between and V Heater current Heater start up surge current max max A A Nominal value between and A, 15 min max mn kW max max kW kW Pulse repetition rate Preheating period Average collector power Average output power Average body and window power Peak RF drive power Output circuit VSWR A x kV x3.5 µs x 100 Hz 50 MW x 1.0 µs x100 Hz W 1.5 max Pref < 1.8 MW, 4% of reflected power Table 1: Characteristics of Toshiba or SLAC klystron 4. Oil tank The high voltage oil tank supports the klystron and it will contain the gun and all elements at high voltage (pulse transformer). The tank will be provided by the supplier. The oil properties are given in Table 2: Parameters Dielectric strength Oil temperature Specifications Observations 16 kV/mm min. 40 kV min for a 2.5 mm gap 50 °C max. Table 2: Insulating oil specifications The tank must be equipped with an expansion tank (transparent container) to control the oil level. A cooling system can be included to keep the oil temperature under 50 °C. The tank must be tight to avoid any entry of humidity. The modulator must include an additional tank in case of leakage from the main tank. The tank will have to be designed in such a way that it is easy and fast to manipulate and change the klystron. 4/11 5. Power supplies requirements 5.1 High voltage pulsed power supply The power supply must deliver a maximum high voltage pulse of 500kV during 3.5µs (at 75% pulse width) with a pulse repetition rate of 100 Hz. The power supply polarity is negative. The specifications are given in Table 3. Parameters Specifications Units Observations Peak voltage 500 kV tight Peak current 360 A Pulse length (flat top) 1.0 min µs tight Klystron setting area Pulse repetition rate 100 max Hz tight Inverse voltage 75 max kV Pulse voltage ripple % ±0.5 max Pulse to pulse stability % ±0.1 max Rise time 10 – 90 % 1 max µs Fall time 90 – 10 % 2 max µs Pulse width at 75 % 3.5 max µs Table 3: Specifications of the high voltage pulsed power supply Particular attention must be made to minimize the pulse voltage ripple and to provide the best pulse to pulse stability. These two parameters will be optimized for the nominal operating value of the klystron. The voltage rise times and fall times for the high voltage pulse must be fast enough to obtain maximum width state while attaining the 1.0 µs flat top. In any case, the pulse width at 75 % must not be more than 3.5 µs. The voltage must be tuneable between 50 and 100 % of the maximum voltage. 5.2 Filament power supply This power supply is at high voltage potential. The power supply can be either a DC or an AC supply. If a DC supply is used, the positive pole must be connected to filament / cathode connection and the negative pole to filament connection. The filament power supply specifications are given in Table 4: Parameters Heater voltage Heater current Heater start up surge current Preheating period Specifications ? max ? max Units V A ? max A Observations Nominal value between ? and ? V Nominal value between ? and ? A 15 min mn Table 4: Filament power supply specifications 5/11 5.3 Ion pump power supplies The ion pump power supply is voltage regulated. A maximum security threshold for the current must be included. This threshold must be tuneable from 0 to 0.1 mA. The specifications are given in Table 5: Parameters Number of power supply Ion pump voltage Ion pump current Ion pump dissipation power Specifications 1 5 0.1 max Unit kV mA 50 max W Observations Between 3 and 5.5 kV Table 5: Ion pump power supply specifications 6. Fast protective network The modulator needs a crow bar or other related protective network in case of a klystron fault (electrical arc). When a discharge occurs, the energy dissipation in the klystron must be limited to 10 joule. 7. Cooling The modulator includes the hydraulic network for the klystron and the electromagnet cooling. The hydraulic specifications are given in Table 6: Parameters Specifications Unit Observations Water inlet temperature ? max °C Water pressure at klystron ?max bar Absolute pressure collector inlet Water pressure at klystron ? max bar Absolute pressure body and window inlet Collector water flow ? min dm3/mn Body / window water flow ? min dm3/mn Table 6: Hydraulic specifications of the klystron-electromagnet A hydraulic network will be available for the supplier. This network is equipped with flow meters and temperature probes. The supplier will only have to do the connections between the network and the elements. All the metallic parts of the connectors must be in copper or stainless steel. 8. Electrical network The electrical network is 380 V ± 10 %, 50 Hz 3-phase line with neutral at ground. The supplier must define what electrical connectivity is required for the modulator. 6/11 9. X-ray shielding, HV protection The modulator will include a shielding to protect users from X-ray radiations. The maximum acceptable dose is 3 µSv / hr from any part of the system. The shielding must be designed to achieve this goal. The users must be protected from any risks of high voltage electrocution. 10. Local control, status and interlocking The control system to be provided must be based on a Siemens SIMATIC Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) S7-300. The slow changing signals are directly managed by the PLC. Faster signals must have electronics to monitor from pulse to pulse and the interlock information will be sent to the PLC. Local supervision and control commands will be made by a SIEMENS Touch Panel. Personal security interlocks must be treated by hard-wired interlocks. 10.1 Status The modulator system can be found in one of the four control status: OFF, HEATER, STANDBY, PULSING OFF status: the water cooling and the ion pump are on. The high voltage tank temperature is checked and the filament power supply is off. HEATER status: the klystron filament power is on. A delay of 15 minutes must be respected. The ion pump current and voltage are checked. STANDBY status: When this status is on, the premagnetisation of the pulse transformer is activated at this level. The following interlocks are also on: - Klystron water temperature input and output - RF network vacuum or SF6 pressure, RF network water flow - Klystron high voltage pulse (interlock levels given by “pulse surveyor” cards) - RF pulses (interlock levels on incidents and reflected powers, given by “pulse surveyor” cards) The high voltage and RF pulses interlocks are dynamics interlocks. It means that the waveform is controlled for every pulse. For example, on the CERN modulator, the system is switched off if we detect more than 3 pulses faults in 2000 pulses. Should the PLC not be fast enough to react to a pulse to pulse monitoring, electronic modules supplying the signals to the PLC need to ne included PULSING status: the high voltage pulses are applied on the klystron. 10.2 Measurements The following measurements will be available in local or remote: - Klystron cathode voltage and current - Klystron filament voltage and current - Electromagnet currents - Ion pump voltage and current - Inlet and outlet body water temperature - Oil temperature. This list is not exhaustive and additional measurement can be included depending on the chosen technology of the modulator. 7/11 10.3 Interlocks All the interlock levels must be available in local or remote. The complete list of the interlocks must be provided by the supplier. 11. Remote control The PLC will have an Ethernet module to communicate with the CERN network. The PLC will include a specific library which is developed and supplied by CERN. 8/11 12. Mechanical specifications for the installation The modulator system will be installed in the CLic EXperiment Gallery (CLEX-G). The maximum acceptable dimensions are given in Figure 2: Modulator H = 2.6 m L = 5.9 m (zone A) L = 9.2 m (zone B) w = 2.7m (zone A) w = 4.5m (zone B) Figure 2: Mechanical dimensions for a mounted modulator system The maximum charge of the building is about 500 kg/m². There is no crane in the building. Every pieces of the system must be transported with a chariot. Transportation from the outside to CLEX-G: The building is at the second floor (ground floor + one floor). Every piece must be transferred via an elevator which is 2.4 m height. The passageway from the elevator to CLEX-G crosses the LIL gallery. The element to transport must be 1.1 m maximum width and 1.5 m maximum length (seeError! Reference source not found.: Top view of the LIL and CLEX gallery 9/11 Changing a klystron: It is very important that the klystron can be changed easily and quickly. On the CERN modulator, the assembling composed of the oil tank, the klystron and the X-ray shielding can be independently moved. It has to be transported to a place where a crane is available (2500 kg, 4 m maximum height under crane). To go to this place, the assembly must go through the same passageway as described above (see figure 4) 13. Transport The supplier is responsible for the packing, the transport to CERN 14. Acceptance tests Acceptance will be given by CERN after all tests specified have been successfully completed and all the documentation has been supplied. CERN will agree on a date with the supplier to do the acceptance at least 15 days before. An Acceptance Test Data Sheet will be signed after the test by CERN and the supplier. The Acceptance Test will involve the transfer of property of the supply. 15. Guarantee of operation This guarantee covers repairs (pieces, displacement and manpower) during the 24 months as from the on-site acceptance test. 16. Maintenance The supplier must ensure the maintenance of the material after the guarantee period if request by CERN 17. Management The supplier will indicate only one contact person for technical management. The supplier will provide a schedule for manufacturing, making reference to T 0 of the signature of the contract. The design, the procurements, the manufacture, the delivery and installation at CERN will be explicitly mentioned on the schedule. A report will be written by the supplier and co-signed after every meetings with the updates of the schedule. 18. Deliverable documents The supplier will deliver the following documentation at least the last day of the delivery (in French or English language): - The electrical and mechanical drawings of the modulator - The software of the PLC - The Acceptance Test Data Sheet and the Acceptance Test Procedure - An operating and maintenance manual of the modulator - An operating and maintenance manuals of commercial components if it exists 10/11 - a list of reference for components of replacement and, if possible, European sales offices packing and unpacking manuals any other useful documents 19. Schedule The supplier will respect the following schedule: T0 + 12 months: design, procurements and manufacture T0 + 14.5 months: delivery, on-site installation and acceptance tests 11/11