* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
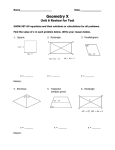
Study for Test 2 – Chapters 4,5 – Geometry MATH 0470 – David Hubbard Note: First problem is a construction – either “perpendicular bisector”, “angle bisector”, or “copy angle”. 4. Quadrilaterals 4.1. Parallelogram properties 4.1.1. Opposite sides are congruent 4.1.2. Opposite sides are parallel 4.1.3. Consecutive angles are supplementary 4.1.4. Diagonals bisect each other 4.1.5. Use properties of a parallelogram to solve problems 4.2. The parallelogram and kite 4.2.1. A kite is a quadrilateral with adjacent sides congruent. One pair of opposite angles is congruent. 4.2.2. For a triangle ABC with median MN, MN = ½(AB) if AB is the base and also MN is parallel to AB. 4.2.3. Know how to prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram 4.3. Rectangle, square, and rhombus 4.3.1. Rectangle – all 4 angles are right angles and diagonals are Rhombus – all 4 sides are congruent and diagonals are perpendicular 4.3.2. Find the length of the diagonal of a rectangle 4.3.3. Square – properties of both a rectangle and a rhombus 4.4. Trapezoid 4.4.1. Isosceles trapezoid – sides are congruent, base angles are congruent, and diagonals are congruent 4.4.2. Median of a trapezoid – if MN is the median of trapezoid ABCD then MN = ½(AB +DC) and MN is parallel to both bases 4.4.3. If 3 parallel lines intercept congruent segments on a transversal, any other transversal will also intercept congruent segments. 5. Similar Triangles 5.1. Ratios, rates and proportions – be able to use properties to solve proportions. 5.2. Similar Polygons 5.2.1. Be able to use proportionality relationships in geometry problems 5.3. Proving Triangles Similar 5.3.1. Be able to prove triangles are similar using AA, SAS~, SSS~. 5.3.2. Know how to use CSSTP in a proof. 5.4. The Pythagorean theorem 5.4.1. Be able to determine whether a triangle is right, acute, or obtuse 5.5. Special right triangles 5.5.1. 45-45-90 triangle: Given one length be able to find the other 2 5.5.2. 30-60-90 triangle: Given one length be able to find the other 2 5.6. Segments divided proportionally 5.6.1. Line parallel to one side of triangle 5.6.2. 3 or more parallel lines 5.6.3. Angle bisector theorem