* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer Sheet to Review Questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
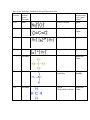
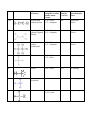
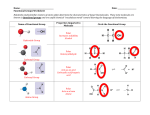
Answer Sheet to Review Questions Worksheet numbered 1-20 where the first question is 1. Which compounds contain only polar bonds? Answers: 1. Ignore this question for now, given what we’ve spoken about, technically 1 AND 3 would be correct 2. 4 3. 3 4. 4 5. 4 Remember that diamond = all carbons covalently bonded to each other = network solid 6. 4 7. 3 8. 1 9. 3 10. 1 11. 2 12. 3 13. 2 14. 2 15. 3 16. 3 17. 2 18. 2 19. 3 20. 4 Worksheet numbered 1-14 where the first question is 1. A compound is made up of iron and oxygen, only. The ratio of iron to oxide ions is 2:3 in this compound. The IUPAC name for this compound is: 1. C 2 B 3. A 4. D 5. C 6. A 7. B 8. B 9. A 10. D 11. B 12. C 13. D 14. D Back of the Worksheet I handed out this past Thursday/Friday Molecular Type of Lewis-Dot Structure Name of Compound Formula bonding (IonicCovalent) NaCl Sodium Chloride Ionic Predominant Intermolecular Force (ignore if ionic) Ignore CO2 Covalent Carbon Dioxide Dispersion Forces. SrBr2 Ionic Strontium Bromide Ignore KBr Ionic Potassium Bromide Ignore CCl4 Covalent Carbon Tetrachloride Dispersion Forces. NH3 Covalent Nitrogen trihyrdride (ammonia) Hydrogen Bonding CH4 Covalent Carbon Dispersion tetrahyrdride( methane) Forces. Answers to 113-116 in Review Book (RED BOOK WITH GRAINY BLUE/BLACK PICTURES) Answers: 1. 4 2. 2 3. 3 4. 1 5. 3 6. 3 7. 3 8. 2 9. 3 10. 2 11. 1 12. 3 13. 1 14. 2 15. 3 16. 4 17. 3 18. 1 19. 3 20. 2 21. 1 22. 2 23. 1 24. 4 25. 2 26. 1 27. 1 28. 3 29. 2 30. 31. Fluorine has a higher electronegativity value than iodine and therefore has a greater pull on the shared electrons causing the bond to be more polar. 32. Sulfur (S) 33. It is a symmetrical molecule 34. The electronegativity values of C and O are different and produce a polar bond, while the two fluorine atoms have the same electronegativity and produce a nonpolar bond. 35. 36. The extrapolated boiling point appears to be -70oC. The attractive forces between water molecules holding them in the liquid phase are hydrogen bond, which are stronger than dipole-dipole attractions between the other molecules. 37. Diagrams of the molecules should be like the ammonia molecule. Dotted lines (NOT COVALENT BONDS) connect the Nitrogen atom of one molecule to the to the Hydrogen atoms of another molecule. 38. Ethane (C2H6) Ethene (C2H4) Ethyne (C2H2) CH4 Answers to Lewis-Dot Structure Sheet (Handout from Thanksgiving Week) Name: Period: For the following compounds fill in the following table: Nonpolar covalent = electronegativity difference between the two bonding atoms is 0. Intermolecular forces. 1. Hydrogen Bonding. 2. Dipole-Dipole. 3. Dispersion Forces Lewis Structure Molecular Identify polar and Molecular Predominant (most Polarity significant) Geometry nonpolar covalent (Yes/No) intermolecular bonds (Atomforce Atom) Tetrahedral C-H = polar No Dispersion forces Br2 Linear Br-Br = nonpolar No Dispersion forces H2O Bent O-H = polar Yes H-bonding H2S Bent S-H = Polar Yes Dipole-Dipole CO2 Linear C-O = Polar No Dispersion forces CO Linear C-O = Polar Yes Dipole-Dipole Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Identify polar and nonpolar covalent bonds (AtomAtom) C-H = Polar C-C = Nonpolar Molecular Polarity (Yes/No) Predominant intermolecular force No Dispersion forces C2H2 Around each carbon (Linear) C2H4 Around each carbon (Trigonal Planar) C-H = Polar C-C = Nonpolar No Dispersion forces C2H6 Around each carbon (tetrahedral) C-H = Polar C-C = Nonpolar No Dispersion forces CHF3 Tetrahedral C-H = Polar C-F = Polar Yes Dipole-Dipole HF Linear H-F = Polar Yes H-bonding NH3 Trigonal Pyramidal N-H = Polar Yes H-bonding CH3Cl Tetrahedral C-H = Polar C-Cl = Polar Yes Dipole-Dipole