* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lessons 9-1 to 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
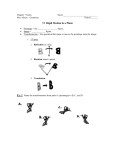
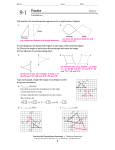
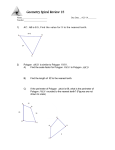
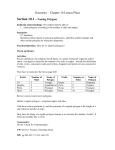
Honors Geometry Lessons 9-1 to 9-3 Review Name ____________________________________ SHOW ALL WORK FOR FULL CREDIT!! 1.) Use the translation (x, y) (x + 6, y – 3). a.) What is the image of A(3, 2)? b.) What is the image of B(–4, 1)? c.) What is the preimage of C'(2, –7)? d.) What is the preimage of D'(–3, –2)? 2.) The vertices of ABC are A(-1, 1), B(4, -1), and C(2, 4). Graph the image of the triangle using prime notation. a.) (x, y) (x - 3, y + 5) b.) (x, y) (x – 4, y –2) 3.) A'B'C is the image of ABC after a translation. Write a rule for the translation. Then verify that the translation is an isometry. a.) b.) 4.) Name the vector and write its component form. a.) b.) c.) 5.) Use the point P(5, -2). Find the component form of the vector that describes the translation to P'. a.) P' (2, 0) b.) P' (8, –3) c.) P' (0, 4) 6.) The vertices of ABC are A(1. 2), B(2, 6), and C(3, 1). Translate ABC using the given vector. Graph ABC and its image. a.) 8, 2 b.) -7, –3 7.) Find the value of each variable in the translation. a.) b.) 8.) Add or subtract. 3 5 2 1 4 6 4 2 7 2 6 1 8 4 4 6 a.) 4 5 6 1 b.) 9 1 9 _ 5 c.) 2 6 7 0 1.4 1.3 1.4 3 d.) 5 6. 5 _ 3.9 4 2 4 1.3 3.9 b.) P' (–5,–4) 9.) Find the image matrix that represents the translation of the polygon. Then graph the polygon and its image. A B C a.) 1 5 3 5 units right and 3 units down ; 2 2 6 b.) M N O P 6 units left and 2 units up 3 7 5 1 ; 1 2 6 5 10.) Multiply a.) 2 3 1 4 5 4 7 5 b.) –4 5 0 – 4 –3 0 c.) 2 5 5 4 1 0 3 2 11.) Use the described translation and the graph of the image to find the matrix that represents the preimage. a.) 3 units right and 4 units up b.) 2 units left and 3 units down 12.) Graph the reflection of the polygon in the given line. a.) y = 1 b.) y = –x c.) y = x 13.) Use matrix multiplication to find the image. Graph the polygon and its image. A B C A B C D a.) Reflect 3 1 6 in the x-axis. b.) Reflect 2 5 7 1 in the y-axis 4 7 2 6 4 5 3 14.) Write a matrix for the polygon. Then find the image matrix that represents the polygon after a reflection in the given line. a.) x-axis b.) y-axis c.) x-axis 15.) The vertices of ∆ABC are A(-2, 1), B(3, 4), and C(3, 1). Reflect ∆ABC in the first line. Then reflect ∆A’B’C’ in the second line. Graph ∆A’B’C’’ and ∆A”B”C”. a.) In y = 1, then in y = – 2 b.) In x = 4, then in y = –1 c.) In y = x, then in x = –2