* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What causes volcanoes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
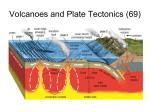
Notes: Volcanoes What causes volcanoes? Magma under heat & pressure is less dense than rock. It flows out of vent and cools quickly becoming solid, igneous rock that builds up around the vent. The crater is the steep walled depression around the vent. Volcanoes may vent from the top or laterally (on the side) Where are volcanoes located? They are related to the Earth’s plates: Diverging plates-create rifts where magma flows and cools quickly in seawater. Can build up above sealevel and become island- Ex Iceland Converging plates-magma created in subduction zone is less dense than surrounding material and is forced outward. Ex-Mt. St. Helens (Cascade range) Hot spots- places in the mantle that are unusually hot. Magma from deep in Earth’s mantle has melted the crust to form volcanoes. Ex- Hawaiian Islands Types of Eruptions: Explosive, violent (1)Trapped gases (water, carbon dioxide) Under pressure eventually escape. Mt. St. Helens (2)Composition magma- granite converging plates, subduction zones, dense, thick, lots of silica. Gets trapped in vents, pressure builds beneath itexplosive eruption, gases expand rapidly often carrying pieces of lava in explosion Mt. St. Helens If the water content is high the eruption is more explosive. Composition magma- basalt – Less silica, less dense, more fluid produces quiet, nonexplosive eruptions. Mt. Kilauea Form or shape of volcano has to do with type lava: basaltic, granitic, intermediate. Shield Volocano Quiet, spreads basaltic lava in flat layers which build up to be broad volcano with gently sloping sides. Ex-Mauna Loalargest active volcano on Earth. Cinder cone Volcano Explosive, throws lava in the air which cools, hardens and falls as cinders, rocks(bombs) Becomes steep sided, cinder cone. Ex-Paricutin, Mexico Composite- has explosive period and quiet period. Forms at convergent plate, lava and rock forms in layers.