Giant Tortoises of the Galápagos Islands
... • Hutton and Lyell (geologists) helped scientists recognize that Earth is many millions of years old, and the processes that changed Earth in the past are the same processes that operate in the present. ...
... • Hutton and Lyell (geologists) helped scientists recognize that Earth is many millions of years old, and the processes that changed Earth in the past are the same processes that operate in the present. ...
natural selection - Northern Highlands
... - In stable environments, mutations often result in little or no benefit to an organism, or are often harmful - Mutations are more beneficial (rare) in changing environments (Example: HIV resistance to antiviral drugs) ...
... - In stable environments, mutations often result in little or no benefit to an organism, or are often harmful - Mutations are more beneficial (rare) in changing environments (Example: HIV resistance to antiviral drugs) ...
Evolution
... species to change over time. Species alive today are descended with modification from ancestral species that lived in the distant past. This process, by which diverse species evolved from common ancestors, unites all organisms on Earth into a single tree of life. ...
... species to change over time. Species alive today are descended with modification from ancestral species that lived in the distant past. This process, by which diverse species evolved from common ancestors, unites all organisms on Earth into a single tree of life. ...
2014 answers to Study guide for test on end of chapter 2 and
... __around the horn South America (south from central Brazil), around the world to Australia, around the Horn of Africa 4. He found many different organisms on the trip. Each type was _well suited_ for the _environment_ in which it lived. 5. Darwin wondered how one could explain both the similarities_ ...
... __around the horn South America (south from central Brazil), around the world to Australia, around the Horn of Africa 4. He found many different organisms on the trip. Each type was _well suited_ for the _environment_ in which it lived. 5. Darwin wondered how one could explain both the similarities_ ...
File
... Some organisms have genes that improve their ability to survive and reproduce. If the genes also help their offspring survive and reproduce, then which of the following will most likely increase? A The frequency of the genes in one individual B The frequency of the genes in the population C The numb ...
... Some organisms have genes that improve their ability to survive and reproduce. If the genes also help their offspring survive and reproduce, then which of the following will most likely increase? A The frequency of the genes in one individual B The frequency of the genes in the population C The numb ...
Darwin developed a theory of evolution
... • How did the work of Lyell and Malthus influence Darwin as he developed his theory of evolution? • What characteristics of the Galápagos Islands were particularly important for Darwin? • What is natural selection? • Which of the following is an adaptation: the sharp teeth of a house cat, or a scar ...
... • How did the work of Lyell and Malthus influence Darwin as he developed his theory of evolution? • What characteristics of the Galápagos Islands were particularly important for Darwin? • What is natural selection? • Which of the following is an adaptation: the sharp teeth of a house cat, or a scar ...
Chapter 15 Evolution: Evidence and Theory
... were also interested in the natural sciences. - In 1831, one of his teachers recommended him to be an unofficial naturalist on the HMS Beagle. - The Beagle sailed on Dec. 27, 1831 and eventually ended up on the Galapagos Islands. o On the voyage, Darwin read Charles Lyell’s book “Principles of Geolo ...
... were also interested in the natural sciences. - In 1831, one of his teachers recommended him to be an unofficial naturalist on the HMS Beagle. - The Beagle sailed on Dec. 27, 1831 and eventually ended up on the Galapagos Islands. o On the voyage, Darwin read Charles Lyell’s book “Principles of Geolo ...
Evolution - Ms
... increase an organisms fitness Those that are best able to survive and reproduce are the fittest, hence Survival of the Fittest ...
... increase an organisms fitness Those that are best able to survive and reproduce are the fittest, hence Survival of the Fittest ...
Evolution Summative Assessment DO NOT WRITE ON TEST
... b. Natural selection accounts for these losses by the principle of use and disuse. c. Under particular circumstances that persisted for long periods, each of these structures presented greater costs than benefits. d. The ancestors of these organisms experienced harmful mutations that forced the ...
... b. Natural selection accounts for these losses by the principle of use and disuse. c. Under particular circumstances that persisted for long periods, each of these structures presented greater costs than benefits. d. The ancestors of these organisms experienced harmful mutations that forced the ...
Review Packet - Unit 15 Populations and Natural Selection Short
... environmental factors restrict population growth – these can be interspeficif interations or abiotic factors, normally competition for resources – some individuals win the competition, others lose 2. Describe the difference between density dependent and density independent factors in your answer. De ...
... environmental factors restrict population growth – these can be interspeficif interations or abiotic factors, normally competition for resources – some individuals win the competition, others lose 2. Describe the difference between density dependent and density independent factors in your answer. De ...
Units 8 & 9: Evolution and Classification
... Populations evolve not the individual organism Natural Selection acts upon the phenotypic expression of a gene in the life time of an individual organism new features do not evolve in a life time ...
... Populations evolve not the individual organism Natural Selection acts upon the phenotypic expression of a gene in the life time of an individual organism new features do not evolve in a life time ...
1199703darwin
... • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occur during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. ...
... • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occur during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. ...
What is Evolution?
... 1. Use the stick worm activity to write your own description of Natural Selection to show me that you understand how variation, adaptation, selective forces and reproduction play a role in natural selection and thus evolution. 2. Write a paragraph describing how artificial selection supports the the ...
... 1. Use the stick worm activity to write your own description of Natural Selection to show me that you understand how variation, adaptation, selective forces and reproduction play a role in natural selection and thus evolution. 2. Write a paragraph describing how artificial selection supports the the ...
name date ______ period
... make up labs/quizzes/tests, etc. before or after school. BIOLOGY CALENDAR SEMESTER 2 WEEK 3 TOPIC: ENZYMES AND EVOLUTION Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. As a basis for understanding this concept: ...
... make up labs/quizzes/tests, etc. before or after school. BIOLOGY CALENDAR SEMESTER 2 WEEK 3 TOPIC: ENZYMES AND EVOLUTION Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. As a basis for understanding this concept: ...
Answer Key evolution study guide
... Multiple examples: size of corn, chicken, cows, bananas, types of vegetables coming from the mustard plant, dog breeds. There are other correct examples that are not listed. Natural Selection 17. What is Charles Darwin often referred to as? How were Darwin’s ideas different than Lamarck's? Darwin: T ...
... Multiple examples: size of corn, chicken, cows, bananas, types of vegetables coming from the mustard plant, dog breeds. There are other correct examples that are not listed. Natural Selection 17. What is Charles Darwin often referred to as? How were Darwin’s ideas different than Lamarck's? Darwin: T ...
species change - New Braunfels ISD
... Galapagos Islands Created the idea of Natural Selection Author ...
... Galapagos Islands Created the idea of Natural Selection Author ...
Water Test 1 Review Sheet
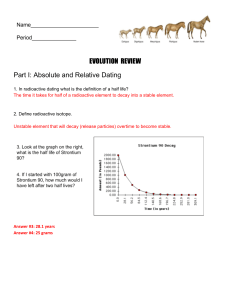
... What is the difference between radioactive dating and the law of superposition and what does each tell us? ...
... What is the difference between radioactive dating and the law of superposition and what does each tell us? ...
Unit 4 Evolution Study Guide (TEST WEDNESDAY MARCH 16, 2016)
... The exact age of the fossils, determining exactly how the organisms look, and the type of habitat each species required for survival. 16. What does radiocarbon dating technique show about the way organisms evolved? It shows the relative time period where plants and animals evolved spanning hundreds ...
... The exact age of the fossils, determining exactly how the organisms look, and the type of habitat each species required for survival. 16. What does radiocarbon dating technique show about the way organisms evolved? It shows the relative time period where plants and animals evolved spanning hundreds ...
Bio07_TR_U05_CH15.QXD - BellevilleBiology.com
... 13. survival of the fittest _______________________________________________________________ A. a phrase the expresses that those with mutations that are favorable will live the longest and reproduce B. A phrase that expresses that only those that fit into their habit, will survive ...
... 13. survival of the fittest _______________________________________________________________ A. a phrase the expresses that those with mutations that are favorable will live the longest and reproduce B. A phrase that expresses that only those that fit into their habit, will survive ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... What did he say? 3. Selection: In an environment, having a particular trait can make individuals more or less likely to survive and have successful reproduction. So, some individuals leave more offspring than others. 4. Adaptation: Over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction ...
... What did he say? 3. Selection: In an environment, having a particular trait can make individuals more or less likely to survive and have successful reproduction. So, some individuals leave more offspring than others. 4. Adaptation: Over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction ...
Evolution Powerpoint
... of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. Over many generations, changes in the genetic makeup of populations may affect biodiversity through speciation and extinction. ...
... of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. Over many generations, changes in the genetic makeup of populations may affect biodiversity through speciation and extinction. ...
Printable Version
... This is the process by which one species evolves into two or more species. It occurs as a result of different populations becoming reproductively isolated from each other, usually by adapting to different environments. An evolutionary mechanism that occurs when some individuals of a population are b ...
... This is the process by which one species evolves into two or more species. It occurs as a result of different populations becoming reproductively isolated from each other, usually by adapting to different environments. An evolutionary mechanism that occurs when some individuals of a population are b ...
Study Guide
... A natural environment does not have enough food, water, and other resources. Only some survive to adulthood. 6. Successful reproduction The individual that are best adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce (think natural selection) 7. Genetic variation Individuals in a population are ...
... A natural environment does not have enough food, water, and other resources. Only some survive to adulthood. 6. Successful reproduction The individual that are best adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce (think natural selection) 7. Genetic variation Individuals in a population are ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.