Embedded SQL Guide for RM/Cobol
... 1. Program Structure 1.1. General An embedded SQL application is an application in which the SQL statements needed to access data from the database manager are coded directly into the source code of the application. These SQL statements are compiled into code, executable by the database manager, at ...
... 1. Program Structure 1.1. General An embedded SQL application is an application in which the SQL statements needed to access data from the database manager are coded directly into the source code of the application. These SQL statements are compiled into code, executable by the database manager, at ...
Accounting Information Systems: The Crossroads of Accounting and
... Objective: Q2.2 What is the role of the database in the enterprise? 15) How are hierarchical databases and network databases similar? How are they different? Answer: Hierarchical databases and network databases are similar in that they store data in records that are not grouped into database tables. ...
... Objective: Q2.2 What is the role of the database in the enterprise? 15) How are hierarchical databases and network databases similar? How are they different? Answer: Hierarchical databases and network databases are similar in that they store data in records that are not grouped into database tables. ...
Document
... – Automatically handles setting certain system parameters that can otherwise cause problems during upgrade (E.g. set job_queue_processes = 0) DBMS_REGISTRY package and system table are used to record and manage information about all the component upgrades – E.g. ...
... – Automatically handles setting certain system parameters that can otherwise cause problems during upgrade (E.g. set job_queue_processes = 0) DBMS_REGISTRY package and system table are used to record and manage information about all the component upgrades – E.g. ...
Transaction Commit Options - Entity beans in the EJB container of BES
... The pooled state is where an entity bean instance is not associated with a primary key. ...
... The pooled state is where an entity bean instance is not associated with a primary key. ...
Sample
... 13) What are the structures of a relational database, hierarchical database, and a network database? How is data retrieved from each of these types of databases? Answer: A relational database is structured as tables. A record is a row in one of the tables. The tables are related to each other by in ...
... 13) What are the structures of a relational database, hierarchical database, and a network database? How is data retrieved from each of these types of databases? Answer: A relational database is structured as tables. A record is a row in one of the tables. The tables are related to each other by in ...
SQL Server Replication: Providing High Availability using Database
... transactions. When the database is not synchronized, the mirror server is typically available as a warm standby server (with possible data loss). A database mirroring session runs with either synchronous or asynchronous operation. Under asynchronous operation (also called high-performance mode), tra ...
... transactions. When the database is not synchronized, the mirror server is typically available as a warm standby server (with possible data loss). A database mirroring session runs with either synchronous or asynchronous operation. Under asynchronous operation (also called high-performance mode), tra ...
CODESOFT 10 Database Manager
... Duplicate a record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Modify a record. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sort a series of records by alphanumerical order. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Duplicate a record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Modify a record. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sort a series of records by alphanumerical order. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Joins and subqueries
... A subquery can be defined as a SELECT query that returns a single value Subqueries are nested within a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement Subqueries can be used to retrieve data from multiple tables and can be used as an alternative to a join Subqueries can also be used inside the WHERE ...
... A subquery can be defined as a SELECT query that returns a single value Subqueries are nested within a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement Subqueries can be used to retrieve data from multiple tables and can be used as an alternative to a join Subqueries can also be used inside the WHERE ...
Log File Viewer | Microsoft Docs
... To connect to offline log files, an instance of SQL Server must be installed on the computer that you are using to view the offline log files, and on the computer where the log files that you want to view are located. If an instance of SQL Server is installed on both computers, you can view offline ...
... To connect to offline log files, an instance of SQL Server must be installed on the computer that you are using to view the offline log files, and on the computer where the log files that you want to view are located. If an instance of SQL Server is installed on both computers, you can view offline ...
Chapter B: Hierarchical Model
... type> within the designated subtree to resume search. Use currency pointer to determine where to resume search. DB-status is set to a nonzero value if no such record exists in the ...
... type> within the designated subtree to resume search. Use currency pointer to determine where to resume search. DB-status is set to a nonzero value if no such record exists in the ...
Migrating Applications and Databases to Oracle Database 12c
... Since its introduction, the VARCHAR2 data type has had a max size of 4,000 bytes, which equates to 4,000 characters in single byte character sets. Table column definitions exceeding this size would be migrated as Character Large Objects, or CLOBs. This presented a challenge for many customers migrat ...
... Since its introduction, the VARCHAR2 data type has had a max size of 4,000 bytes, which equates to 4,000 characters in single byte character sets. Table column definitions exceeding this size would be migrated as Character Large Objects, or CLOBs. This presented a challenge for many customers migrat ...
DBMS - Department of Higher Education
... elements require no change in the computer programs processing them or so that these changes can be made automatically by the database management system. These are the techniques that allow data to be changed without affecting the applications that process it. There are two kinds of data independenc ...
... elements require no change in the computer programs processing them or so that these changes can be made automatically by the database management system. These are the techniques that allow data to be changed without affecting the applications that process it. There are two kinds of data independenc ...
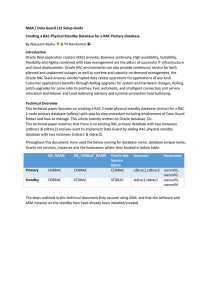
MAA / Data Guard 12c Setup Guide Creating a RAC Physical
... duplicate internally it performs bounce of standby database and whenever instance is closed there will be no more services registered with the listener and hence by setting, we can escape from “ORA-12514: TNS:listener does not currently know of service requested in connect descriptor” and Oracle can ...
... duplicate internally it performs bounce of standby database and whenever instance is closed there will be no more services registered with the listener and hence by setting, we can escape from “ORA-12514: TNS:listener does not currently know of service requested in connect descriptor” and Oracle can ...
Solutions
... Identify objects what will be lost during TSPITR by querying TS_PITR_OBJECTS_TO_BE_DROPPED view on the primary database ...
... Identify objects what will be lost during TSPITR by querying TS_PITR_OBJECTS_TO_BE_DROPPED view on the primary database ...
(A) R - Avi Silberschatz
... A relation schema R is in BCNF with respect to a set F of functional dependencies if for all functional dependencies in F+ of the form , where R and R, at least one of the following holds: ...
... A relation schema R is in BCNF with respect to a set F of functional dependencies if for all functional dependencies in F+ of the form , where R and R, at least one of the following holds: ...
Integration Service Database Installation Guide
... 1. Only a qualified Oracle Database Administrator (DBA) must handle the Oracle Database setup in order to successfully complete the Kony database deployment. 2. Customer with Oracle standard edition should install Oracle Locator feature. For more information, see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/ ...
... 1. Only a qualified Oracle Database Administrator (DBA) must handle the Oracle Database setup in order to successfully complete the Kony database deployment. 2. Customer with Oracle standard edition should install Oracle Locator feature. For more information, see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/ ...
With Oracle Database 12c, there is all the more reason to use
... • The granularity of the editioned state of the name of a PL/SQL unit, a view, or a synonym is now the single occurring name. New DDL statements control this new degree of freedom. This means that, for example, Scott.Name_1 can be chosen to be editioned and can denote a procedure in one edition and ...
... • The granularity of the editioned state of the name of a PL/SQL unit, a view, or a synonym is now the single occurring name. New DDL statements control this new degree of freedom. This means that, for example, Scott.Name_1 can be chosen to be editioned and can denote a procedure in one edition and ...
CIM Database Model
... services that control the administration, usage, monitoring, and maintenance of a database. ...
... services that control the administration, usage, monitoring, and maintenance of a database. ...
ECDL / ICDL Using Databases Level 1 Syllabus Version 1.0 (UK)
... as permitted by ECDL Foundation. Enquiries for permission to reproduce material should be directed to ECDL Foundation. Disclaimer Although every care has been taken by ECDL Foundation in the preparation of this publication, no warranty is given by ECDL Foundation, as publisher, as to the completenes ...
... as permitted by ECDL Foundation. Enquiries for permission to reproduce material should be directed to ECDL Foundation. Disclaimer Although every care has been taken by ECDL Foundation in the preparation of this publication, no warranty is given by ECDL Foundation, as publisher, as to the completenes ...
Evolution Database Maintenance Guide
... : Database name to be restored b. To a point time : Most recent possible c. Source for restore : Select the option From device and provide the backup file location. d. Click the Options menu in the left panel, provide separate hard drive location for the transaction log files, i.e., if the file type ...
... : Database name to be restored b. To a point time : Most recent possible c. Source for restore : Select the option From device and provide the backup file location. d. Click the Options menu in the left panel, provide separate hard drive location for the transaction log files, i.e., if the file type ...
File Organization
... surface associated with it as the disk rotates, we would create a circular figure called track. The tracks at the same position on every surface of the disk form the surface of an imaginary cylinder. In disk terminology, therefore, a cylinder consists of the tracks under the heads on each of its sur ...
... surface associated with it as the disk rotates, we would create a circular figure called track. The tracks at the same position on every surface of the disk form the surface of an imaginary cylinder. In disk terminology, therefore, a cylinder consists of the tracks under the heads on each of its sur ...
SQL Server Replication
... replication stream) in the order in which they occur, and typically there is low latency between the time the change is made on the Publisher and the time the change takes effect on the Subscriber. This enables a number of scenarios, such as scaling out a query workload or propagating data from a ce ...
... replication stream) in the order in which they occur, and typically there is low latency between the time the change is made on the Publisher and the time the change takes effect on the Subscriber. This enables a number of scenarios, such as scaling out a query workload or propagating data from a ce ...