Slide 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Physicists were both mystified and intrigued by Bohr’s theory. They questioned why the energies of hydrogen electron are quantized, or, why is the electron in a Bohr atom restricted or orbiting the nucleus at certain fixed distance? For a decade there is no logical explanation. In 1924, Louis de Bro ...
... Physicists were both mystified and intrigued by Bohr’s theory. They questioned why the energies of hydrogen electron are quantized, or, why is the electron in a Bohr atom restricted or orbiting the nucleus at certain fixed distance? For a decade there is no logical explanation. In 1924, Louis de Bro ...
Chemistry 681 Introduction to Quantum
... 2. Rules and tools of QM • Schrödinger equation and wavefunction. • Operators and measurements. • Postulates of QM. 3. Two-level system 4. One-dimensional systems • Qualitative analysis of 1D systems. • Particle-in-a-box. • Harmonic oscillator. • 1D scattering. Barriers and tunneling. • Particle-on ...
... 2. Rules and tools of QM • Schrödinger equation and wavefunction. • Operators and measurements. • Postulates of QM. 3. Two-level system 4. One-dimensional systems • Qualitative analysis of 1D systems. • Particle-in-a-box. • Harmonic oscillator. • 1D scattering. Barriers and tunneling. • Particle-on ...
PHYS 481/681 Quantum Mechanics Stephen Lepp August 29, 2016
... Introduction to Quantum Mechanics nd the interpretation of its solutions, the uncertainty principles, one-dimensional problems, harmonic oscillator, angular momentum, the hydrogen atom. 3 credits. • Class MW 11:30-12:45 BPB 249. • Office Hours TTh 12:45-1:30 or by arrangement. • Textbook “Quantum Me ...
... Introduction to Quantum Mechanics nd the interpretation of its solutions, the uncertainty principles, one-dimensional problems, harmonic oscillator, angular momentum, the hydrogen atom. 3 credits. • Class MW 11:30-12:45 BPB 249. • Office Hours TTh 12:45-1:30 or by arrangement. • Textbook “Quantum Me ...
CONJECTURING THE MATHEMATICAL AXIOM THAT
... been ignored, but it has been neglected. In quantum physics, it has been unjustly neglected. One usually considers situations that are too idealized, and one investigates problems for which the directedness of time and for which irreversibility do not play a prominent role. An example is classical m ...
... been ignored, but it has been neglected. In quantum physics, it has been unjustly neglected. One usually considers situations that are too idealized, and one investigates problems for which the directedness of time and for which irreversibility do not play a prominent role. An example is classical m ...
Some Families of Probability Distributions Within Quantum Theory
... Some basics of quantum theory are presented including the way an experiment is modeled. Then states, observables, expected values, spectral measure, and probabilities are introduced. An example of spin measurement is discussed in the context of Stern Gerlach experiments. In order to describe an exam ...
... Some basics of quantum theory are presented including the way an experiment is modeled. Then states, observables, expected values, spectral measure, and probabilities are introduced. An example of spin measurement is discussed in the context of Stern Gerlach experiments. In order to describe an exam ...
Exercises in Statistical Mechanics
... Exercises in Statistical Mechanics Based on course by Doron Cohen, has to be proofed Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel This exercises pool is intended for a graduate course in “statistical mechanics”. Some of the problems are original, while other were assembled ...
... Exercises in Statistical Mechanics Based on course by Doron Cohen, has to be proofed Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel This exercises pool is intended for a graduate course in “statistical mechanics”. Some of the problems are original, while other were assembled ...
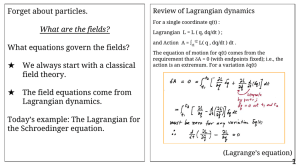
Forget about particles. What equations govern the fields? What are the fields?
... The equation of motion for q(t) comes from the requirement that δA = 0 (with endpoints fixed); i.e., the action is an extremum. For a variation δq(t) ...
... The equation of motion for q(t) comes from the requirement that δA = 0 (with endpoints fixed); i.e., the action is an extremum. For a variation δq(t) ...
7.2.4. Normal Ordering
... 7.2.4. Normal Ordering In the last section, we get rid of an infinite vacuum energy on the ground that only relative energies have physical meaning. However, if the structure of spacetime is to be determined by matter distribution, the vacuum must be at zero energy. Therefore, we must impose some ru ...
... 7.2.4. Normal Ordering In the last section, we get rid of an infinite vacuum energy on the ground that only relative energies have physical meaning. However, if the structure of spacetime is to be determined by matter distribution, the vacuum must be at zero energy. Therefore, we must impose some ru ...
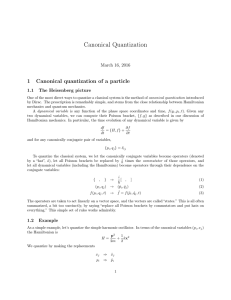
Canonical Quantization
... One of the most direct ways to quantize a classical system is the method of canonical quantization introduced by Dirac. The prescription is remarkably simple, and stems from the close relationship between Hamiltonian mechanics and quantum mechanics. A dynamical variable is any function of the phase ...
... One of the most direct ways to quantize a classical system is the method of canonical quantization introduced by Dirac. The prescription is remarkably simple, and stems from the close relationship between Hamiltonian mechanics and quantum mechanics. A dynamical variable is any function of the phase ...
Lecture notes for FYS610 Many particle Quantum Mechanics
... Quantum Mechanics, or more precisely Quantum Field Theory, is presumably a fundamental theory of nature, and as such cannot be derived from some other physical theory. But in practice, we are often in the situation that we have a classical theory which describes physical phenomena well, and want to ...
... Quantum Mechanics, or more precisely Quantum Field Theory, is presumably a fundamental theory of nature, and as such cannot be derived from some other physical theory. But in practice, we are often in the situation that we have a classical theory which describes physical phenomena well, and want to ...
Prof. Bertrand Reulet, Université de Sherbrooke, Canada Talk: 23. May 2014
... Prof. Bertrand Reulet, Université de Sherbrooke, Canada Talk: 23. May 2014 ...
... Prof. Bertrand Reulet, Université de Sherbrooke, Canada Talk: 23. May 2014 ...
SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION FOR A PARTICLE ON A CURVED SPACE AND SUPERINTEGRABILITY
... Abstract. A formulation of quantum mechanics on spaces of constant curvature is studied by quantizing the Noether momenta and using these to form the quantum Hamiltonian. This approach gives the opportunity of studying a superintegrable quantum system. It is shown there are three different ways of o ...
... Abstract. A formulation of quantum mechanics on spaces of constant curvature is studied by quantizing the Noether momenta and using these to form the quantum Hamiltonian. This approach gives the opportunity of studying a superintegrable quantum system. It is shown there are three different ways of o ...
... rise to the canonical quantization, while the Lagrangian approach is used in the path-integral quantization. Usually, in classical mechanics, there is a transformation that relates these two approaches. However, for a reparametrizationinvariant systems there are problems when changing from the Lagra ...
1.1 What has to be explained by Quantum mechanics?
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...