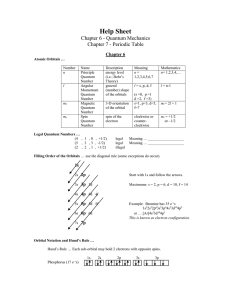
Summary of Important Ideas in Quantum Physics
... A -particle is a high-energy electron. In some barely-bound nuclei, a second, much weaker nuclear force known as the weak force can compete with the strong force and cause a neutron to decay even though it is in the presence of protons. As noted in Item (4), the decaying neutron gives off an electr ...
... A -particle is a high-energy electron. In some barely-bound nuclei, a second, much weaker nuclear force known as the weak force can compete with the strong force and cause a neutron to decay even though it is in the presence of protons. As noted in Item (4), the decaying neutron gives off an electr ...
QUANTUM NUMBERS
... For an electron in an atom with l=0 is said to be in an s state. For an electron in an atom with l=1 is said to be in an p state. For an electron in an atom with l=2 is said to be in an d state. For an electron in an atom with l=3 is said to be in an e state. ...
... For an electron in an atom with l=0 is said to be in an s state. For an electron in an atom with l=1 is said to be in an p state. For an electron in an atom with l=2 is said to be in an d state. For an electron in an atom with l=3 is said to be in an e state. ...
New Evidence that Quantum Mechanics is Hard to Simulate on
... circuit C for FOURIER SAMPLING, then we could violate a known AC0 lower bound, by “sneaking a MAJORITY problem” into the estimation of some random Fourier coefficient fˆ s Obvious problem: How do we know C will output the particular s we’re interested in, thereby revealing anything ...
... circuit C for FOURIER SAMPLING, then we could violate a known AC0 lower bound, by “sneaking a MAJORITY problem” into the estimation of some random Fourier coefficient fˆ s Obvious problem: How do we know C will output the particular s we’re interested in, thereby revealing anything ...
Lecture XV
... The wave function must be square-integrable. In other words, the integral of |Ψ|2 over all space must be finite. This is another way of saying that it must be possible to use |Ψ|2 as a probability density, since any probability density must integrate over all space to give a value of 1, which is cle ...
... The wave function must be square-integrable. In other words, the integral of |Ψ|2 over all space must be finite. This is another way of saying that it must be possible to use |Ψ|2 as a probability density, since any probability density must integrate over all space to give a value of 1, which is cle ...
Density Matrix
... state variables are microscopic, and a state is specified by giving the positions and velocities of all particles as a function of time. Obviously, this does not generalize to the quantum theory very easily, thus in our work we will try to adhere as closely as possible to the first meaning, but it n ...
... state variables are microscopic, and a state is specified by giving the positions and velocities of all particles as a function of time. Obviously, this does not generalize to the quantum theory very easily, thus in our work we will try to adhere as closely as possible to the first meaning, but it n ...
A phase-space study of the quantum Loschmidt Echo in the
... time t on R. Therefore, for every ε > 0, there exists Tε > 0 and for every k ∈ Z there exists tk ∈ [kTε , (k + 1)Tε [ such that |a(tk ) − 1| ≤ ε. This fact can be interpreted as a quantum analog of the famous return Poincaré theorem in classical mechanics. But we have no information here on the alm ...
... time t on R. Therefore, for every ε > 0, there exists Tε > 0 and for every k ∈ Z there exists tk ∈ [kTε , (k + 1)Tε [ such that |a(tk ) − 1| ≤ ε. This fact can be interpreted as a quantum analog of the famous return Poincaré theorem in classical mechanics. But we have no information here on the alm ...
Principles of Scientific Simulation
... • This is a fundamental description of the microscopic world. You would in principle use it to describe everything but this is both unnecessary and too difficult both computationally and analytically. • Quantum Physics problems are typified by Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) calculations and these end ...
... • This is a fundamental description of the microscopic world. You would in principle use it to describe everything but this is both unnecessary and too difficult both computationally and analytically. • Quantum Physics problems are typified by Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) calculations and these end ...
Effective Field Theory of General Relativity
... Interactions from sewing together tree amplitudes - only involves on-shell gravitons - classical and quantum corrections emerge from low q2 limit Tree amplitudes easier to calculate than loops Universality of low energy limit: - leading corrections identical for different spins ...
... Interactions from sewing together tree amplitudes - only involves on-shell gravitons - classical and quantum corrections emerge from low q2 limit Tree amplitudes easier to calculate than loops Universality of low energy limit: - leading corrections identical for different spins ...
6.2 Growth and structure of semiconductor quantum wells
... a useful starting point for the discussion because of its simplicity. Note that the separation of the first two electron level is more than three times the thermal energy at RT, where kBT 25 meV. ...
... a useful starting point for the discussion because of its simplicity. Note that the separation of the first two electron level is more than three times the thermal energy at RT, where kBT 25 meV. ...
Serway_PSE_quick_ch41
... The wavelengths of the wave functions in Figure 41.8 are longer than those in Figure 41.4 because the wave function spreads out into the classically forbidden region. For an infinite and a finite square well of the same length L, the quantized energies of the particle in a finite well are ...
... The wavelengths of the wave functions in Figure 41.8 are longer than those in Figure 41.4 because the wave function spreads out into the classically forbidden region. For an infinite and a finite square well of the same length L, the quantized energies of the particle in a finite well are ...
Gedanken and real experiments in modern physics - IPN-Kiel
... Ion traps capable of trapping a single ion were developed in the late ’70. They consists of electrodes providing static and oscillating electromagnetic field. In addition a laser beam, resonant with the electronic transition illuminates the ion. The electrodes are placed in a vacuum chamber, ions ar ...
... Ion traps capable of trapping a single ion were developed in the late ’70. They consists of electrodes providing static and oscillating electromagnetic field. In addition a laser beam, resonant with the electronic transition illuminates the ion. The electrodes are placed in a vacuum chamber, ions ar ...
6. INTERACTION OF LIGHT AND MATTER 6.1. Introduction
... One of the most important topics in time-dependent quantum mechanics is the description of spectroscopy, which refers to the study of matter through its interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Classically, light–matter interactions are a result of an oscillating electromagnetic field resonantly ...
... One of the most important topics in time-dependent quantum mechanics is the description of spectroscopy, which refers to the study of matter through its interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Classically, light–matter interactions are a result of an oscillating electromagnetic field resonantly ...
Is Classical Statistical Mechanics Self-Consistent? (A paper in honor of C. F. von Weizsäcker, 1912–2007)
... can be avoided from the very beginning when working with Newton’s notion of state, as can be seen from Einstein’s 1907 paper discussed above. 4 Summary and discussion Contrary to Einstein’s results, Ehrenfest (1880–1933) [14] and Natanson (1864–1937) [15] explained the difference between the classic ...
... can be avoided from the very beginning when working with Newton’s notion of state, as can be seen from Einstein’s 1907 paper discussed above. 4 Summary and discussion Contrary to Einstein’s results, Ehrenfest (1880–1933) [14] and Natanson (1864–1937) [15] explained the difference between the classic ...
K - Christian J. Bordé
... demonstrated to a much better level simply suggests that possible corrections would involve other combinations of fundamental constants: functions of α, mass ratios, … The hydrogen spectrum provides an illustrating example of a similar situation. The energy of the levels of atomic hydrogen is given ...
... demonstrated to a much better level simply suggests that possible corrections would involve other combinations of fundamental constants: functions of α, mass ratios, … The hydrogen spectrum provides an illustrating example of a similar situation. The energy of the levels of atomic hydrogen is given ...
pdf
... the later stages of both courses. The two slides shown in Figure 2 are illustrative of how the differences between the two courses could be more subtle, yet still significant. Both slides summarize the results for the system referred to in PHYS3A as the Infinite Square Well, but which Instructor B c ...
... the later stages of both courses. The two slides shown in Figure 2 are illustrative of how the differences between the two courses could be more subtle, yet still significant. Both slides summarize the results for the system referred to in PHYS3A as the Infinite Square Well, but which Instructor B c ...