Lesson 19 - Ampere`s Law As Modified by Maxwell
... In 1865, James Clerk Maxwell, one of the great physicists of all times, solved this paradox and developed electromagnetic theory (one of the major branches of physics). II. ...
... In 1865, James Clerk Maxwell, one of the great physicists of all times, solved this paradox and developed electromagnetic theory (one of the major branches of physics). II. ...
PHY160-4
... In circuit D, the motor runs normally when the switch is in the “up” position, but the motor does not run at all when the switch is in the “down” position. The “down” position creates a short-circuit, a potentially dangerous situation. In circuit E, the motor again runs normally when the switch is “ ...
... In circuit D, the motor runs normally when the switch is in the “up” position, but the motor does not run at all when the switch is in the “down” position. The “down” position creates a short-circuit, a potentially dangerous situation. In circuit E, the motor again runs normally when the switch is “ ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... Brushes – contact point between the Commutator and the power source Permanent magnet- attracts & repels the coils w/in the armature thus allowing the motor to spin rapidly Current source – supplies the electrical energy needed to the brushes which transfers to the commutator Armature – instead of ...
... Brushes – contact point between the Commutator and the power source Permanent magnet- attracts & repels the coils w/in the armature thus allowing the motor to spin rapidly Current source – supplies the electrical energy needed to the brushes which transfers to the commutator Armature – instead of ...
Electromagnetic radiation
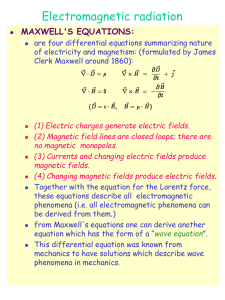
... are four differential equations summarizing nature of electricity and magnetism: (formulated by James Clerk Maxwell around 1860): ...
... are four differential equations summarizing nature of electricity and magnetism: (formulated by James Clerk Maxwell around 1860): ...
magnetic
... matter in which there is a force of attraction or repulsion between like and unlike poles ...
... matter in which there is a force of attraction or repulsion between like and unlike poles ...
Slide 1
... – Every magnet has at least two poles, N and S (dipole) – Like magnetic poles repel each other, while unlike poles attract – Force between two magnets varies inversely as the square of the distance between ...
... – Every magnet has at least two poles, N and S (dipole) – Like magnetic poles repel each other, while unlike poles attract – Force between two magnets varies inversely as the square of the distance between ...
Study problems – Magnetic Fields – With Solutions Not to be turned
... Question 4 (3 points) A wire loop is bent into the shape of a square with each side of length 4.5 cm. The loop is placed horizontally on a tabletop with two of the sides oriented north/south and two of the sides oriented east/west. A battery is connected so that a current of 24 mA is produced around ...
... Question 4 (3 points) A wire loop is bent into the shape of a square with each side of length 4.5 cm. The loop is placed horizontally on a tabletop with two of the sides oriented north/south and two of the sides oriented east/west. A battery is connected so that a current of 24 mA is produced around ...
Final Exam - University of Louisville Physics
... PHYS 222 – Spring 2012 – Final Exam Closed books, notes, etc. No electronic device except a calculator. ...
... PHYS 222 – Spring 2012 – Final Exam Closed books, notes, etc. No electronic device except a calculator. ...
Unit I: Electrostatics -Chapter–1: Electric Charges and Fields
... wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen's principle. Interference, Young's double slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maxim ...
... wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen's principle. Interference, Young's double slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maxim ...
CIRCUITS AND SAFETY
... getting shocked: they make contact with the circuit at only one point. Many times, one side of a power system will be intentionally connected to earth ground, and so the person touching a single wire is actually making contact between two points in the circuit (the wire and earth ground): ...
... getting shocked: they make contact with the circuit at only one point. Many times, one side of a power system will be intentionally connected to earth ground, and so the person touching a single wire is actually making contact between two points in the circuit (the wire and earth ground): ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.