N2-1,2,3 Study Guide
... both the geographic North Pole and geographic South Pole Electromagnetism – the interaction between electricity and magnetism Solenoid – a coil of wire with an electric current Electromagnet - made of a solenoid (coil of wire) that has an iron core and acts as a magnet when an electric current is in ...
... both the geographic North Pole and geographic South Pole Electromagnetism – the interaction between electricity and magnetism Solenoid – a coil of wire with an electric current Electromagnet - made of a solenoid (coil of wire) that has an iron core and acts as a magnet when an electric current is in ...
Skill Phases for
... Chaining angular momentum is transferred in the body from one set of muscle groups to another Lever action for speed or force ...
... Chaining angular momentum is transferred in the body from one set of muscle groups to another Lever action for speed or force ...
Presentation
... • Electric charges vibrate • Electric field around it changes • The magnetic field around the charge changes • Both fields change continuously creating the wave ...
... • Electric charges vibrate • Electric field around it changes • The magnetic field around the charge changes • Both fields change continuously creating the wave ...
Foundations of Scalar Diffraction Theory
... the edges of objects. That is realm of geometric optics. However, this book treats many situations in which geometric optics are inadequate to describe observed phenomena like diffraction. Therefore, the starting point is classical electrodynamics with solutions provided by scalar diffraction theory ...
... the edges of objects. That is realm of geometric optics. However, this book treats many situations in which geometric optics are inadequate to describe observed phenomena like diffraction. Therefore, the starting point is classical electrodynamics with solutions provided by scalar diffraction theory ...
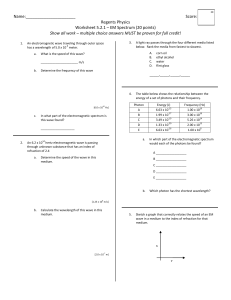
Name: Score: Regents Physics Worksheet 5.2.1 – EM Spectrum (20
... moving at constant speed upward only. moving at constant speed downward only. accelerating alternately upward and downward. ...
... moving at constant speed upward only. moving at constant speed downward only. accelerating alternately upward and downward. ...
Sample Final File
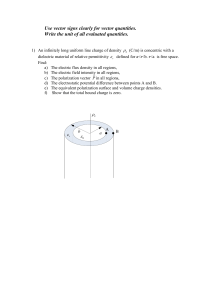
... Use vector signs clearly for vector quantities. Write the unit of all evaluated quantities. 1) An infinitely long uniform line charge of density L (C/m) is concentric with a dielectric material of relative permittivity r defined for a
... Use vector signs clearly for vector quantities. Write the unit of all evaluated quantities. 1) An infinitely long uniform line charge of density L (C/m) is concentric with a dielectric material of relative permittivity r defined for a
Topics covered in PH112 - Rose
... Torque, moment arm, line of action of F Newton’s second law in angular form Work and rotational kinetic energy Rolling bodies, KE in terms of center of mass Angular momentum of a system of particles, and of a rigid body Conservation of angular momentum Simple harmonic motion: frequency, period, ampl ...
... Torque, moment arm, line of action of F Newton’s second law in angular form Work and rotational kinetic energy Rolling bodies, KE in terms of center of mass Angular momentum of a system of particles, and of a rigid body Conservation of angular momentum Simple harmonic motion: frequency, period, ampl ...
Heat, Electricity, and Magnetism Vocabulary
... 7. Current Electricity – The flow of electrical charges through a circuit. 8. Simple Circuit – The path along which electric current flows. 9. Open Circuit – A circuit with gaps, so that it is not complete, and therefore, electricity will not flow through it. 10. Closed Circuit – A complete, unbroke ...
... 7. Current Electricity – The flow of electrical charges through a circuit. 8. Simple Circuit – The path along which electric current flows. 9. Open Circuit – A circuit with gaps, so that it is not complete, and therefore, electricity will not flow through it. 10. Closed Circuit – A complete, unbroke ...
Electromagnetic radiation – the nature of light
... molecules and atoms that move from one energy level to another. The light we see with our eyes is really a very small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. A rainbow shows the optical (visible) part of the electromagnetic spectrum; infrared (if you could see it) would be located just beyond the r ...
... molecules and atoms that move from one energy level to another. The light we see with our eyes is really a very small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. A rainbow shows the optical (visible) part of the electromagnetic spectrum; infrared (if you could see it) would be located just beyond the r ...
D1 : Introduction to Electromagnetic exploration methods
... (3) Time variations of the primary magnetic field induce secondary electric currents in a conductor (ore body). (4) The secondary magnetic field passes through the RX, which is also a loop of wire. Time variations (oscillations) in the secondary magnetic field generate a secondary voltage in the RX. ...
... (3) Time variations of the primary magnetic field induce secondary electric currents in a conductor (ore body). (4) The secondary magnetic field passes through the RX, which is also a loop of wire. Time variations (oscillations) in the secondary magnetic field generate a secondary voltage in the RX. ...
PPT
... The electric field due to charges in the wire will be zero, so the force on the test charge will be magnetic. May, 2008 ...
... The electric field due to charges in the wire will be zero, so the force on the test charge will be magnetic. May, 2008 ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.