Phys202_Final_Exam_Spr2006.doc
... 33. Two parallel wires a distance 8 m apart carry 7 A and 8 A respectively in the opposite direction. What is the force per unit length between them? a. ~1.1o b. 160 o c. 16 o d. 10 o ...
... 33. Two parallel wires a distance 8 m apart carry 7 A and 8 A respectively in the opposite direction. What is the force per unit length between them? a. ~1.1o b. 160 o c. 16 o d. 10 o ...
I Directed Reading B antinued UNBALANCED FORCES: VELOCITY
... 15. What type of force is needed to cause a static object to start moving? 14. Give an example of an object that continues to move when an unbalanced force is removed. 15. Give an example of an object tttat moves in a direction diffierent from the direction of an unbalanced force acting on it. ...
... 15. What type of force is needed to cause a static object to start moving? 14. Give an example of an object that continues to move when an unbalanced force is removed. 15. Give an example of an object tttat moves in a direction diffierent from the direction of an unbalanced force acting on it. ...
Electric fields ppt File
... in their beaks to detect the electric fields produced by muscles in their prey ...
... in their beaks to detect the electric fields produced by muscles in their prey ...
• Maxwell`s equations and electromagnetic waves • sinusoidal
... • Maxwell’s equations and electromagnetic waves • sinusoidal electromagnetic waves • Passage of electromagnetic waves through matter • Energy and momentum of electromagnetic waves • *(Not required)Wave addition and the formation of a standing electromagnetic wave ...
... • Maxwell’s equations and electromagnetic waves • sinusoidal electromagnetic waves • Passage of electromagnetic waves through matter • Energy and momentum of electromagnetic waves • *(Not required)Wave addition and the formation of a standing electromagnetic wave ...
Exercise 4 (Electromagnetism)
... (b) (i) When s is pressed, current flows through the coil and the soft iron is magnetised. It attracts the spring towards the left. The hammer strikes the left metal plate to produce the first note. When S is released, the iron core is demagnetised, the hammer springs back to strike the right metal ...
... (b) (i) When s is pressed, current flows through the coil and the soft iron is magnetised. It attracts the spring towards the left. The hammer strikes the left metal plate to produce the first note. When S is released, the iron core is demagnetised, the hammer springs back to strike the right metal ...
Recitation Week 7
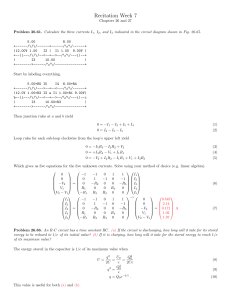
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
Chapter 3
... 7) When a single charge q is placed at one corner of a square, the electric field at the center of the square is F/q. If two other equal charges are placed at the adjacent corners of the square, the electric field at the center of the square due to these three equal charges is A) F/q. B) F/(4q). C) ...
... 7) When a single charge q is placed at one corner of a square, the electric field at the center of the square is F/q. If two other equal charges are placed at the adjacent corners of the square, the electric field at the center of the square due to these three equal charges is A) F/q. B) F/(4q). C) ...
Lecture 1 - web page for staff
... varies spatially in a direction normal to its orientation direction • Knowledge of fields in media and boundary conditions allows useful applications of material properties to microwave components • A uniform plane wave, both electric and magnetic fields lie in the transverse plane, the plane whose ...
... varies spatially in a direction normal to its orientation direction • Knowledge of fields in media and boundary conditions allows useful applications of material properties to microwave components • A uniform plane wave, both electric and magnetic fields lie in the transverse plane, the plane whose ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.