magnetism
... according to their direction. A large number is painted on the end of the runway so that it can be read by the pilot of an incoming airplane. This number describes the direction in which the airplane is traveling, expressed as the magnetic heading, in degrees measured clockwise from magnetic north d ...
... according to their direction. A large number is painted on the end of the runway so that it can be read by the pilot of an incoming airplane. This number describes the direction in which the airplane is traveling, expressed as the magnetic heading, in degrees measured clockwise from magnetic north d ...
Magnetic Induction
... electrical power supply. When a conductive projectile is inserted between the rails (from the end connected to the power supply), it completes the circuit. Electrons flow from the negative terminal of the power supply up the negative rail, across the projectile, and down the positive rail, back to t ...
... electrical power supply. When a conductive projectile is inserted between the rails (from the end connected to the power supply), it completes the circuit. Electrons flow from the negative terminal of the power supply up the negative rail, across the projectile, and down the positive rail, back to t ...
magnetic field
... Right Hand Rule No. 1. Extend the right hand so the fingers point along the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb points along the velocity of the charge. The palm of the hand then faces in the direction of the magnetic force that acts on a positive charge. If the moving charge is negative, ...
... Right Hand Rule No. 1. Extend the right hand so the fingers point along the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb points along the velocity of the charge. The palm of the hand then faces in the direction of the magnetic force that acts on a positive charge. If the moving charge is negative, ...
PHY481 - Lecture 19: The vector potential, boundary conditions on
... A very important integral relation between A The vector potential is related to the magnetic flux through, Z Z I ~ · d~a = φB . ~ · d~l = (∇ ~ ∧ A) ~ · d~a = B A ...
... A very important integral relation between A The vector potential is related to the magnetic flux through, Z Z I ~ · d~a = φB . ~ · d~l = (∇ ~ ∧ A) ~ · d~a = B A ...
File
... acceleration points up. This means the net force on you must also point up, which means that the normal force must be larger than gravity. This is why you feel heavy! ...
... acceleration points up. This means the net force on you must also point up, which means that the normal force must be larger than gravity. This is why you feel heavy! ...
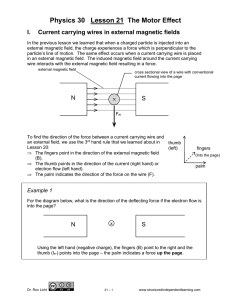
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
Document
... Ex- (Serway 31-12). An aluminum ring of radius r1 and Resistance R is placed on top of a long air-core solenoid with n turns per meter and radius r2 as shown below. Suppose the magnetic field due to the current in the solenoid at the end of the solenoid is half that at the center of the solenoid, a ...
... Ex- (Serway 31-12). An aluminum ring of radius r1 and Resistance R is placed on top of a long air-core solenoid with n turns per meter and radius r2 as shown below. Suppose the magnetic field due to the current in the solenoid at the end of the solenoid is half that at the center of the solenoid, a ...
Document
... If the rotation frequency of the ions decreases during acceleration, let’s make a cyclotron where the RF is modulated in frequency to follow the frequency decrease of the protons The frequency of the main RF resonator is modulated at 200….600 Hz by a rotating variable capacitor Actually, it’s ...
... If the rotation frequency of the ions decreases during acceleration, let’s make a cyclotron where the RF is modulated in frequency to follow the frequency decrease of the protons The frequency of the main RF resonator is modulated at 200….600 Hz by a rotating variable capacitor Actually, it’s ...
Chapter 2 Newton`s Laws
... Force Fields: Certain forces must exist independent of the presence of an object, because when the object moves there it has a force. For example the moon is always moving about the earth, but it always is attracted to it, regardless of its location. Thus we use the concept of a force field, the for ...
... Force Fields: Certain forces must exist independent of the presence of an object, because when the object moves there it has a force. For example the moon is always moving about the earth, but it always is attracted to it, regardless of its location. Thus we use the concept of a force field, the for ...
Exam 3
... Referring to the previous problem, if the wire frame is now placed in a region where the magnetic field is uniform and is equal to 0.6 T pointing up, what is the magnitude of the torque on the frame, and in which direction will the top wire move as a result of the torque? ...
... Referring to the previous problem, if the wire frame is now placed in a region where the magnetic field is uniform and is equal to 0.6 T pointing up, what is the magnitude of the torque on the frame, and in which direction will the top wire move as a result of the torque? ...
Electromotive force, also called emf (denoted and measured in volts
... Devices that can provide emf include electrochemical cells, thermoelectric devices, solar cells, photodiodes, electrical generators, transformer and even Van de Graaff generators.[5][6] In nature, emf is generated whenever magnetic field fluctuations occur through a surface. The shifting of the Eart ...
... Devices that can provide emf include electrochemical cells, thermoelectric devices, solar cells, photodiodes, electrical generators, transformer and even Van de Graaff generators.[5][6] In nature, emf is generated whenever magnetic field fluctuations occur through a surface. The shifting of the Eart ...
Notes Forces- Gravitational, Mag., Elec. File
... Magnetic fields exist around magnetic objects. If a second magnetic object is placed in the field, the two objects experience magnetic forces that can attract or repel them, depending on the objects involved. Magnetic force weakens rapidly with increasing distance. Magnetic field lines can be seen ...
... Magnetic fields exist around magnetic objects. If a second magnetic object is placed in the field, the two objects experience magnetic forces that can attract or repel them, depending on the objects involved. Magnetic force weakens rapidly with increasing distance. Magnetic field lines can be seen ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.