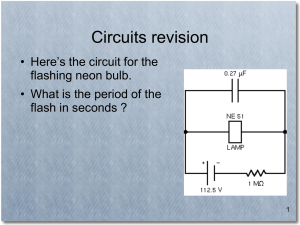
Equilibrium Forces Worksheet
... A person weighing 612 N sits in the middle of a hammock that is 3.0 m long and sags 1.0 m below the points of support. If the maximum force the hammock ropes can support is 445 N, will the hammock hold? (460 N in each rope – CRASH!) ...
... A person weighing 612 N sits in the middle of a hammock that is 3.0 m long and sags 1.0 m below the points of support. If the maximum force the hammock ropes can support is 445 N, will the hammock hold? (460 N in each rope – CRASH!) ...
1. A solid of mass m starts from rest and travels for a given time
... In the circuit above, V is an a.c. source, X is an air-cored solenoid and R is a heating coil used to boil some liquid in a vessel. Which of the following adjustments would decrease the time required to boil the liquid? (1) The frequency of the a.c. supply is increased. (2) A soft iron cylinder is i ...
... In the circuit above, V is an a.c. source, X is an air-cored solenoid and R is a heating coil used to boil some liquid in a vessel. Which of the following adjustments would decrease the time required to boil the liquid? (1) The frequency of the a.c. supply is increased. (2) A soft iron cylinder is i ...
Experimental Verification of Filter Characteristics Using
... 1. An electron whose velocity is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field will move in a circular orbit. 2. The value of e/m can be calculated if we can measure the accelerating potential, the radius of the orbit, and the magnetic field. 3. By using a special arrangement of coils called Helmholtz c ...
... 1. An electron whose velocity is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field will move in a circular orbit. 2. The value of e/m can be calculated if we can measure the accelerating potential, the radius of the orbit, and the magnetic field. 3. By using a special arrangement of coils called Helmholtz c ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... determine the field with much precision. One can do reasonably well with just a compass and a dip meter. The point where the field is perpendicular to Earth’s surface and inward is not located at the geomagnetic north pole off Greenland as ...
... determine the field with much precision. One can do reasonably well with just a compass and a dip meter. The point where the field is perpendicular to Earth’s surface and inward is not located at the geomagnetic north pole off Greenland as ...
Powerpointreviewchap16
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Inductance
... the device (geometry, windings) and does not depend on the current. Inductance is measured in units of “henrys”, where 1 henry = 1 volt-second/ampere. For circuit analysis, it is enough to know just the inductance of the device and not the specific geometry. As per Lenz’s Law, the sign of the EMF is ...
... the device (geometry, windings) and does not depend on the current. Inductance is measured in units of “henrys”, where 1 henry = 1 volt-second/ampere. For circuit analysis, it is enough to know just the inductance of the device and not the specific geometry. As per Lenz’s Law, the sign of the EMF is ...
MAGENTIC FIELD
... 3. Orient the plane of the wires so they align with the compass needle. Rotate the compass case to zero the measuring needles (the long needles). Be patient and give the needle time to settle, and then make fine adjustments. It is critical that the field generated by the tangent galvanometer is perp ...
... 3. Orient the plane of the wires so they align with the compass needle. Rotate the compass case to zero the measuring needles (the long needles). Be patient and give the needle time to settle, and then make fine adjustments. It is critical that the field generated by the tangent galvanometer is perp ...
Grades 9-12 Science Curriculum
... addressed conceptually and quantified from force diagrams; and forces required for circular motion were introduced conceptually. In this course, Newton’s laws of motion are applied to mathematically describe and predict the effects of forces on more complex systems of objects and to analyze objects ...
... addressed conceptually and quantified from force diagrams; and forces required for circular motion were introduced conceptually. In this course, Newton’s laws of motion are applied to mathematically describe and predict the effects of forces on more complex systems of objects and to analyze objects ...
Illustrations of the Relativistic Conservation Law for the Center of
... We notice that even though the linear momentum P can be made as small as desired by taking the external forces sufficiently small, the time integral of the linear momentum gives a finite non-zero value independent of the magnitude of the small external force in the limit dr/dt → 0. The change in the ...
... We notice that even though the linear momentum P can be made as small as desired by taking the external forces sufficiently small, the time integral of the linear momentum gives a finite non-zero value independent of the magnitude of the small external force in the limit dr/dt → 0. The change in the ...
Science of Sun activity
... Sudden, rapid, and intense increases in brightness in relatively small regions in the Sun’s atmosphere Solar flares occur when magnetic fields in the Sun’s atmosphere rapidly change shape and generate currents of electrically charged plasmas. ...
... Sudden, rapid, and intense increases in brightness in relatively small regions in the Sun’s atmosphere Solar flares occur when magnetic fields in the Sun’s atmosphere rapidly change shape and generate currents of electrically charged plasmas. ...
Magnetic Fields
... order for a current to exist in a conductor, there must be an electromotive force (emf), or potential difference, between the conductor's ends. An electric cell, a battery of cells, and a generator are all sources of electromotive force; any such source with an external conductor connected from one ...
... order for a current to exist in a conductor, there must be an electromotive force (emf), or potential difference, between the conductor's ends. An electric cell, a battery of cells, and a generator are all sources of electromotive force; any such source with an external conductor connected from one ...
Chapter 7 Newton’s third law of motion – Action and Reaction
... For every force, there is an equal and opposite force. Define force as part of an interaction (7.1) State Newton’s third law of motion (7.2) Describe how to identify a pair of action reaction forces (7.3) Explain why the accelerations caused by an action force and by a reaction force do not ...
... For every force, there is an equal and opposite force. Define force as part of an interaction (7.1) State Newton’s third law of motion (7.2) Describe how to identify a pair of action reaction forces (7.3) Explain why the accelerations caused by an action force and by a reaction force do not ...
Atomic View of Dielectrics -Electric Dipole in an Electric Field
... U f -U i = pE(cos i - cos f ) Assume i 90o , U i 0 ...
... U f -U i = pE(cos i - cos f ) Assume i 90o , U i 0 ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.