equations
... potential energy of a dipole (angle is measured between direction of electric field & direction of dipole) ...
... potential energy of a dipole (angle is measured between direction of electric field & direction of dipole) ...
Unit 4side 2 - Little Heath Sixth Form
... I can explain how to show that an emf can be induced by cutting magnetic field lines and apply Faraday’s law to explain how we can increase the size of the induced emf. I can use the equation E = Blv for the induced emf for a conductor cutting a magnetic field at rightangles. Where B = Magnetic flux ...
... I can explain how to show that an emf can be induced by cutting magnetic field lines and apply Faraday’s law to explain how we can increase the size of the induced emf. I can use the equation E = Blv for the induced emf for a conductor cutting a magnetic field at rightangles. Where B = Magnetic flux ...
Adobe Acrobat file ()
... Consider the mass spectrometer. The electric field between the plates of the velocity selector is 950 V/m, and the magnetic fields in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber have magnitudes of 0.930 T. Calculate the radius of the path in the system for a singly charged ion with mass m= ...
... Consider the mass spectrometer. The electric field between the plates of the velocity selector is 950 V/m, and the magnetic fields in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber have magnitudes of 0.930 T. Calculate the radius of the path in the system for a singly charged ion with mass m= ...
Tunnelling Chapter 5. Coulomb Repulsion and ...
... When a Si-MOSFET is taken to low temperature (typically 1K and below), it is found that temperature independent conductance peaks appear as a function of gate voltage when the gate voltage is below threshold. In this regime, the electronic states in the device are localized and the experimental obse ...
... When a Si-MOSFET is taken to low temperature (typically 1K and below), it is found that temperature independent conductance peaks appear as a function of gate voltage when the gate voltage is below threshold. In this regime, the electronic states in the device are localized and the experimental obse ...
Magnetic Field and High-Voltage Power Lines
... I am looking for a new home, and I think I found my dream house. It seems perfect, but there is something bothering me: the house is located right beside a high-voltage power transmission line. I have heard that electric wires that carry these currents create a magnetic field. So I am worried. Will ...
... I am looking for a new home, and I think I found my dream house. It seems perfect, but there is something bothering me: the house is located right beside a high-voltage power transmission line. I have heard that electric wires that carry these currents create a magnetic field. So I am worried. Will ...
13.3 Oersted`s Discovery
... conductor. They sometimes miss that the field gets weaker as the distance from the wire increases, or they do not draw the magnetic field lines farther apart to represent this. Students often have trouble picturing the true nature of the field around a long, straight wire so careful observations dur ...
... conductor. They sometimes miss that the field gets weaker as the distance from the wire increases, or they do not draw the magnetic field lines farther apart to represent this. Students often have trouble picturing the true nature of the field around a long, straight wire so careful observations dur ...
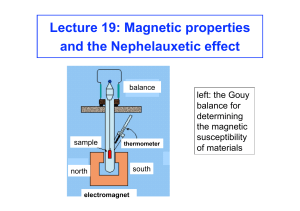
Lecture 19: Magnetic properties and the Nephelauxetic effect
... increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row analogues. Most 2nd and 3rd row d-block elements are low-sp ...
... increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row analogues. Most 2nd and 3rd row d-block elements are low-sp ...
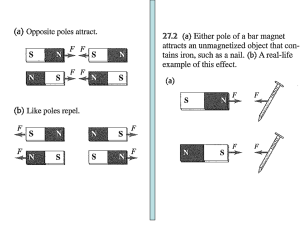
Permanent magnets are just collections of little current loops
... The unit of the magnetic field B (the Tesla) A] is the same as the electric field times a velocity B] is the same as the electric field divided by a velocity C] cannot be expressed as either of these ...
... The unit of the magnetic field B (the Tesla) A] is the same as the electric field times a velocity B] is the same as the electric field divided by a velocity C] cannot be expressed as either of these ...
Word
... Currents and fields There is a relationship between electricity and magnetism, which was discovered by Hans Christian Oersted in 1819. During a lecture demonstration he noticed that a wire carrying an electric current deflected the needle in a nearby compass. Not only are magnetic fields produced by ...
... Currents and fields There is a relationship between electricity and magnetism, which was discovered by Hans Christian Oersted in 1819. During a lecture demonstration he noticed that a wire carrying an electric current deflected the needle in a nearby compass. Not only are magnetic fields produced by ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.