4. One mole of a monatomic ideal gas initially at temperature 0 T
... b. (20) Now consider the related problem of an electron moving through superfluid helium. Show that in this case the electron can emit a phonon as long as it moves with a velocity exceeding a critical velocity vc and find vc . The excitation spectrum of the phonons in superfluid helium is given by E ...
... b. (20) Now consider the related problem of an electron moving through superfluid helium. Show that in this case the electron can emit a phonon as long as it moves with a velocity exceeding a critical velocity vc and find vc . The excitation spectrum of the phonons in superfluid helium is given by E ...
DATA SHEET - EXAM 3 Constants: & Electric potential:
... Ohm's law: V =R⋅I Temperature dependence of resistivity: =0 1T −T 0 Equivalent resistance for resistors in series: R Series= R1R 2 Kirchhoff's junction rule: ∑ I IN =∑ I OUT and loop rule: ∑ V UP =∑ V DOWN Equivalent capacitance for capacitors in parallel C Parallel =C 1C 2 ...
... Ohm's law: V =R⋅I Temperature dependence of resistivity: =0 1T −T 0 Equivalent resistance for resistors in series: R Series= R1R 2 Kirchhoff's junction rule: ∑ I IN =∑ I OUT and loop rule: ∑ V UP =∑ V DOWN Equivalent capacitance for capacitors in parallel C Parallel =C 1C 2 ...
21.2 Electromagnetism
... • The magnetic field produced by the current causes the iron rod to become a magnet. • An electromagnet is a solenoid with a ferromagnetic core. • The current can be used to turn the magnetic field on and off. ...
... • The magnetic field produced by the current causes the iron rod to become a magnet. • An electromagnet is a solenoid with a ferromagnetic core. • The current can be used to turn the magnetic field on and off. ...
SAMPLE PAPER – I
... What is photo electric efect. Two monochromatic radiations, blue and violet, of the same intensity, are incident on a photo sensitive surface and cause photo electric emission. Would (i) the number of electrons emitted per second and (ii) the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons, be equal in the ...
... What is photo electric efect. Two monochromatic radiations, blue and violet, of the same intensity, are incident on a photo sensitive surface and cause photo electric emission. Would (i) the number of electrons emitted per second and (ii) the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons, be equal in the ...
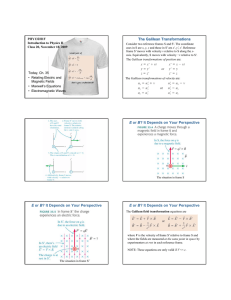
The Galilean Transformations E or B?
... Consider two reference frames S and S'. The coordinate axes in S are x, y, z and those in S' are x', y', z'. Reference frame S' moves with velocity v relative to S along the xaxis. Equivalently, S moves with velocity −v relative to S'. The Galilean transformations of position are: ...
... Consider two reference frames S and S'. The coordinate axes in S are x, y, z and those in S' are x', y', z'. Reference frame S' moves with velocity v relative to S along the xaxis. Equivalently, S moves with velocity −v relative to S'. The Galilean transformations of position are: ...
08 electromagnetic induction
... In 1752, prior to electricity being identified with the electron, Ben Franklin chose a convention regarding the direction of current flow. Franklin assumed that electrons (being assumed positive) flow from positive to negative terminals. We now know this is incorrect. The charge on an electron is ne ...
... In 1752, prior to electricity being identified with the electron, Ben Franklin chose a convention regarding the direction of current flow. Franklin assumed that electrons (being assumed positive) flow from positive to negative terminals. We now know this is incorrect. The charge on an electron is ne ...
Problem Set 10
... current i = 100 A through the long straight wire at distance a = 10.0 mm from the loop sets up a (nonuniform) magnetic field through the loop. Find the (a) emf and (b) current induced in the loop. (c) At what rate is thermal energy generated in the rod? (d) What is the magnitude of the force that mu ...
... current i = 100 A through the long straight wire at distance a = 10.0 mm from the loop sets up a (nonuniform) magnetic field through the loop. Find the (a) emf and (b) current induced in the loop. (c) At what rate is thermal energy generated in the rod? (d) What is the magnitude of the force that mu ...
- Physics
... Lenz’s Law: The direction of the induced current is such as to oppose the change in flux. We will practice with Lenz’s Law in class. We will examine the nature of the change in flux, and how the induced current might oppose the change in flux. The key concept in this is that the induced current crea ...
... Lenz’s Law: The direction of the induced current is such as to oppose the change in flux. We will practice with Lenz’s Law in class. We will examine the nature of the change in flux, and how the induced current might oppose the change in flux. The key concept in this is that the induced current crea ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.