Photon Fishing
... Such schemes require simultaneous input of several single photons (Fock states). With current technologies this is difficult as although large rates of production of two photons are achievable (eg 460,000/s), the production of greater than two photons is considerably slower (eg 0.0065/s for 4). In Q ...
... Such schemes require simultaneous input of several single photons (Fock states). With current technologies this is difficult as although large rates of production of two photons are achievable (eg 460,000/s), the production of greater than two photons is considerably slower (eg 0.0065/s for 4). In Q ...
Slide 1
... The end of classical physics: photons, electrons, atoms Last time: Discovery of the electron: Charge quantization photo-electric effect: light behaves as a particle Discovery of the nucleus: Rutherford scattering experiment Today: Atomic spectra: emission and absorption. Evidence for atomic ener ...
... The end of classical physics: photons, electrons, atoms Last time: Discovery of the electron: Charge quantization photo-electric effect: light behaves as a particle Discovery of the nucleus: Rutherford scattering experiment Today: Atomic spectra: emission and absorption. Evidence for atomic ener ...
OBJECTIVE WORKSHEET Quantum Theory 1. How did
... 2. What does it mean when a scientist says, "the energies of electrons are quantized." 3. How many energy levels for electrons does the chapter discuss? 4. Who discovered the QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL? 5. What shape does the s and p orbitals have? 6. What does "n" stand for when we discuss atomic orb ...
... 2. What does it mean when a scientist says, "the energies of electrons are quantized." 3. How many energy levels for electrons does the chapter discuss? 4. Who discovered the QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL? 5. What shape does the s and p orbitals have? 6. What does "n" stand for when we discuss atomic orb ...
Elec Structure of Atom
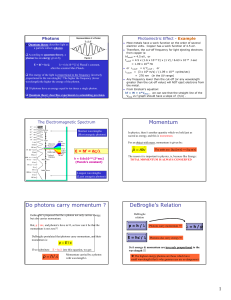
... Wavelength λ: distance between peaks Frequency ν: periods per unit time v λ=c ; c = speed of light ...
... Wavelength λ: distance between peaks Frequency ν: periods per unit time v λ=c ; c = speed of light ...
Liad Elmelech 7.1-7.3 The Nature of Light, Atomic Spectroscopy
... More about the photoelectric effect - Emissions of electrons from metal depends on whether a photon has enough energy to dislodge a single electron. This energy is ionization energy. • Threshold frequency reached when energy of a photon (hv) = binding energy(φ) • hv = φ • Low frequency light does n ...
... More about the photoelectric effect - Emissions of electrons from metal depends on whether a photon has enough energy to dislodge a single electron. This energy is ionization energy. • Threshold frequency reached when energy of a photon (hv) = binding energy(φ) • hv = φ • Low frequency light does n ...
supplemental problems
... a) What is the cutoff wavelength for this PMT? b) Will this PMT work in the visible portion of the spectrum? Why? Assume you are measuring 550 nm light at one point in the experiment and that 20 picoWatts of the light is incident upon the detector. The photocathode has a quantum efficiency of 22% at ...
... a) What is the cutoff wavelength for this PMT? b) Will this PMT work in the visible portion of the spectrum? Why? Assume you are measuring 550 nm light at one point in the experiment and that 20 picoWatts of the light is incident upon the detector. The photocathode has a quantum efficiency of 22% at ...
Chapter 2 Waves and Particles De Broglie wavelength: λ=h/p, where
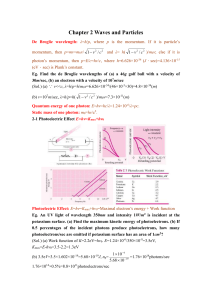
... The shortest wavelength of X-ray due to electron bombard: λmin=1.24×10-6/V, where V is the accelerating voltage. Eg. Find the shortest wavelength present in the radiation from an X-ray machine whose accelerating potential is 50000V. (Sol.) λmin=1.24×10-6/50000=2.5×10-11m=0.025nm 2-2 Bragg’s Reflecti ...
... The shortest wavelength of X-ray due to electron bombard: λmin=1.24×10-6/V, where V is the accelerating voltage. Eg. Find the shortest wavelength present in the radiation from an X-ray machine whose accelerating potential is 50000V. (Sol.) λmin=1.24×10-6/50000=2.5×10-11m=0.025nm 2-2 Bragg’s Reflecti ...
DOC - 嘉義大學
... 2. Suppose that light of total intensity 1.0 W/cm2 falls on a clean zinc (Zn) sample which the area is 1.01.0 cm2. Assume that the Zn sample reflects 95% of the light (absorbs 5% of the light) and that only 3% of the absorbed energy lies in the ultraviolet (UV) region of the spectrum above the cut ...
... 2. Suppose that light of total intensity 1.0 W/cm2 falls on a clean zinc (Zn) sample which the area is 1.01.0 cm2. Assume that the Zn sample reflects 95% of the light (absorbs 5% of the light) and that only 3% of the absorbed energy lies in the ultraviolet (UV) region of the spectrum above the cut ...
科目名稱:普通化學 期中考(I) 日期:99年10月18日 學號 姓名 I. 名詞
... III. 計算題 (35%) 1. Calculate the wavelength (in nm) of a photon emitted by a hydrogen atom when its electron drops from the n = 5 state to the n = 3 state. (5%) 2. A cube made of platinum (Pt) has an edge length of 1.0 cm. (a) Calculate the number of Pt atoms in the cube, (b) Atoms are spherical in s ...
... III. 計算題 (35%) 1. Calculate the wavelength (in nm) of a photon emitted by a hydrogen atom when its electron drops from the n = 5 state to the n = 3 state. (5%) 2. A cube made of platinum (Pt) has an edge length of 1.0 cm. (a) Calculate the number of Pt atoms in the cube, (b) Atoms are spherical in s ...
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics AEP3610 Professor Scott
... the de Broglie wavelength for a moving particle, and the Born interpretion of the wave function • to ‘derive’ the Schrödinger equation(s) for said wave function for a particle in (or not in) a potential V(x) • to discuss (review?) several important potential energy cases • to explore the alternative ...
... the de Broglie wavelength for a moving particle, and the Born interpretion of the wave function • to ‘derive’ the Schrödinger equation(s) for said wave function for a particle in (or not in) a potential V(x) • to discuss (review?) several important potential energy cases • to explore the alternative ...
P114 PROBLEM SET 9 Spring 2014
... [1] A penny weighs 2.0 g. Calculate the rest energy for a penny. If you convert this energy completely to electrical energy and sell it at 10 cent/kW-hour, how much money will you make? [2] Your friend, who is exactly the same age as you, travels at a speed of 0.9990c to a star 25 light-years away. ...
... [1] A penny weighs 2.0 g. Calculate the rest energy for a penny. If you convert this energy completely to electrical energy and sell it at 10 cent/kW-hour, how much money will you make? [2] Your friend, who is exactly the same age as you, travels at a speed of 0.9990c to a star 25 light-years away. ...
6.1.1
... • Physicists in this era were still unable to explain THREE important phenomenon Blackbody Radiation Wave Theory: A blackbody will emit radiation that directly relates to its temperature. The higher the temperature, the more frequencies can be emitted. Experiment: The intensity of radiation does not ...
... • Physicists in this era were still unable to explain THREE important phenomenon Blackbody Radiation Wave Theory: A blackbody will emit radiation that directly relates to its temperature. The higher the temperature, the more frequencies can be emitted. Experiment: The intensity of radiation does not ...
Moderne Methoden der Materialcharakterisierung
... Cathode material determines emission current density ...
... Cathode material determines emission current density ...
Lecture 5: Molecular Astrophysics
... X-ray machines, CTscanners ~ 100 KVp Linear Accelerators: 6-15 MVp Broadband bremsstrahlung radiation is harmful because it is not energy specific to targeted tissue for imaging or therapy ...
... X-ray machines, CTscanners ~ 100 KVp Linear Accelerators: 6-15 MVp Broadband bremsstrahlung radiation is harmful because it is not energy specific to targeted tissue for imaging or therapy ...
Quantum Physics 2 - More About
... Plot the results from the vacuum photocell to determine Planck’s constant and the work function. ...
... Plot the results from the vacuum photocell to determine Planck’s constant and the work function. ...
Electron configuration Jeopardy
... wave characteristic. 500 – What is the difference between a continuous spectrum and a line spectrum and give an example of where you could find each. Continuous spectrum is like the rainbow. You could look out the window to see that. Line spectrum is certain colors show up in lines. You could pass e ...
... wave characteristic. 500 – What is the difference between a continuous spectrum and a line spectrum and give an example of where you could find each. Continuous spectrum is like the rainbow. You could look out the window to see that. Line spectrum is certain colors show up in lines. You could pass e ...
2.2.3.- X-ray diffraction
... The x-ray spectra were obtained in a step-scan mode. This means that the sample and the detector rotated in steps instead of in a continuous way. The appropriate step size for each experiment was selected in order to have at least 10 experimental points above the half height width. Therefore, depend ...
... The x-ray spectra were obtained in a step-scan mode. This means that the sample and the detector rotated in steps instead of in a continuous way. The appropriate step size for each experiment was selected in order to have at least 10 experimental points above the half height width. Therefore, depend ...
2710 PS3 1 Problem Set #3 Comparing classical electromagnetic
... Problem 2 refers to: A single photon in a quantum wire stretching between x = 0 and x = L is described by the wavefunction Ψ(x,t) = Ψ max sin(3π x L)exp(− ic3π t L) . Let L= 900 nm. 2.(a) How does the photon kinetic energy vary in space and time? What is the average photon kinetic energy measured ma ...
... Problem 2 refers to: A single photon in a quantum wire stretching between x = 0 and x = L is described by the wavefunction Ψ(x,t) = Ψ max sin(3π x L)exp(− ic3π t L) . Let L= 900 nm. 2.(a) How does the photon kinetic energy vary in space and time? What is the average photon kinetic energy measured ma ...
UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy
... Effect of Scattered Radiation at Wavelength Extremes of an Instrument Wavelength extremes of an instrument are dependent on type of source, detector and optical components used in the manufacture of the instrument. Outside the working range of the instrument, it is not possible to use it for accura ...
... Effect of Scattered Radiation at Wavelength Extremes of an Instrument Wavelength extremes of an instrument are dependent on type of source, detector and optical components used in the manufacture of the instrument. Outside the working range of the instrument, it is not possible to use it for accura ...
CH1710 HW#7 (2017)-Quanta, electron config
... from a mercury discharge within the tube. Much of this light has a wavelength of 436 nm. a. What is the energy (in J) of one photon of this light? ...
... from a mercury discharge within the tube. Much of this light has a wavelength of 436 nm. a. What is the energy (in J) of one photon of this light? ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.