Chapter 4 Radiation By Moving Charges
... interested in the power radiated per unit solid angle, fl,, subtended by the area at the point of radiation. By definition of solid angle, a small area of the sphere, A, subtends a solid angle AIR2. Consequently the power per unit solid angle is R2E2/cPo. The extra term R2 cancels the R2 occurring i ...
... interested in the power radiated per unit solid angle, fl,, subtended by the area at the point of radiation. By definition of solid angle, a small area of the sphere, A, subtends a solid angle AIR2. Consequently the power per unit solid angle is R2E2/cPo. The extra term R2 cancels the R2 occurring i ...
Non Traditional Machining Processes MIME - 6980
... Machine Tools The three major subsystems that make up an electron beam machining system are – power supply, – electron beam gun, and – the vacuum system. ...
... Machine Tools The three major subsystems that make up an electron beam machining system are – power supply, – electron beam gun, and – the vacuum system. ...
Stimulated Emission and Inversion 9.2.2 Laser Diodes
... Of course, you have the usual quantum mechanical paradox that the incoming photon is in resonance with something it has not yet created; it is just, so to speak, probing possible outcomes of possible processes. From the resonance argument it follows that two photons have the same wavelenth and are e ...
... Of course, you have the usual quantum mechanical paradox that the incoming photon is in resonance with something it has not yet created; it is just, so to speak, probing possible outcomes of possible processes. From the resonance argument it follows that two photons have the same wavelenth and are e ...
Gas Chromatography
... compound. The comparison of retention times is what gives GC its analytical usefulness. A gas chromatograph uses a flow-through narrow tube known as the column, through which different chemical constituents of a sample pass in a gas stream (carrier gas, mobile phase) at different rates depending on ...
... compound. The comparison of retention times is what gives GC its analytical usefulness. A gas chromatograph uses a flow-through narrow tube known as the column, through which different chemical constituents of a sample pass in a gas stream (carrier gas, mobile phase) at different rates depending on ...
Illustrating the Superposition Principle with Single Photon
... informs the chemists view of atomic and molecular structure, and is especially important in unifying the many facets of chemical bonding (10). ...
... informs the chemists view of atomic and molecular structure, and is especially important in unifying the many facets of chemical bonding (10). ...
Worksheet
... 1) Summarize the contributions of each of the following individuals to our understanding of the atom and atomic structure (you may have to look back into CH 4 for the first 3…or the summary on page 133). Include a sketch of what the atom would look like according to their explanations. • Dalton: ...
... 1) Summarize the contributions of each of the following individuals to our understanding of the atom and atomic structure (you may have to look back into CH 4 for the first 3…or the summary on page 133). Include a sketch of what the atom would look like according to their explanations. • Dalton: ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... 37. The principal quantum number for the outermost electrons in a Br atom in the ground state is __________. (a). 2 (b). 3 (c). 4 (d). 5 Explanation: The electronic configuration of bromine is [Ar]3d104s24p5 shows that the outermost electrons are in the s and p orbitals in the 4th energy level makin ...
... 37. The principal quantum number for the outermost electrons in a Br atom in the ground state is __________. (a). 2 (b). 3 (c). 4 (d). 5 Explanation: The electronic configuration of bromine is [Ar]3d104s24p5 shows that the outermost electrons are in the s and p orbitals in the 4th energy level makin ...
Bohr Model, Quantum Mechanical Model
... b. energy is involved in moving an electron from one level to another. 4. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- It is impossible to know the momentum (mass of electron times velocity) of an electron and its position in space at the same time. One or the other. 5. Quantum Mechanical Model- a mathematical ...
... b. energy is involved in moving an electron from one level to another. 4. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- It is impossible to know the momentum (mass of electron times velocity) of an electron and its position in space at the same time. One or the other. 5. Quantum Mechanical Model- a mathematical ...
Part no: 55000-280 *(Shown with
... (1 to 15Hz, 1 to 2.7µm), flickering infra-red radiation emitted by flames during combustion. Since it responds to flickering radiation, the XP95 Dual IR Flame Detector can operate even if the lens is contaminated by a layer of oil, dust, water-vapour or ice. False alarms due to such factors as flick ...
... (1 to 15Hz, 1 to 2.7µm), flickering infra-red radiation emitted by flames during combustion. Since it responds to flickering radiation, the XP95 Dual IR Flame Detector can operate even if the lens is contaminated by a layer of oil, dust, water-vapour or ice. False alarms due to such factors as flick ...
Recitation Activity 6 (Chem 121) Chapter 6
... (b) What equation relates all 3 of the above (frequency, wavelength and energy)? E=hν E=hc/λ (c) Use the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom to determine the wavelength of the photon given off following transition B. Identify the region of the electromagnetic spectrum (IR, Visible, UV, X-rays, etc.) tha ...
... (b) What equation relates all 3 of the above (frequency, wavelength and energy)? E=hν E=hc/λ (c) Use the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom to determine the wavelength of the photon given off following transition B. Identify the region of the electromagnetic spectrum (IR, Visible, UV, X-rays, etc.) tha ...
Parametric Poisson Process Imaging
... in to several regions of recovered depth maps. We clearly see that our computational imager can finely resolve object gradients and even make out objects in the far field region, where background photons are more likely to be detected. Figure 4 shows the high photon efficiency of PPPI compared to th ...
... in to several regions of recovered depth maps. We clearly see that our computational imager can finely resolve object gradients and even make out objects in the far field region, where background photons are more likely to be detected. Figure 4 shows the high photon efficiency of PPPI compared to th ...
here - TCD Maths home - Trinity College Dublin
... by Köhler and Rohr, allowed for an increase in resolving power of about a factor of two, but required more expensive quartz optical components. At this point it was believed that obtaining an image with sub-micrometer information was simply impossible due to this wavelength constraint. In 1891 it wa ...
... by Köhler and Rohr, allowed for an increase in resolving power of about a factor of two, but required more expensive quartz optical components. At this point it was believed that obtaining an image with sub-micrometer information was simply impossible due to this wavelength constraint. In 1891 it wa ...
Final Exam Practice Problems Set 2
... Ethylene glycol, used as a coolant in automotive engines, has a specific heat capacity of 2.42 J/(g•K). Calculate q when 3.65 kg of ethylene glycol is cooled from 132 ˚C to 85 ˚C. ...
... Ethylene glycol, used as a coolant in automotive engines, has a specific heat capacity of 2.42 J/(g•K). Calculate q when 3.65 kg of ethylene glycol is cooled from 132 ˚C to 85 ˚C. ...
Atomic spectra and the Bohr atom
... • Werner Heisenberg stated in 1927 that it is impossible to know with precision both the position and the momentum of an electron. • The observer affects the observed. • Only noticeable on the sub-atomic scale (e.g. an electron, not a baseball, nor dust). • It is not possible to define a point in ...
... • Werner Heisenberg stated in 1927 that it is impossible to know with precision both the position and the momentum of an electron. • The observer affects the observed. • Only noticeable on the sub-atomic scale (e.g. an electron, not a baseball, nor dust). • It is not possible to define a point in ...
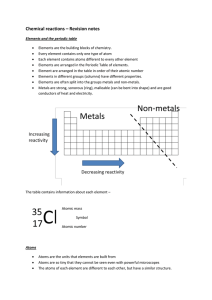
Chemical reactions revision
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Chapter 8 - Clayton State University
... numbers of different kinds of photons. With large numbers of different sized photons, almost any amount of radiation can be formed, but there is a minimum amount of radiation (a photon) that we would never perceive, because it is so small. In a similar way, it looks as though a digital camera forms ...
... numbers of different kinds of photons. With large numbers of different sized photons, almost any amount of radiation can be formed, but there is a minimum amount of radiation (a photon) that we would never perceive, because it is so small. In a similar way, it looks as though a digital camera forms ...
chapter 3.4: the bohr atomic theory
... Read and make notes on: The Photoelectric Effect (pg 170-172) Each of these specific quantities is called a quantum of energy. In other words, Planck said that the energy of an atom is quantized. Something that is quantized can exist only in certain discrete amounts. It is not continuous. Although P ...
... Read and make notes on: The Photoelectric Effect (pg 170-172) Each of these specific quantities is called a quantum of energy. In other words, Planck said that the energy of an atom is quantized. Something that is quantized can exist only in certain discrete amounts. It is not continuous. Although P ...
Atomic Physics - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... • Lowest energy state = “ground state” • Higher states = “excited states” • Photon energy equals difference in state energies • Hydrogen atom example – Energy levels – Line spectra ...
... • Lowest energy state = “ground state” • Higher states = “excited states” • Photon energy equals difference in state energies • Hydrogen atom example – Energy levels – Line spectra ...
Chapter 11: Electromagnetic Waves
... difference is the light source is a laser that emits one photon (particle) of light at a time The photon passes through the slit in the first partition and travels to the second partition Photosensitive Screen where it passes through both slits. (Think about it, one particle passing through two diff ...
... difference is the light source is a laser that emits one photon (particle) of light at a time The photon passes through the slit in the first partition and travels to the second partition Photosensitive Screen where it passes through both slits. (Think about it, one particle passing through two diff ...
Lecture9,ch4
... The scattering is proportional to the square of the atomic number of both the incident particle (Z1) and the target scatterer (Z2). The number of scattered particles is inversely proportional to the square of the kinetic energy of the incident particle. For the scattering angle , the scattering is ...
... The scattering is proportional to the square of the atomic number of both the incident particle (Z1) and the target scatterer (Z2). The number of scattered particles is inversely proportional to the square of the kinetic energy of the incident particle. For the scattering angle , the scattering is ...
A Wave Theory of Light and Electrons
... of source and background waves. 13. No Independent Knowledge of Emitters: In any laboratory setup, the location, timing, number, direction and spread of emitted quanta are unknown. Statements about emissions are only inferences from detection events. 14. Statistical Prediction: Since the quantum emi ...
... of source and background waves. 13. No Independent Knowledge of Emitters: In any laboratory setup, the location, timing, number, direction and spread of emitted quanta are unknown. Statements about emissions are only inferences from detection events. 14. Statistical Prediction: Since the quantum emi ...
- BUGS McGill
... 4. A photoactive metal is irradiated with light at 440 nm and photoelectrons with a velocity of 6.11 x 105 ms-1 are produced. Wha is the longest radiation wavelength (nm) that would result in the production of photoelectrons? ...
... 4. A photoactive metal is irradiated with light at 440 nm and photoelectrons with a velocity of 6.11 x 105 ms-1 are produced. Wha is the longest radiation wavelength (nm) that would result in the production of photoelectrons? ...
The Chemical Context of Life Chapter 2 Notes
... Atomic number: # of protons Mass number: sum of protons + neutrons Isotopes: different atomic forms of an element. -ex. Carbon-12 (99%), Carbon-13 (1%), Carbon-14 (<1%) ...
... Atomic number: # of protons Mass number: sum of protons + neutrons Isotopes: different atomic forms of an element. -ex. Carbon-12 (99%), Carbon-13 (1%), Carbon-14 (<1%) ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.