Single Photon Sources - University of Rochester
... also be used [9]. For use as a single photon source, nanodiamonds are immersed in a photonic bandgap host to enhance emission and ensure a definite polarization. In our case, a cholesteric liquid crystal provided a one-dimensional bandgap that’s chiral nature allowed for the transmission of left-ha ...
... also be used [9]. For use as a single photon source, nanodiamonds are immersed in a photonic bandgap host to enhance emission and ensure a definite polarization. In our case, a cholesteric liquid crystal provided a one-dimensional bandgap that’s chiral nature allowed for the transmission of left-ha ...
Optical Monte Carlo modeling of a true port wine stain anatomy
... propagation and energy deposition in arbitrarily complex geometries. A trade-off is made, however, with increased complexity of the tissues studied. The results presented above may present an extremely realistic determination of the energy deposition in this particular PWS, but complexity makes the ...
... propagation and energy deposition in arbitrarily complex geometries. A trade-off is made, however, with increased complexity of the tissues studied. The results presented above may present an extremely realistic determination of the energy deposition in this particular PWS, but complexity makes the ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... are made from two or more pure substances and you can oOen separate the components of mixtures or soluBons by using physical separa1on techniques (note that some mixtures, like concrete or glass, cannot ...
... are made from two or more pure substances and you can oOen separate the components of mixtures or soluBons by using physical separa1on techniques (note that some mixtures, like concrete or glass, cannot ...
Solution
... C) pH of 0.01 M NH4Cl > pH of 0.01 M NH3 D) pH of 0.01 M NaCN > pH of 0.01 M CaCl2 14.) A blue advertising signs emits light with a wavelength of 400 nm. Which relationship is appropriate for directly calculating the frequency of this light? A) E = ½ mv2 B) En = -(Z2/n2) R∞ C) λ = c/ν D) E = hc/ λ E ...
... C) pH of 0.01 M NH4Cl > pH of 0.01 M NH3 D) pH of 0.01 M NaCN > pH of 0.01 M CaCl2 14.) A blue advertising signs emits light with a wavelength of 400 nm. Which relationship is appropriate for directly calculating the frequency of this light? A) E = ½ mv2 B) En = -(Z2/n2) R∞ C) λ = c/ν D) E = hc/ λ E ...
Scanning Electron Microscope - i-Explore International Research
... higher the accelerating voltage the faster the electrons travel down the column and the more penetrating power they have. There are two types of FEGs: Cold and thermally assisted Field emission guns. Both types of field emission require that the tip remain free of contaminants and oxide and thus the ...
... higher the accelerating voltage the faster the electrons travel down the column and the more penetrating power they have. There are two types of FEGs: Cold and thermally assisted Field emission guns. Both types of field emission require that the tip remain free of contaminants and oxide and thus the ...
I. Waves & Particles
... B. Bohr Model 2) e- exist only in orbits with specific amounts of energy called energy levels When e- are in these orbitals, they have fixed energy Energy of e- are higher when they are further from the nucleus ...
... B. Bohr Model 2) e- exist only in orbits with specific amounts of energy called energy levels When e- are in these orbitals, they have fixed energy Energy of e- are higher when they are further from the nucleus ...
Unit 1 - Morgan Science
... Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
in PPT
... If indistinguishable amps and = p, destructive interference (P11 = 0) suppress any pairs from “splitting” at 50/50 leaves photon hole pairs in constant laser background ...
... If indistinguishable amps and = p, destructive interference (P11 = 0) suppress any pairs from “splitting” at 50/50 leaves photon hole pairs in constant laser background ...
the reflectivity and transmissivity - quantum view
... where the constants A, B and C represent the magnitude of the incident, reflected, and transmitted wave function respectively. We can write the reflectivity and transmissivity for the cases of perpendicular and parallel polarization. In our will be replaced by the square moduli of the wave function ...
... where the constants A, B and C represent the magnitude of the incident, reflected, and transmitted wave function respectively. We can write the reflectivity and transmissivity for the cases of perpendicular and parallel polarization. In our will be replaced by the square moduli of the wave function ...
Slide 1
... Ptotal = PA + PB + PC + ..... At low temperatures and high pressures real gases do not behave ideally. The reasons for the deviations from ideality are: 1. The molecules are very close to one another, thus their volume is important. 2. The molecular interactions also become important. ...
... Ptotal = PA + PB + PC + ..... At low temperatures and high pressures real gases do not behave ideally. The reasons for the deviations from ideality are: 1. The molecules are very close to one another, thus their volume is important. 2. The molecular interactions also become important. ...
phase diagrams and IMF
... 1.) Explain why the formation of solid and/or liquid phase(s) would be favored under conditions of: Explain using the ideas of kinetic energy (molecular motion), how close together molecules are/could be, ability to be attracted to its neighbor: ...
... 1.) Explain why the formation of solid and/or liquid phase(s) would be favored under conditions of: Explain using the ideas of kinetic energy (molecular motion), how close together molecules are/could be, ability to be attracted to its neighbor: ...
How to Study? • Reading ( ) • Ask questions (
... Nuclear model - an atom of atomic number Z consists of a nucleus of charge +Ze surrounded by Z electrons each of charge –e (e is the fundamental charge). These electrons occupy atomic orbitals, which are regions of space where they are most likely to be found, with no more than two electrons in any ...
... Nuclear model - an atom of atomic number Z consists of a nucleus of charge +Ze surrounded by Z electrons each of charge –e (e is the fundamental charge). These electrons occupy atomic orbitals, which are regions of space where they are most likely to be found, with no more than two electrons in any ...
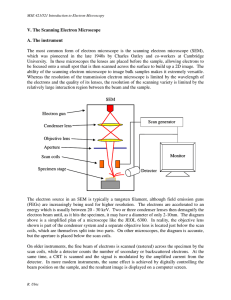
V. The Scanning Electron Microscope A. The instrument The most
... Bakcscattered electrons travelling in the appropriate direction will also hit the Everhart-Thornely detector and contribute to the secondary electron image; therefore, the secondary electron signal always contains some backscattered component as well. If the scintillator is switched off or given a s ...
... Bakcscattered electrons travelling in the appropriate direction will also hit the Everhart-Thornely detector and contribute to the secondary electron image; therefore, the secondary electron signal always contains some backscattered component as well. If the scintillator is switched off or given a s ...
Chemistry Study Guide What is matter made of? Matter is anything
... properties that are the same or very similar. The elements in each group also have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. The horizontal rows are called periods. The elements in each period are arranged by atomic number and have the same number of electron shells around the nucleus. Eac ...
... properties that are the same or very similar. The elements in each group also have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. The horizontal rows are called periods. The elements in each period are arranged by atomic number and have the same number of electron shells around the nucleus. Eac ...
APES Ch. 3 Notes
... b. Low Quality Matter – disorganized, dilute, deep underground or dispersed in oceans or the atmosphere, and has little potential for use as a matter resource. Entropy – measure of the disorder or randomness of a system or its environment ...
... b. Low Quality Matter – disorganized, dilute, deep underground or dispersed in oceans or the atmosphere, and has little potential for use as a matter resource. Entropy – measure of the disorder or randomness of a system or its environment ...
Quantum and Photo-electric effects - Delivery guide
... Extension activities could include shining a UV lamp onto a zinc plate sitting on a Coulombmeter (see later section) or researching how the CCD in a digital camera works. The following three sections are arguably the most engaging of the A Level, particularly for the students; not because they are f ...
... Extension activities could include shining a UV lamp onto a zinc plate sitting on a Coulombmeter (see later section) or researching how the CCD in a digital camera works. The following three sections are arguably the most engaging of the A Level, particularly for the students; not because they are f ...
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... allows us to image a sample using s-SNOM using multiple wavelengths without having to change the laser. Second, it allows us to probe the sample for certain molecules with known resonance frequencies so that we can image the position of these molecules within nanometer resolution. The IR laser light ...
... allows us to image a sample using s-SNOM using multiple wavelengths without having to change the laser. Second, it allows us to probe the sample for certain molecules with known resonance frequencies so that we can image the position of these molecules within nanometer resolution. The IR laser light ...
Supplement
... To accurately measure the atom number variance it is necessary to eliminate patterns in the absorption images whose fluctuations increase the observed noise. Weak reflections of the probe beam from the walls of the glass cell and from optical elements in the imaging system can interfere with the probe ...
... To accurately measure the atom number variance it is necessary to eliminate patterns in the absorption images whose fluctuations increase the observed noise. Weak reflections of the probe beam from the walls of the glass cell and from optical elements in the imaging system can interfere with the probe ...
Atomic Term Symbols
... respectively, 9 states in total. A 2 D level (S=1/2, L=2), splits into J=5/2 (6 states) and J=3/2 (4 states), hence 10 states in total. The atomic term values are 2 D5/ 2 , 2 D3/ 2 . You may notice that the splittings discussed for the hydrogen atom follow this rule also. The energy splittings betwe ...
... respectively, 9 states in total. A 2 D level (S=1/2, L=2), splits into J=5/2 (6 states) and J=3/2 (4 states), hence 10 states in total. The atomic term values are 2 D5/ 2 , 2 D3/ 2 . You may notice that the splittings discussed for the hydrogen atom follow this rule also. The energy splittings betwe ...
Bonding
... difference between sets of d orbitals is comparable to the energy of visible light. In zinc ions, all the d orbitals are paired and all the orbitals are degenerate. (d) Arsenic atoms have one more valence electron than silicon atoms and can lose an electron to form As+ ions which can occupy some of ...
... difference between sets of d orbitals is comparable to the energy of visible light. In zinc ions, all the d orbitals are paired and all the orbitals are degenerate. (d) Arsenic atoms have one more valence electron than silicon atoms and can lose an electron to form As+ ions which can occupy some of ...
Boltzmann/Saha Equation Problems/Questions
... However, this will not be the distribution that actually occurs as T→ ∞ because at such high temperatures all of the hydrogen atoms will have ionized. ...
... However, this will not be the distribution that actually occurs as T→ ∞ because at such high temperatures all of the hydrogen atoms will have ionized. ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.