Retrograde CP - WordPress.com
... MYOCARDIAL PROTECTION DEFINITION: It is defined as specific intra op technique designed to protect heart from ischemic state associated with extra corporeal circulation. ...
... MYOCARDIAL PROTECTION DEFINITION: It is defined as specific intra op technique designed to protect heart from ischemic state associated with extra corporeal circulation. ...
Circulatory System Process Grid teacher version
... How does the heart beat? Before each beat, your heart fills with blood. Then its muscle contracts to squirt the blood along. When the heart contracts, it squeezes — try squeezing your hand into a fist. That's sort of like what your heart does so it can squirt out the blood. Your heart does this all ...
... How does the heart beat? Before each beat, your heart fills with blood. Then its muscle contracts to squirt the blood along. When the heart contracts, it squeezes — try squeezing your hand into a fist. That's sort of like what your heart does so it can squirt out the blood. Your heart does this all ...
backgrounder
... The Medtronic Arctic Front Advance™ Cardiac CryoAblation Catheter System Overview A catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to treat atrial fibrillation (AF), an irregular quivering or rapid rhythm in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart. The goal of the procedure is to stop ...
... The Medtronic Arctic Front Advance™ Cardiac CryoAblation Catheter System Overview A catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to treat atrial fibrillation (AF), an irregular quivering or rapid rhythm in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart. The goal of the procedure is to stop ...
The Cardiac Cycle Cardiac conduction system Cardiac Muscle
... during ventricular diastole Dicrotic notch- blood rebounding off SL valves as they close ...
... during ventricular diastole Dicrotic notch- blood rebounding off SL valves as they close ...
Artificial Heart Valves
... When the velocity of the blood flow is too low, stagnation may take place in such areas as on the minor outflow side of a tilting disk valve, with consequent clotting or buildup of extra endothelial tissue. When the various problems are considered, the value of the research goals of learning more ab ...
... When the velocity of the blood flow is too low, stagnation may take place in such areas as on the minor outflow side of a tilting disk valve, with consequent clotting or buildup of extra endothelial tissue. When the various problems are considered, the value of the research goals of learning more ab ...
Cardiovascular System: Physiology
... incompetent valve - does not close properly valvular stenosis - valve stiffening due to bacterial infection ...
... incompetent valve - does not close properly valvular stenosis - valve stiffening due to bacterial infection ...
Cardiovascular Disease - Dartmouth
... Cardiovascular Disease? • Cardiovascular disease is the number one killer • About 42% of all deaths • Nationwide: 921,819 annually • NH: 3468 • VT: 1751 ...
... Cardiovascular Disease? • Cardiovascular disease is the number one killer • About 42% of all deaths • Nationwide: 921,819 annually • NH: 3468 • VT: 1751 ...
HISTORY TAKING AND EXAMINING THE GERIATRIC PATIENT
... each may be due to a variety of etiologies. Systolic dysfunction — The most common causes are coronary (ischemic) heart disease, idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), hypertension, and valvular disease. Diastolic dysfunction — Diastolic dysfunction can be induced by many of the same conditions ...
... each may be due to a variety of etiologies. Systolic dysfunction — The most common causes are coronary (ischemic) heart disease, idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), hypertension, and valvular disease. Diastolic dysfunction — Diastolic dysfunction can be induced by many of the same conditions ...
Powerpoint version
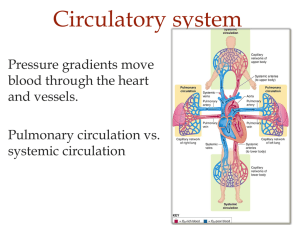
... Circulatory system Pressure gradients move blood through the heart and vessels. Pulmonary circulation vs. systemic circulation ...
... Circulatory system Pressure gradients move blood through the heart and vessels. Pulmonary circulation vs. systemic circulation ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
... Jennifer Terker Professor of Pediatrics Division Chief, Pediatric Cardiology Medical Director, Heart Transplant Program The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine ...
... Jennifer Terker Professor of Pediatrics Division Chief, Pediatric Cardiology Medical Director, Heart Transplant Program The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine ...
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
... ♥ You are at increased risk if you have an immediate blood relative (parent, grandparent, brother, sister) who has had a heart attack or stroke? ♥ If your brother, father or grandfather had a heart attack before age 55, or your sister, mother or grandmother had one before age 65, you may be at risk ...
... ♥ You are at increased risk if you have an immediate blood relative (parent, grandparent, brother, sister) who has had a heart attack or stroke? ♥ If your brother, father or grandfather had a heart attack before age 55, or your sister, mother or grandmother had one before age 65, you may be at risk ...
heart
... artery from the chest to correct blocked coronary arteries Thrombus – blood clot Embolus – moving blood clot Ischemia – lack of blood flow and oxygen to heart Aneurysm – a permanent weakness in an artery Angioplasty – a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and fed into a coronary ar ...
... artery from the chest to correct blocked coronary arteries Thrombus – blood clot Embolus – moving blood clot Ischemia – lack of blood flow and oxygen to heart Aneurysm – a permanent weakness in an artery Angioplasty – a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and fed into a coronary ar ...
heart
... artery from the chest to correct blocked coronary arteries Thrombus – blood clot Embolus – moving blood clot Ischemia – lack of blood flow and oxygen to heart Aneurysm – a permanent weakness in an artery Angioplasty – a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and fed into a coronary ar ...
... artery from the chest to correct blocked coronary arteries Thrombus – blood clot Embolus – moving blood clot Ischemia – lack of blood flow and oxygen to heart Aneurysm – a permanent weakness in an artery Angioplasty – a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and fed into a coronary ar ...
Warfarin - Boston Scientific
... Information for the use only in countries with applicable health authority product registrations. This document may not be used in France. ...
... Information for the use only in countries with applicable health authority product registrations. This document may not be used in France. ...
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart • Heart pumps over 1 million
... – prevents blood from returning to ventricles, blood fills valve cusps, tightly closing the SL valves Blood Circulation Two closed circuits, the systemic and pulmonic Systemic circulation – left side of heart pumps blood through body – left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood into aorta – aorta branche ...
... – prevents blood from returning to ventricles, blood fills valve cusps, tightly closing the SL valves Blood Circulation Two closed circuits, the systemic and pulmonic Systemic circulation – left side of heart pumps blood through body – left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood into aorta – aorta branche ...
SNC2D1 Date: Name: MAIN FUNCTION OF THE CIRCULATORY
... that regulates the by signalling the of the upper and lower chambers to ______________________ after it has filled with blood Valves – keeps blood _______________________ in the ________________________ direction STRUCTURE The heart contains __________ Chambers ...
... that regulates the by signalling the of the upper and lower chambers to ______________________ after it has filled with blood Valves – keeps blood _______________________ in the ________________________ direction STRUCTURE The heart contains __________ Chambers ...
Exam I Study Guide
... 3. Know which veins enter into the right and left atria. 4. Know the 4 heart valves and where each is located. 5. Know where the main coronary arteries, their branches, and where each supplies blood to. 6. Be able to outline pulmonary & systemic circulation. 7. Be able to name and describe the steps ...
... 3. Know which veins enter into the right and left atria. 4. Know the 4 heart valves and where each is located. 5. Know where the main coronary arteries, their branches, and where each supplies blood to. 6. Be able to outline pulmonary & systemic circulation. 7. Be able to name and describe the steps ...
Sudden Cardiac Arrest Forms (2)
... attack is caused by a blockage that stops the flow of blood to the heart. SCA is a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system, causing the heart to suddenly stop beating and the victim to collapse. The malfunction is caused by a congenital or genetic defect in the heart’s structure. How common is ...
... attack is caused by a blockage that stops the flow of blood to the heart. SCA is a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system, causing the heart to suddenly stop beating and the victim to collapse. The malfunction is caused by a congenital or genetic defect in the heart’s structure. How common is ...
Heart Dissection
... atrium down into the left ventricle cutting toward the apex 2. Open the heart. Examine the left atrium. Find the openings of the pulmonary veins form the lungs. Observe the one-way, semi-lunar valves at the entrance to these veins 3. Look for the mitral valve. 4. Examine the left ventricle. Notice t ...
... atrium down into the left ventricle cutting toward the apex 2. Open the heart. Examine the left atrium. Find the openings of the pulmonary veins form the lungs. Observe the one-way, semi-lunar valves at the entrance to these veins 3. Look for the mitral valve. 4. Examine the left ventricle. Notice t ...
Marfan`s Syndrome
... The enlargement of the aorta (caused by the high blood pressure in this vessel) may cause its walls to become thin and weak. In rare cases, they may actually rupture, sometimes resulting in sudden death. If the structure of the aortic or mitral valves is abnormal, there may be the leakage of blood a ...
... The enlargement of the aorta (caused by the high blood pressure in this vessel) may cause its walls to become thin and weak. In rare cases, they may actually rupture, sometimes resulting in sudden death. If the structure of the aortic or mitral valves is abnormal, there may be the leakage of blood a ...
Russia
... Law of the Russian Empire from 1812 the first brevet-privilege was granted for 10 years mechanical engineer Ivan Puadebard for the machine for charging the boats against the current of water on May 29, 1814 ...
... Law of the Russian Empire from 1812 the first brevet-privilege was granted for 10 years mechanical engineer Ivan Puadebard for the machine for charging the boats against the current of water on May 29, 1814 ...
HERE
... • controls activity of the nerves regulating the smooth (circular) muscle contraction of the blood vessel • also controls strength of heartbeat, HR • receives and interprets and responds to sensors through the cardiovascular system (esp. in the walls of the vessels) ...
... • controls activity of the nerves regulating the smooth (circular) muscle contraction of the blood vessel • also controls strength of heartbeat, HR • receives and interprets and responds to sensors through the cardiovascular system (esp. in the walls of the vessels) ...
Chapter 47 - Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... • controls activity of the nerves regulating the smooth (circular) muscle contraction of the blood vessel • also controls strength of heartbeat, HR • receives and interprets and responds to sensors through the cardiovascular system (esp. in the walls of the vessels) ...
... • controls activity of the nerves regulating the smooth (circular) muscle contraction of the blood vessel • also controls strength of heartbeat, HR • receives and interprets and responds to sensors through the cardiovascular system (esp. in the walls of the vessels) ...
Cardiac surgery

Cardiovascular (heart) surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, coronary artery bypass grafting), correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation.