Slide ()
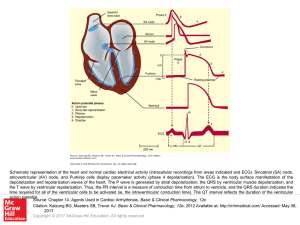
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
Appendix _: Glossary
... effective pumping occurs. Fibrillation may occur in the atria or the ventricles. Heart Block – A condition in which electrical impulses are not conducted in the normal fashion from the atria to the ventricles. May be caused by damage or disease processes within the cardiac conduction system. Haemody ...
... effective pumping occurs. Fibrillation may occur in the atria or the ventricles. Heart Block – A condition in which electrical impulses are not conducted in the normal fashion from the atria to the ventricles. May be caused by damage or disease processes within the cardiac conduction system. Haemody ...
Glossary of Cardiology Terms
... effective pumping occurs. Fibrillation may occur in the atria or the ventricles. Heart Block – A condition in which electrical impulses are not conducted in the normal fashion from the atria to the ventricles. May be caused by damage or disease processes within the cardiac conduction system. Haemody ...
... effective pumping occurs. Fibrillation may occur in the atria or the ventricles. Heart Block – A condition in which electrical impulses are not conducted in the normal fashion from the atria to the ventricles. May be caused by damage or disease processes within the cardiac conduction system. Haemody ...
Circulatory System
... 3. Tissues and cells of the body receive O2 and blood receives CO2 waste 4. Starts over at the RIGHT side for Pulmonary Circulation ...
... 3. Tissues and cells of the body receive O2 and blood receives CO2 waste 4. Starts over at the RIGHT side for Pulmonary Circulation ...
Chapter 11: The Cardiovascular System
... Describe the location of the heart in the body, and identify its major anatomical areas on an appropriate model or diagram. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Compare the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Explain the operation of the heart valves. Name the functional blood supply ...
... Describe the location of the heart in the body, and identify its major anatomical areas on an appropriate model or diagram. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Compare the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Explain the operation of the heart valves. Name the functional blood supply ...
Eur J Heart Fail
... Doppler E/A ratio (p=0.01) increased in the CHF group, with no changes in left ventricular volumes. The healthy subjects had similar responses, but also displayed an increase in cardiac output (p<0.01) and left ventricular volumes (p<0.001). Exercise. Cardiac output and systolic blood pressure incre ...
... Doppler E/A ratio (p=0.01) increased in the CHF group, with no changes in left ventricular volumes. The healthy subjects had similar responses, but also displayed an increase in cardiac output (p<0.01) and left ventricular volumes (p<0.001). Exercise. Cardiac output and systolic blood pressure incre ...
Here
... Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about blood flow through the heart. a) Blood enters the heart through the right and left atria. b) Blood enters the heart through the right and left ventricles c) Blood flows from the ventricles to the atria. d) Blood flows out of the heart through the ...
... Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about blood flow through the heart. a) Blood enters the heart through the right and left atria. b) Blood enters the heart through the right and left ventricles c) Blood flows from the ventricles to the atria. d) Blood flows out of the heart through the ...
Title: The Cardiac Conduction System
... 1- Introduction: The inherent and rhythmical electrical activity in the heart is responsible for its continuous beating. The source of this beating is a group of highly specialized cells called the autorhythmic cells. a- These cells are self-excitable b- They repeatedly generate action potentials th ...
... 1- Introduction: The inherent and rhythmical electrical activity in the heart is responsible for its continuous beating. The source of this beating is a group of highly specialized cells called the autorhythmic cells. a- These cells are self-excitable b- They repeatedly generate action potentials th ...
Clinical Update on Congenital Heart Defects
... Use appropriate sized cuff for accuracy Norms dependent on weight, age Decreases 3-4 hours postnatally, increases to plateau at 4-6 days of age Follow blood pressures for trending ...
... Use appropriate sized cuff for accuracy Norms dependent on weight, age Decreases 3-4 hours postnatally, increases to plateau at 4-6 days of age Follow blood pressures for trending ...
Chapt05 Lecture 13ed Pt 1
... 3. Exchange of nutrients and wastes at the ______________ 4. Regulate _________ as needed ...
... 3. Exchange of nutrients and wastes at the ______________ 4. Regulate _________ as needed ...
C7 Jeopardy (2) - HonorsBiology2015-16
... plug. They release a substance the form prothrombin actavator which in the presence of Ca cause plasma protrombin to thrombin. Thrombin acts as an enzyme to convert soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin. Fibrin forms a network of threads to trap platelets and form a scab. ...
... plug. They release a substance the form prothrombin actavator which in the presence of Ca cause plasma protrombin to thrombin. Thrombin acts as an enzyme to convert soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin. Fibrin forms a network of threads to trap platelets and form a scab. ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Lab
... underlies the visceral pericardium. How can you tell which side of the heart is the ventral surface? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. The line running diagonally down from ...
... underlies the visceral pericardium. How can you tell which side of the heart is the ventral surface? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. The line running diagonally down from ...
The cardiac cycle
... Introduction It is important that the chambers of the heart contract in a coordinated fashion. The sequence of events involved in one heartbeat is called the cardiac cycle. ...
... Introduction It is important that the chambers of the heart contract in a coordinated fashion. The sequence of events involved in one heartbeat is called the cardiac cycle. ...
Unit 9
... Explain the differences between arteries, veins, and capillaries: Arteries – carry blood away from the heart Veins – carry blood toward the heart Capillaries – microscopic vessels where oxygen and nutrient exchange takes place ...
... Explain the differences between arteries, veins, and capillaries: Arteries – carry blood away from the heart Veins – carry blood toward the heart Capillaries – microscopic vessels where oxygen and nutrient exchange takes place ...
lab.2. fall 11
... Observe prepared slides of blood smears taken from patients with the following disorders: pernicious anemia ...
... Observe prepared slides of blood smears taken from patients with the following disorders: pernicious anemia ...
File
... Why does the heart need valves in it? Grade D Where does each side of the heart pump blood? Grade D Why is the left side of the heart thicker than the right side? Grade C Why does the heart need it’s own blood supply if it is full of blood all day? Grade B What would happen if that blood supply was ...
... Why does the heart need valves in it? Grade D Where does each side of the heart pump blood? Grade D Why is the left side of the heart thicker than the right side? Grade C Why does the heart need it’s own blood supply if it is full of blood all day? Grade B What would happen if that blood supply was ...
Review: Blood Flow Through the Heart, Pulmonary, and
... • Changes in blood pressure may affect both stroke volume and heart rate. – Shock occurs when the blood pressure drops substantially. – Animals in shock have rapid, weak pulses. – Because of reduced blood pressure, there is less filling of the heart, the ventricles are not completely full, so strok ...
... • Changes in blood pressure may affect both stroke volume and heart rate. – Shock occurs when the blood pressure drops substantially. – Animals in shock have rapid, weak pulses. – Because of reduced blood pressure, there is less filling of the heart, the ventricles are not completely full, so strok ...
TEXTBOOK PAGES 582-589 Q`S 1
... vessel that contains valves •Carries blood TO the heart •Is a thick blood vessel •Carries blood AWAY from the heart ...
... vessel that contains valves •Carries blood TO the heart •Is a thick blood vessel •Carries blood AWAY from the heart ...
Cardiovascular System
... and relayed throughout the ventricular myocardium. Atrial contraction is completed, and ventricular contraction begins. Elapsed time = 225 msec ...
... and relayed throughout the ventricular myocardium. Atrial contraction is completed, and ventricular contraction begins. Elapsed time = 225 msec ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.























