Cardiovascular System
... • A-V valves closing Dupp • second heart sound • occurs during ventricular diastole • pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves closing Murmur – abnormal heart sound ...
... • A-V valves closing Dupp • second heart sound • occurs during ventricular diastole • pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves closing Murmur – abnormal heart sound ...
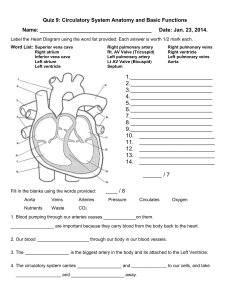
Quiz 9: Circulatory System Anatomy and Basic Functions
... _________________ are important because they carry blood from the body back to the heart. 2. Our blood __________________ through our body in our blood vessels. 3. The _______________ is the biggest artery in the body and its attached to the Left Ventricle. 4. The circulatory system carries ________ ...
... _________________ are important because they carry blood from the body back to the heart. 2. Our blood __________________ through our body in our blood vessels. 3. The _______________ is the biggest artery in the body and its attached to the Left Ventricle. 4. The circulatory system carries ________ ...
the Cardiovascular System
... in and which end do substances move out? 381 What causes varicose veins? 383 ...
... in and which end do substances move out? 381 What causes varicose veins? 383 ...
Coronary CT Angiography
... the confirmation, it should be evaluated at least in 2 other percentages. ...
... the confirmation, it should be evaluated at least in 2 other percentages. ...
Circulatory systems
... • May also be influenced by diet • Contributes to atherosclerosis • “Silent killer”, few outward signs ...
... • May also be influenced by diet • Contributes to atherosclerosis • “Silent killer”, few outward signs ...
The Annals of Thoracic Surgery Highlights Landmark Cardiothoracic
... described 30-year outcomes in patients who underwent the first open-heart repairs for congenital heart defects through the use of cross-circulation between parent and patient. Cross-circulation was pioneered by Dr. Lillehei and was used very early in open heart surgery. Blood flow was routed from th ...
... described 30-year outcomes in patients who underwent the first open-heart repairs for congenital heart defects through the use of cross-circulation between parent and patient. Cross-circulation was pioneered by Dr. Lillehei and was used very early in open heart surgery. Blood flow was routed from th ...
LBBB - EDExam
... Additional features frequently seen in LBBB include: 1) The QRS complexes in some leads may be notched (leads I, aVL, V5 and V6). 2) The QRS complexes in V5, V6, I and aVL tend to have rsR’, "M" pattern or broad monophasic R waves. 3) Secondary ST depression and possibly T wave inversion may be seen ...
... Additional features frequently seen in LBBB include: 1) The QRS complexes in some leads may be notched (leads I, aVL, V5 and V6). 2) The QRS complexes in V5, V6, I and aVL tend to have rsR’, "M" pattern or broad monophasic R waves. 3) Secondary ST depression and possibly T wave inversion may be seen ...
Principles of cardiovascular measurement I and II
... – Antecubital vein vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery – Brachial/femoral artery aorta, left, ventricle, left atrium ...
... – Antecubital vein vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery – Brachial/femoral artery aorta, left, ventricle, left atrium ...
Heart Dissection
... If the pericardial sac is still intact, slit open the pericardium and remove it from the heart. Observe the visceral pericardium (epicardium). Using a sharp probe, carefully prick a little of this serous membrane away from the myocardium. How does the visceral pericardium differ from that of the par ...
... If the pericardial sac is still intact, slit open the pericardium and remove it from the heart. Observe the visceral pericardium (epicardium). Using a sharp probe, carefully prick a little of this serous membrane away from the myocardium. How does the visceral pericardium differ from that of the par ...
Circulation and Heart Structures
... into the aorta, the largest artery in your body. The aorta branches off into smaller arteries, taking blood to all parts of your body. ...
... into the aorta, the largest artery in your body. The aorta branches off into smaller arteries, taking blood to all parts of your body. ...
Turn in Cardiovascular Worksheet in blue basket. get out blood
... Should a reaction occur, you would normally experience symptoms within a few minutes of receiving a transfusion. These may include: a strong feeling that something bad is about to happen fever and chills ...
... Should a reaction occur, you would normally experience symptoms within a few minutes of receiving a transfusion. These may include: a strong feeling that something bad is about to happen fever and chills ...
Cardiovascular System - Pupils Copy
... Oxygenated and Deoxygenated blood • When the blood leaves the lungs it is ...
... Oxygenated and Deoxygenated blood • When the blood leaves the lungs it is ...
Cardiovascular System
... heart a reddish-blue color to be oxygenated again (Systemic Circulation) ...
... heart a reddish-blue color to be oxygenated again (Systemic Circulation) ...
Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
... • The force exerted by the blood on the walls of the arteries (and veins) as the blood is pumped around the circulation. • Measured in units of mmHg. • Most common methods of measuring BP is by ascultation (listening for sounds). ...
... • The force exerted by the blood on the walls of the arteries (and veins) as the blood is pumped around the circulation. • Measured in units of mmHg. • Most common methods of measuring BP is by ascultation (listening for sounds). ...
1. Describe the cardiac conduction system and an ECG. Tell how an
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
Valve Disease - Dr Diana Holdright
... through the valve; and leakage, such that the blood expelled leaks back across the valve making the heart pump inefficiently. Some patients will have a mixture of the two. Valve disease can be congenital, meaning that a patient is born with an abnormal valve, or acquired, developing in later life. I ...
... through the valve; and leakage, such that the blood expelled leaks back across the valve making the heart pump inefficiently. Some patients will have a mixture of the two. Valve disease can be congenital, meaning that a patient is born with an abnormal valve, or acquired, developing in later life. I ...
Congestive Heart Failure
... Air: rapid depressurization causes gas to bubble out of solution; these bubbles block blood vessels causing infarction in muscles, brain, and other organs ...
... Air: rapid depressurization causes gas to bubble out of solution; these bubbles block blood vessels causing infarction in muscles, brain, and other organs ...
Cardiac SPECT - Atlantic General Hospital
... A cardiac SPECT is done to examine the blood flow through the coronary arteries. In addition, a cardiac SPECT can evaluate heart muscle function as well as identify any scarring of the cardiac tissue. Blood flow through coronary arteries is typically adequate during a state of rest. When the body is ...
... A cardiac SPECT is done to examine the blood flow through the coronary arteries. In addition, a cardiac SPECT can evaluate heart muscle function as well as identify any scarring of the cardiac tissue. Blood flow through coronary arteries is typically adequate during a state of rest. When the body is ...
Circulatory System
... Many of these chemicals are also found in consumer products, but these products have warning labels. While the public is warned about the danger of the poisons in these products, there is no such warning for the toxins in tobacco smoke. Here are a few of the chemicals in tobacco smoke, and other ...
... Many of these chemicals are also found in consumer products, but these products have warning labels. While the public is warned about the danger of the poisons in these products, there is no such warning for the toxins in tobacco smoke. Here are a few of the chemicals in tobacco smoke, and other ...
Heart Dynamics
... (d) Ventricular systole— second phase: As ventricular pressure rises and exceeds pressure in the arteries, the semilunar valves open and blood is ejected. ...
... (d) Ventricular systole— second phase: As ventricular pressure rises and exceeds pressure in the arteries, the semilunar valves open and blood is ejected. ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.