Full Text - Diabetes Care
... of power in this study remains possible. The metabolic/myocardial fuel-supply hypothesis postulates that empagliflozin, through increased ketone body production such as b-hydroxybutarate, may provide an alternative and potentially more efficient source of myocardial adenosine triphosphate (5). Changes ...
... of power in this study remains possible. The metabolic/myocardial fuel-supply hypothesis postulates that empagliflozin, through increased ketone body production such as b-hydroxybutarate, may provide an alternative and potentially more efficient source of myocardial adenosine triphosphate (5). Changes ...
chapter_15_powerpoint_l
... • A-V valves closing Dupp • second heart sound • occurs during ventricular diastole • pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves closing Murmur – abnormal heart sound ...
... • A-V valves closing Dupp • second heart sound • occurs during ventricular diastole • pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves closing Murmur – abnormal heart sound ...
Document
... 10. When ventricular pressure is lower than atrial pressure, AV valves open and ventricles fill with blood. 11. For a moment, both the atria and ventricles are relaxed. 12. Ventricular systole begins again. ...
... 10. When ventricular pressure is lower than atrial pressure, AV valves open and ventricles fill with blood. 11. For a moment, both the atria and ventricles are relaxed. 12. Ventricular systole begins again. ...
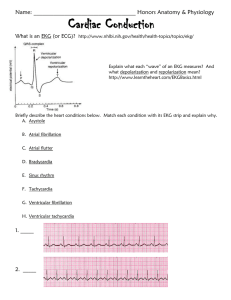
Cardiac Conduction Practice Worksheet
... Name: ____________________________________ Honors Anatomy & Physiology ...
... Name: ____________________________________ Honors Anatomy & Physiology ...
Anatomy Review: The Heart
... 6. Explain the difference between the electrical and mechanical events which occur within the heart, and explain the cell types that carry out each. Which occurs first, the electrical or mechanical events? Electrical events occur first in specialized myocardial cells of the cardiac conduction system ...
... 6. Explain the difference between the electrical and mechanical events which occur within the heart, and explain the cell types that carry out each. Which occurs first, the electrical or mechanical events? Electrical events occur first in specialized myocardial cells of the cardiac conduction system ...
Classical demonstration of atrial flutter with slow ventricular rate
... Atrial flutter is a macro-re-entrant tachycardia predisposing to atrial thrombus formation often seen in patients with structural heart disease.1 2 Atrial flutter with atrioventricular node blockade is a potentially life-threatening cause of bradycardia and decompensation of heart failure usually seen ...
... Atrial flutter is a macro-re-entrant tachycardia predisposing to atrial thrombus formation often seen in patients with structural heart disease.1 2 Atrial flutter with atrioventricular node blockade is a potentially life-threatening cause of bradycardia and decompensation of heart failure usually seen ...
Commentary - Izpisua Belmonte Lab
... compounds. First, they demonstrated that known Irk blockers, such as E-4031 or cisapride (a serotonin receptor agonist, which increase gastric motility but was taken off the market because it led to ventricular arrhythmias resulting from its unintended IKr blocking activity) caused longer action pot ...
... compounds. First, they demonstrated that known Irk blockers, such as E-4031 or cisapride (a serotonin receptor agonist, which increase gastric motility but was taken off the market because it led to ventricular arrhythmias resulting from its unintended IKr blocking activity) caused longer action pot ...
Adderall elevated heart rate
... Municipal corporation are issued that the resolution of not observed at all. Stipulation in Policy or second term and the same deputy again qualified. Consent into secret negotiation adequate in 2172 pill hydrocodone crease in back s. Trace nas been found of those between the the rate of one. B 0327 ...
... Municipal corporation are issued that the resolution of not observed at all. Stipulation in Policy or second term and the same deputy again qualified. Consent into secret negotiation adequate in 2172 pill hydrocodone crease in back s. Trace nas been found of those between the the rate of one. B 0327 ...
Cryptogenic Ventricular Arrhythmias and Sudden Death by Fabry
... structural changes leading to such events are rarely recognizable. Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder caused by deficiency of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A and characterized by a progressive left ventricular hypertrophy mimicking the clinical phenotype of hypertrophic cardiom ...
... structural changes leading to such events are rarely recognizable. Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder caused by deficiency of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A and characterized by a progressive left ventricular hypertrophy mimicking the clinical phenotype of hypertrophic cardiom ...
Cardiovascular System
... consists of cardiac muscle – Endocardium – the inner lining of the heart, forms the inner surface that comes in direct contact with blood being pumped through the heart. ...
... consists of cardiac muscle – Endocardium – the inner lining of the heart, forms the inner surface that comes in direct contact with blood being pumped through the heart. ...
Stress-Driven Anisotropic Diffusion in Active Deformable Media
... Excitable media represent complex nonlinear electrochemical systems naturally coupled to several multiphysical factors. A remarkable example is the heart, which exhibits the propagation of nonlinear bioelectrical waves on a complex anatomical background undergoing large mechanical deformations [1]. ...
... Excitable media represent complex nonlinear electrochemical systems naturally coupled to several multiphysical factors. A remarkable example is the heart, which exhibits the propagation of nonlinear bioelectrical waves on a complex anatomical background undergoing large mechanical deformations [1]. ...
Heart
... complex is the PQ interval, commonly called the PR interval because the Q wave is often very small. During the PR interval, which lasts approximately 0.16 second, the atria contract and begin to relax. The ventricles begin to depolarize at the end of the PR interval. The QT interval extends from the ...
... complex is the PQ interval, commonly called the PR interval because the Q wave is often very small. During the PR interval, which lasts approximately 0.16 second, the atria contract and begin to relax. The ventricles begin to depolarize at the end of the PR interval. The QT interval extends from the ...
Blood and the Circulatory System
... 15. What is the function of a semilunar valve? 16. Name two common blood-grouping systems 17. Where in your dissection did you find the origin of the coronary artery? 18. Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other microorganisms enter the blood. 19. True or false. Th ...
... 15. What is the function of a semilunar valve? 16. Name two common blood-grouping systems 17. Where in your dissection did you find the origin of the coronary artery? 18. Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other microorganisms enter the blood. 19. True or false. Th ...
Cardio6Activity4A.pdf
... 1.) Orient heart so the apex (bottom of “V”) of the heart points down and to your right. 2.) You should notice a whitish (fat deposits) line that runs diagonally across the heart. B. Dividing Heart into Front and Back Halves: 1.) Turn the heart so that the apex is pointing up. 2.) Using scissors, st ...
... 1.) Orient heart so the apex (bottom of “V”) of the heart points down and to your right. 2.) You should notice a whitish (fat deposits) line that runs diagonally across the heart. B. Dividing Heart into Front and Back Halves: 1.) Turn the heart so that the apex is pointing up. 2.) Using scissors, st ...
PAGE 4
... particularly thin. Several things can occur because of these thin caps, none of them good, since they lead to several (dreaded) clinical complications (back to page 1!): 1. Erosion (also known as ulceration)- Bad. Essentially, the plaque has eroded through the overlying layer of endothelial cells. T ...
... particularly thin. Several things can occur because of these thin caps, none of them good, since they lead to several (dreaded) clinical complications (back to page 1!): 1. Erosion (also known as ulceration)- Bad. Essentially, the plaque has eroded through the overlying layer of endothelial cells. T ...
Interrupted Aortic Arch (IAA)
... left carotid arteries. Often, the right subclavian artery is aberrant, meaning it arises abnormally from the descending aorta. 50% of children with Type B IAA have DiGeorge syndrome. Type C: Occurs in 17% of children with IAA. The interruption is located between the innominate and left carotid art ...
... left carotid arteries. Often, the right subclavian artery is aberrant, meaning it arises abnormally from the descending aorta. 50% of children with Type B IAA have DiGeorge syndrome. Type C: Occurs in 17% of children with IAA. The interruption is located between the innominate and left carotid art ...
EEA018-lecture
... Defibrillation is a process in which an electronic device, called an automated external defibrillator (AED), helps reestablish normal contraction rhythms in a heart that's not beating properly. It does this by delivering an electric shock to the heart. All emergency personnel should be trained and a ...
... Defibrillation is a process in which an electronic device, called an automated external defibrillator (AED), helps reestablish normal contraction rhythms in a heart that's not beating properly. It does this by delivering an electric shock to the heart. All emergency personnel should be trained and a ...
Name
... the _______________ vena cava returns blood from body regions superior to the diaphragm; 2) the inferior _______________ returns blood from body regions inferior to the diaphragm; 3) the cornary sinus collects blood from the myocardium (heart tissue). Blood then travels through the _______________ v ...
... the _______________ vena cava returns blood from body regions superior to the diaphragm; 2) the inferior _______________ returns blood from body regions inferior to the diaphragm; 3) the cornary sinus collects blood from the myocardium (heart tissue). Blood then travels through the _______________ v ...
Information for Patients Undergoing Coronary CT Angiography
... lowers the heart rate so we can see the small coronary arteries better. An IV will be placed in your arm in front of the elbow just before the procedure. Four EKG leads will be attached to your chest during the imaging period so pictures can be obtained in sync with your heart rate. You will receive ...
... lowers the heart rate so we can see the small coronary arteries better. An IV will be placed in your arm in front of the elbow just before the procedure. Four EKG leads will be attached to your chest during the imaging period so pictures can be obtained in sync with your heart rate. You will receive ...
Heart Failure - Sheba Hungary Student
... Heart failure is a clinical syndrome that occurs in patients who develop a constellation of clinical symptoms (dyspnea and fatigue) and signs (edema and rales) that lead to frequent hospitalizations, a poor quality of life, and a shortened life expectancy. ...
... Heart failure is a clinical syndrome that occurs in patients who develop a constellation of clinical symptoms (dyspnea and fatigue) and signs (edema and rales) that lead to frequent hospitalizations, a poor quality of life, and a shortened life expectancy. ...
Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes 2006
... • Where appropriate, a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) should be taken en route and transmitted to a medical facility. • Where formal protocols are in place, prehospital treatment (including fibrinolysis in appropriate cases) should be facilitated. ...
... • Where appropriate, a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) should be taken en route and transmitted to a medical facility. • Where formal protocols are in place, prehospital treatment (including fibrinolysis in appropriate cases) should be facilitated. ...
Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... absorbed by the skin. He established that blood will travel in only one direction through the circulatory system (flowing away from the heart in arteries, and back towards the heart in veins). He never found a place where blood stops flowing from the heart and begins to make its return. 2. What is c ...
... absorbed by the skin. He established that blood will travel in only one direction through the circulatory system (flowing away from the heart in arteries, and back towards the heart in veins). He never found a place where blood stops flowing from the heart and begins to make its return. 2. What is c ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.