Cardiac resynchronization was effective for moderate-to
... months with biventricular pacing. Limited information is available at present to predict the subset of patients with congestive heart failure and an intraventricular conduction delay who will benefit from resynchronization pacing therapy. Given the relatively low rate of short-term response to biven ...
... months with biventricular pacing. Limited information is available at present to predict the subset of patients with congestive heart failure and an intraventricular conduction delay who will benefit from resynchronization pacing therapy. Given the relatively low rate of short-term response to biven ...
Ch 11 Heart Anatomy and Circulation
... Oxygen-rich blood flows from the left side of the heart (via the aorta) to body tissues ...
... Oxygen-rich blood flows from the left side of the heart (via the aorta) to body tissues ...
Good Fats, Bad Fats
... 2. For the dressing, melt the butter over medium heat in a small pan. When it is melted, add shallots and cook until soft, about 3 minutes. 3. Add the wine and vinegar and bring to a boil, cooking until reduced ...
... 2. For the dressing, melt the butter over medium heat in a small pan. When it is melted, add shallots and cook until soft, about 3 minutes. 3. Add the wine and vinegar and bring to a boil, cooking until reduced ...
Pulmonary Valve - International Children`s Heart Fund
... To Shanghai Chest Hospital, for the opportunity to spend one year (July 2005- July 2006) in Shanghai, China on behalf of the World Heart Foundation to help initiate a model 6 year cardiothoracic residency program. This experience gained the editor insights into the daily needs of the international a ...
... To Shanghai Chest Hospital, for the opportunity to spend one year (July 2005- July 2006) in Shanghai, China on behalf of the World Heart Foundation to help initiate a model 6 year cardiothoracic residency program. This experience gained the editor insights into the daily needs of the international a ...
Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Fig. 3a Fig. 3c
... some cases, it may cause serious symptoms, and should therefore, be considered as a major complication of surgery. Often the radiologist is the first medical investigator confronted with – the complications of – a retained surgical sponge. The diagnosis of textiloma is usually made as a result of ra ...
... some cases, it may cause serious symptoms, and should therefore, be considered as a major complication of surgery. Often the radiologist is the first medical investigator confronted with – the complications of – a retained surgical sponge. The diagnosis of textiloma is usually made as a result of ra ...
Slide 1
... Aneurysm Aneurysm enlargement of the wall of an artery Most likely to occur in large blood vessels ...
... Aneurysm Aneurysm enlargement of the wall of an artery Most likely to occur in large blood vessels ...
4-Cardiac Arrhythmias
... is usually invisible.The QRS duration is usually normal, but occasionally, aberrancy increases the QRS duration, making differentiation from ventricular tachycardia difficult .the most common tachyarrhythmia seen in the pediatric age group.Patients with accessory pathways frequently have WPW preexci ...
... is usually invisible.The QRS duration is usually normal, but occasionally, aberrancy increases the QRS duration, making differentiation from ventricular tachycardia difficult .the most common tachyarrhythmia seen in the pediatric age group.Patients with accessory pathways frequently have WPW preexci ...
Basic concepts to Understand Basic concepts to Understand
... i ti b between t left l ft heart h t structure t t and d right i ht heart structure allowing blood flow (shunting) from the left heart to the right g heart • No obstruction to right heart blood flow • 2 well-formed ventricles ...
... i ti b between t left l ft heart h t structure t t and d right i ht heart structure allowing blood flow (shunting) from the left heart to the right g heart • No obstruction to right heart blood flow • 2 well-formed ventricles ...
Blood vessels - INAYA Medical College
... Both atria contract at the same time Followed by contraction of both ventricles together ...
... Both atria contract at the same time Followed by contraction of both ventricles together ...
St Elmo Veterinary Clinic
... Older animals, especially if they are arthritic, will really feel the cold and can be noticeably stiff. If they are already on medication, have a chat to us about increasing or altering their doses to make them more comfortable. If they are not on any treatment, this is often a good time to start. I ...
... Older animals, especially if they are arthritic, will really feel the cold and can be noticeably stiff. If they are already on medication, have a chat to us about increasing or altering their doses to make them more comfortable. If they are not on any treatment, this is often a good time to start. I ...
Lorna LVNC
... thought to represent a failure of this “compaction” process. There are several hypotheses proposed to explain the occurrence of LVHT: (1) it represents persistence of embryonal sinusoids and results from an arrest in the compaction process of the myocardium (Bellet & Gouley, 1932), (2) it might res ...
... thought to represent a failure of this “compaction” process. There are several hypotheses proposed to explain the occurrence of LVHT: (1) it represents persistence of embryonal sinusoids and results from an arrest in the compaction process of the myocardium (Bellet & Gouley, 1932), (2) it might res ...
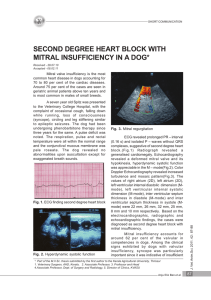
second degree heart block with mitral insufficiency in a dog
... turbulence and mosaic pattern(Fig.3). The values of right atrium (2D), left atrium (2D), left ventricular internal diastolic dimension (Mmode), left ventricular internal systolic dimension (M-mode), inter ventricular septum thickness in diastole (M-mode) and inter ventricular septum thickness in sys ...
... turbulence and mosaic pattern(Fig.3). The values of right atrium (2D), left atrium (2D), left ventricular internal diastolic dimension (Mmode), left ventricular internal systolic dimension (M-mode), inter ventricular septum thickness in diastole (M-mode) and inter ventricular septum thickness in sys ...
Cardiac Physiology and Chronobiology
... Third degree AV block, also known as complete heart block, condition when impulse generated in the sinus node does not propagate to the ventricles ...
... Third degree AV block, also known as complete heart block, condition when impulse generated in the sinus node does not propagate to the ventricles ...
Membranous Ventricular Septal Aneurysm
... Fig. 3 Cardiac computed tomographic 3-dimensional reconstruction, limited to the portions of the heart that contain iodinated contrast medium. The aneurysm (arrow) is seen arising from the membranous portion of the interventricular septum just beneath the right coronary sinus of Valsalva; the arter ...
... Fig. 3 Cardiac computed tomographic 3-dimensional reconstruction, limited to the portions of the heart that contain iodinated contrast medium. The aneurysm (arrow) is seen arising from the membranous portion of the interventricular septum just beneath the right coronary sinus of Valsalva; the arter ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... Parasympathetic nerve fibers which originate in the medulla pass to the heart in the vague nerve. These fibers release acetylcholine when stimulated and cause a reduction in the heart rate. There is some doubt whether sympathetic accelerator fibers are found in the frog, however in other verte ...
... Parasympathetic nerve fibers which originate in the medulla pass to the heart in the vague nerve. These fibers release acetylcholine when stimulated and cause a reduction in the heart rate. There is some doubt whether sympathetic accelerator fibers are found in the frog, however in other verte ...
Circulatory System
... arterial walls. Eating foods high in cholesterol and saturated fats can cause these deposits to form. This can occur in any artery of the body, but is especially serious in coronary arteries. Hypertension or high blood pressure is caused when blood pressure is higher than normal. Most of the time, e ...
... arterial walls. Eating foods high in cholesterol and saturated fats can cause these deposits to form. This can occur in any artery of the body, but is especially serious in coronary arteries. Hypertension or high blood pressure is caused when blood pressure is higher than normal. Most of the time, e ...
Medical Technology Bionics Experiments
... sources, plan, choose equipment or resources for, perform a first-hand investigation and analyse information about changes in the heartbeat rate before and after physical activity ...
... sources, plan, choose equipment or resources for, perform a first-hand investigation and analyse information about changes in the heartbeat rate before and after physical activity ...
Risk of heart failure following Hodgkin lymphoma
... M Anthracycline doses used currently are typically higher than the doses received by most patients in this study M Salvage therapy with anthracyclines after primary treatment with mediastinal radiotherapy appears to be less harmful than primary treatment with mediastinal radiotherapy and anthracycli ...
... M Anthracycline doses used currently are typically higher than the doses received by most patients in this study M Salvage therapy with anthracyclines after primary treatment with mediastinal radiotherapy appears to be less harmful than primary treatment with mediastinal radiotherapy and anthracycli ...
circulation - WordPress.com
... The heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs. In the human heart there is one atrium and one ventricle for each circulation, and with both a systemic and a pulmonary circulation there are four chambers in total: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium and right ...
... The heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs. In the human heart there is one atrium and one ventricle for each circulation, and with both a systemic and a pulmonary circulation there are four chambers in total: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium and right ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.