Unit # 5 Cardiovascular Disease
... – Can lead to hypertension, low HDL, type II diabetes Diabetes Mellitus: impaired ability of the blood to store glucose (sugar) ...
... – Can lead to hypertension, low HDL, type II diabetes Diabetes Mellitus: impaired ability of the blood to store glucose (sugar) ...
Management of cardiovascular system
... On completion of this chapter, the learner will be able to: 1. Define blood pressure and identify risk factors for hypertension. 2. Explain the difference between normal blood pressure and hypertension and discuss the significance of hypertension. 3. Describe the treatment approach for hypertension, ...
... On completion of this chapter, the learner will be able to: 1. Define blood pressure and identify risk factors for hypertension. 2. Explain the difference between normal blood pressure and hypertension and discuss the significance of hypertension. 3. Describe the treatment approach for hypertension, ...
PSYC7910_Appendix2
... Complications of Hypertension Myocardial ischemia Ventricular failure Pulmonary edema Aortic dissection Intracerebral hemorrhage ...
... Complications of Hypertension Myocardial ischemia Ventricular failure Pulmonary edema Aortic dissection Intracerebral hemorrhage ...
Slide 1
... Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): A Syndrome of Epidemic Proportions • Approximately 4.9 million cases in the United States today • Over 400,000 new cases per year • The most common cause of hospitalization in people over 65 years • Increasing numbers of CHF patients due to the aging population ...
... Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): A Syndrome of Epidemic Proportions • Approximately 4.9 million cases in the United States today • Over 400,000 new cases per year • The most common cause of hospitalization in people over 65 years • Increasing numbers of CHF patients due to the aging population ...
Review- Pathway of blood flow through the
... pressure – Diastolic (i.e. The pressure when the ventricles relax; heart is at rest) 4. Healthy = 120/80 (units = mmHg) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u6saTO8_o2g ...
... pressure – Diastolic (i.e. The pressure when the ventricles relax; heart is at rest) 4. Healthy = 120/80 (units = mmHg) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u6saTO8_o2g ...
Pressures Within the Heart Factsheet
... of the heart does not cause an increase in pressure. However, a large amount of blood will increase the pressure in the right side of the heart. This raises the pressure in the pulmonary arteries. Prolonged high pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension) can cause damage to their more delicate t ...
... of the heart does not cause an increase in pressure. However, a large amount of blood will increase the pressure in the right side of the heart. This raises the pressure in the pulmonary arteries. Prolonged high pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension) can cause damage to their more delicate t ...
HST_CRF_04_02_03.qxd
... 9. The right side of the heart pumps oxygen-poor blood to the a. body. c. right ventricle. b. lungs. d. left atrium. 10. The left side of the heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the a. body. c. right ventricle. b. lungs. d. left atrium. ...
... 9. The right side of the heart pumps oxygen-poor blood to the a. body. c. right ventricle. b. lungs. d. left atrium. 10. The left side of the heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the a. body. c. right ventricle. b. lungs. d. left atrium. ...
Alternatives to Nifedipine in the Oral Treatment of Hypertensive
... It is important to distinguish HU from true hypertensive emergencies which usually require IV therapy (with nitroprusside, nitroglycerin, labetalol, etc.) and hospitalization. The presence of acute or ongoing end organ damage constitutes a hypertensive emergency rather than a HU. Asymptomatic patien ...
... It is important to distinguish HU from true hypertensive emergencies which usually require IV therapy (with nitroprusside, nitroglycerin, labetalol, etc.) and hospitalization. The presence of acute or ongoing end organ damage constitutes a hypertensive emergency rather than a HU. Asymptomatic patien ...
The Heart - OnCourse
... 1. Increase both contractility and HR 2. influence peripheral resistance a. causes vasoconstriction in many vessels i. Epinephrine causes vasodialation in Skeletal Muscle ii) Venous control of BP and flow (1) Blood pressure decreases as it reaches the veins (a) Blood flow is not a direct result of h ...
... 1. Increase both contractility and HR 2. influence peripheral resistance a. causes vasoconstriction in many vessels i. Epinephrine causes vasodialation in Skeletal Muscle ii) Venous control of BP and flow (1) Blood pressure decreases as it reaches the veins (a) Blood flow is not a direct result of h ...
Arterial and venous blood pressures
... beverage within the last 15 minutes the readings will be altered. If they haven’t sat quietly for at least 5 minutes or are talking during the procedure, the readings will be altered. Systolic and diastolic BP's in hypertensive and normotensive patients increase with talking And if you have placed t ...
... beverage within the last 15 minutes the readings will be altered. If they haven’t sat quietly for at least 5 minutes or are talking during the procedure, the readings will be altered. Systolic and diastolic BP's in hypertensive and normotensive patients increase with talking And if you have placed t ...
Airgas template - Acupuncture and Massage College
... Assessing the PMI, or point of maximal impulse • Inspect the left anterior chest for a visible PMI • Using you fingerpads, palpate at the apex for the PMI • The PMI may be: – Tapping, or normal – Sustained — suggests LV hypertrophy from hypertension or aortic stenosis, or – Diffuse — suggests a di ...
... Assessing the PMI, or point of maximal impulse • Inspect the left anterior chest for a visible PMI • Using you fingerpads, palpate at the apex for the PMI • The PMI may be: – Tapping, or normal – Sustained — suggests LV hypertrophy from hypertension or aortic stenosis, or – Diffuse — suggests a di ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Aucun titre de diapositive
... a) Reduce afterload with a RAAS blocker (ie ARB or ACEi) • This helps treat symptoms of diastolic heart failure and achieve better control of blood pressure • Helps to raise his potassium • Reduces the chance of first episode of atrial fibrillation Expected results: BP 130/78, HR is 85, SAO2 96%, R ...
... a) Reduce afterload with a RAAS blocker (ie ARB or ACEi) • This helps treat symptoms of diastolic heart failure and achieve better control of blood pressure • Helps to raise his potassium • Reduces the chance of first episode of atrial fibrillation Expected results: BP 130/78, HR is 85, SAO2 96%, R ...
Cardiovascular Test ID # Directions: Read each section carefully
... answer, first refer to your notes and the book, then the Internet. Referring back to previous chapters and their notes may be beneficial as well. Please answer with COMPLETE sentences and correct spelling (if a word has the red marks from spellchecker, then double check to make sure you spelled it c ...
... answer, first refer to your notes and the book, then the Internet. Referring back to previous chapters and their notes may be beneficial as well. Please answer with COMPLETE sentences and correct spelling (if a word has the red marks from spellchecker, then double check to make sure you spelled it c ...
File - Lambeth academy sport
... disease. Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol!) levels and increases the tendency for blood to clot, which can lead to serious problems such as heart attacks or strokes! • Alcohol in moderation is believed to increase HDL and so in the long term can help lower blood pressure. However, to ...
... disease. Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol!) levels and increases the tendency for blood to clot, which can lead to serious problems such as heart attacks or strokes! • Alcohol in moderation is believed to increase HDL and so in the long term can help lower blood pressure. However, to ...
The Circulatory System
... The circulatory system is divided into 3 sections: a. coronary circulation b. pulmonary circulation c. systemic circulation ...
... The circulatory system is divided into 3 sections: a. coronary circulation b. pulmonary circulation c. systemic circulation ...
Figure 19.4E Gross anatomy of the heart
... • Between atria and ventricle-open when pressure increases due to a lot of blood in atria • Below ventricle-opens when ventricle contracts, pushing blood out through valve. • Slamming shut makes your heart beat. • What is a pulse? ...
... • Between atria and ventricle-open when pressure increases due to a lot of blood in atria • Below ventricle-opens when ventricle contracts, pushing blood out through valve. • Slamming shut makes your heart beat. • What is a pulse? ...
Lesson 6. Cardiovascular Diseases - Blyth-Biology11
... – CPR: 30 two-handed, rapid, deep-chested, firm compressions – Follow with head-tilt, chin-lift + two mouth-to-mouth breaths – And repeat... ...
... – CPR: 30 two-handed, rapid, deep-chested, firm compressions – Follow with head-tilt, chin-lift + two mouth-to-mouth breaths – And repeat... ...
File the circulatory system
... The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC VII) uses the following guidelines to define HTN in adults: (Brashers, 2006, Category Systolic Diastolic p.1) Normal Pre-hypertension ...
... The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC VII) uses the following guidelines to define HTN in adults: (Brashers, 2006, Category Systolic Diastolic p.1) Normal Pre-hypertension ...
Chapter 14
... to an increase or decrease of blood pressure to keep the blood flow within the blood vessel constant • The smooth muscle of the blood vessels reacts to the stretching of the muscle by opening ion channels, which cause the muscle to depolarize, leading to muscle contraction. This significantly reduce ...
... to an increase or decrease of blood pressure to keep the blood flow within the blood vessel constant • The smooth muscle of the blood vessels reacts to the stretching of the muscle by opening ion channels, which cause the muscle to depolarize, leading to muscle contraction. This significantly reduce ...
How to strengthen your heart muscle (failing heart)? Daniel Pella, MD, PhD.
... ACE-inhibitors (IA) ...
... ACE-inhibitors (IA) ...
Circulatory - Bishop Ireton High School
... Blood pressure Force exerted on arteries as ventricles contract Measured with sphyngmometer Normal blood pressure for an adult: ...
... Blood pressure Force exerted on arteries as ventricles contract Measured with sphyngmometer Normal blood pressure for an adult: ...
10. (StI-FIZO) PHYSIOLOGY I
... complex regulatory mechanisms homeostatskih parameters of functional systems. Introduction to the complex nervous and humoral regulatory mechanisms of various functional systems. Students should master the general principles and rules of conduct in the laboratory. Students should become familiar wit ...
... complex regulatory mechanisms homeostatskih parameters of functional systems. Introduction to the complex nervous and humoral regulatory mechanisms of various functional systems. Students should master the general principles and rules of conduct in the laboratory. Students should become familiar wit ...
Supplemental Table 1
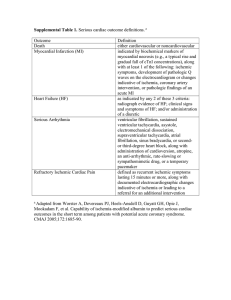
... indicated by biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis (e.g., a typical rise and gradual fall of cTnI concentrations), along with at least 1 of the following: ischemic symptoms, development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram or changes indicative of ischemia, coronary artery interventio ...
... indicated by biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis (e.g., a typical rise and gradual fall of cTnI concentrations), along with at least 1 of the following: ischemic symptoms, development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram or changes indicative of ischemia, coronary artery interventio ...
Antihypertensive drug

Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used drugs are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental goal of treatment should be the prevention of the important endpoints of hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke and heart failure. Patient age, associated clinical conditions and end-organ damage also play a part in determining dosage and type of medication administered. The several classes of antihypertensives differ in side effect profiles, ability to prevent endpoints, and cost. The choice of more expensive agents, where cheaper ones would be equally effective, may have negative impacts on national healthcare budgets. As of 2009, the best available evidence favors the thiazide diuretics as the first-line treatment of choice for high blood pressure when drugs are necessary. Although clinical evidence shows calcium channel blockers and thiazide-type diuretics are preferred first-line treatments for most people (from both efficacy and cost points of view), an ACE inhibitor is recommended by NICE in the UK for those under 55 years old.