B3_2_transporting_ma..
... 31. Blood vessel which carries blood to the heart. It usually carries deoxygenated blood and has valves to prevent the backflow of blood. 32. The smallest blood vessels which run between individual cells. They have a wall that is only one cell thick. Down 1. The system by which blood is pumped aroun ...
... 31. Blood vessel which carries blood to the heart. It usually carries deoxygenated blood and has valves to prevent the backflow of blood. 32. The smallest blood vessels which run between individual cells. They have a wall that is only one cell thick. Down 1. The system by which blood is pumped aroun ...
Heart
... from the friction on blood from b.v. walls (expansion or dilation of b.v. changes resistance) 4. Viscosity = ease w/which blood flows (an incr. of RBCs incr. viscosity; anemia or hemorrhage decr. it) ...
... from the friction on blood from b.v. walls (expansion or dilation of b.v. changes resistance) 4. Viscosity = ease w/which blood flows (an incr. of RBCs incr. viscosity; anemia or hemorrhage decr. it) ...
The Circulatory System
... attached to the haemoglobin molecules in the red blood cells. It is bright red because the attached oxygen makes the normally blue haemoglobin molecules turn red. • Deoxygenated blood: When blood has delivered oxygen to the cells, it is described as deoxygenated. It now looks a very dark red because ...
... attached to the haemoglobin molecules in the red blood cells. It is bright red because the attached oxygen makes the normally blue haemoglobin molecules turn red. • Deoxygenated blood: When blood has delivered oxygen to the cells, it is described as deoxygenated. It now looks a very dark red because ...
Donor
... S3 = Rarely, there may be a third heart sound. It occurs just after S2 and is lower in pitch than S1 or S2 as it is not of valvular origin. The third heart sound is normal in youth and some trained athletes, but if it re-emerges later in life it may ...
... S3 = Rarely, there may be a third heart sound. It occurs just after S2 and is lower in pitch than S1 or S2 as it is not of valvular origin. The third heart sound is normal in youth and some trained athletes, but if it re-emerges later in life it may ...
E - Bio @ Horton AP Biology
... a. Blood is a circulatory fluid contained within blood vessels b. Hemolymph is a circulatory fluid which flows into the sinus of certain arthropods and mollusks; it is a mixture of blood and intercellular fluid. 2. Certain arthropods and mollusks have an open circulatory system. a. Hemolymph is pump ...
... a. Blood is a circulatory fluid contained within blood vessels b. Hemolymph is a circulatory fluid which flows into the sinus of certain arthropods and mollusks; it is a mixture of blood and intercellular fluid. 2. Certain arthropods and mollusks have an open circulatory system. a. Hemolymph is pump ...
Ppts/hemodynamics dental 2009
... In response, vascular smooth muscle contracts and T returns to normal ...
... In response, vascular smooth muscle contracts and T returns to normal ...
Cardiovascular System
... Carry blood low in oxygen back to the heart? Have higher BP and thick walls, high in oxygen? Are one cell thick ? ...
... Carry blood low in oxygen back to the heart? Have higher BP and thick walls, high in oxygen? Are one cell thick ? ...
Understanding How Your Heart Works
... What can I do? You should change any unhealthy habits (also called risk factors) that helped to create your heart problems in the first place. Some risk factors are smoking, eating too much fat, not getting enough exercise, high blood pressure, diabetes, and stress. Making changes to reduce risk fac ...
... What can I do? You should change any unhealthy habits (also called risk factors) that helped to create your heart problems in the first place. Some risk factors are smoking, eating too much fat, not getting enough exercise, high blood pressure, diabetes, and stress. Making changes to reduce risk fac ...
Interactive Tutorial Worksheet
... cholesterol and saturated fats, getting regular cardiovascular exercise, and managing stress are good ways to avoid heart attacks, strokes and high blood pressure. For someone suddenly experiencing a cardiovascular emergency, surgery can be performed, medication can be prescribed by a doctor, and ...
... cholesterol and saturated fats, getting regular cardiovascular exercise, and managing stress are good ways to avoid heart attacks, strokes and high blood pressure. For someone suddenly experiencing a cardiovascular emergency, surgery can be performed, medication can be prescribed by a doctor, and ...
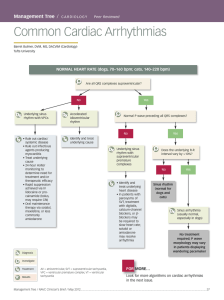
Common Cardiac Arrhythmias
... determine need for treatment and/or therapeutic efficacy • Rapid suppression achieved via IV lidocaine or procainamide (bolus, may require CRI) • Oral maintenance therapy via sotalol, mexiletine, or less commonly amiodarone ...
... determine need for treatment and/or therapeutic efficacy • Rapid suppression achieved via IV lidocaine or procainamide (bolus, may require CRI) • Oral maintenance therapy via sotalol, mexiletine, or less commonly amiodarone ...
Cardiovascular Drugs
... the brain stem. This action results in reduced sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system and in decreased in peripheral resistance, renal vascular resistance, heart rate and blood pressure ...
... the brain stem. This action results in reduced sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system and in decreased in peripheral resistance, renal vascular resistance, heart rate and blood pressure ...
File
... 1. The cuff is inflated until it stops blood flow 2. The cuff is allowed to deflate gradually until the pressure in the artery is greater than the pressure in the cuff. The blood starts to flow( detected by a pulse) at systolic pressure 3. More air is released from the cuff until no pulse detected – ...
... 1. The cuff is inflated until it stops blood flow 2. The cuff is allowed to deflate gradually until the pressure in the artery is greater than the pressure in the cuff. The blood starts to flow( detected by a pulse) at systolic pressure 3. More air is released from the cuff until no pulse detected – ...
Acupuncture, Intention and Emotional Release Techniques
... Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic pain and is therefore a reasonable referral option. Significant differences between true and sham acupuncture indicate that acupuncture is more than a placebo. ...
... Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic pain and is therefore a reasonable referral option. Significant differences between true and sham acupuncture indicate that acupuncture is more than a placebo. ...
High Blood Pressure in Children
... If your child doesn't have high blood pressure but is likely to develop it, these changes can also be used to help prevent high blood pressure. If your child is likely to develop high blood pressure, you may be able to prevent it by being sure that your child eats a healthy diet, is active, and stay ...
... If your child doesn't have high blood pressure but is likely to develop it, these changes can also be used to help prevent high blood pressure. If your child is likely to develop high blood pressure, you may be able to prevent it by being sure that your child eats a healthy diet, is active, and stay ...
The Cardiovascular System
... • Neural factors – Autonomic nervous system adjustments (sympathetic division) ...
... • Neural factors – Autonomic nervous system adjustments (sympathetic division) ...
Cardiovascular Physiology - San Diego Miramar College
... What would this do to SV if Q remains constant? This answer is a result of Starling’s Law that states ⇑EDV = ⇑ SV SV ⇑ with training, so what happens to exercising HR at a particular intensity (10 min. mile) as one becomes more trained? ...
... What would this do to SV if Q remains constant? This answer is a result of Starling’s Law that states ⇑EDV = ⇑ SV SV ⇑ with training, so what happens to exercising HR at a particular intensity (10 min. mile) as one becomes more trained? ...
Chapter 37 Circulatory System Respiratory System
... enclosed in protective tissue called pericardium Contractions pump blood through the C. S. average 72 times/min The heart has its own blood supply through the coronary arteries bark scorpion venom Heart is divided in the middle by the septum ...
... enclosed in protective tissue called pericardium Contractions pump blood through the C. S. average 72 times/min The heart has its own blood supply through the coronary arteries bark scorpion venom Heart is divided in the middle by the septum ...
File
... blood through the heart Some terms and functions ventricles – pump blood through the body or to the lungs atria – pump blood to the ventricles valves – prevent blood from going the wrong direction (backflow) arteries – carry blood away from the heart (the aorta is the main artery) veins – carry bloo ...
... blood through the heart Some terms and functions ventricles – pump blood through the body or to the lungs atria – pump blood to the ventricles valves – prevent blood from going the wrong direction (backflow) arteries – carry blood away from the heart (the aorta is the main artery) veins – carry bloo ...
Antihypertensive drug

Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used drugs are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental goal of treatment should be the prevention of the important endpoints of hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke and heart failure. Patient age, associated clinical conditions and end-organ damage also play a part in determining dosage and type of medication administered. The several classes of antihypertensives differ in side effect profiles, ability to prevent endpoints, and cost. The choice of more expensive agents, where cheaper ones would be equally effective, may have negative impacts on national healthcare budgets. As of 2009, the best available evidence favors the thiazide diuretics as the first-line treatment of choice for high blood pressure when drugs are necessary. Although clinical evidence shows calcium channel blockers and thiazide-type diuretics are preferred first-line treatments for most people (from both efficacy and cost points of view), an ACE inhibitor is recommended by NICE in the UK for those under 55 years old.