Pathophysiology of Right Heart Failure
... tending to drive fluid out of the vasculature. Decreasing right heart function, the haemostatic pressure will ultimately exceed the forces tending to retain fluid in the vasculature colloid osmotic pressure resistance provided by the basement membrane the lymphatic drainage oedema in the tissues ...
... tending to drive fluid out of the vasculature. Decreasing right heart function, the haemostatic pressure will ultimately exceed the forces tending to retain fluid in the vasculature colloid osmotic pressure resistance provided by the basement membrane the lymphatic drainage oedema in the tissues ...
Interventional Cardiology
... RAS blockers [11] . There is evidence from prospective studies that ACE inhibitors can be safely started in hypertensive patients with mild or moderate AS and preserved LV function [17] . If they are well tolerated, these drugs do not need to be stopped despite progression to severe AS [18] . Noneth ...
... RAS blockers [11] . There is evidence from prospective studies that ACE inhibitors can be safely started in hypertensive patients with mild or moderate AS and preserved LV function [17] . If they are well tolerated, these drugs do not need to be stopped despite progression to severe AS [18] . Noneth ...
Management of Patients Post MI - STA HealthCare Communications
... (Table 1).1 Although extensive clinical investigation has demonstrated the benefit of medical therapy, it appears significant gaps between proven therapy and actual care remain. A multifaceted approach that is individualized to each patient, therefore, is required. The goal of post ST-AMI management ...
... (Table 1).1 Although extensive clinical investigation has demonstrated the benefit of medical therapy, it appears significant gaps between proven therapy and actual care remain. A multifaceted approach that is individualized to each patient, therefore, is required. The goal of post ST-AMI management ...
H 5 - The transport system - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... heart disease than premenopausal women because they have less estrogen, as estrogen protects against heart disease smoking – nicotine causes vasoconstriction of blood vessels, increases blood pressure, heart-rate & decreases oxygenation of heart muscle ...
... heart disease than premenopausal women because they have less estrogen, as estrogen protects against heart disease smoking – nicotine causes vasoconstriction of blood vessels, increases blood pressure, heart-rate & decreases oxygenation of heart muscle ...
Qualitative Abstract Structure
... Heart failure affects nearly 6-million Americans and is associated with frequent and costly acute care hospitalizations. Although current guidelines emphasize the importance of implementing systems to coordinate and deliver effective care, hospital readmission rates in the heart failure population h ...
... Heart failure affects nearly 6-million Americans and is associated with frequent and costly acute care hospitalizations. Although current guidelines emphasize the importance of implementing systems to coordinate and deliver effective care, hospital readmission rates in the heart failure population h ...
left ventricle
... Explain that specialised tissues in the heart produce an electrical signal that stimulates rhythmic contractions of the ...
... Explain that specialised tissues in the heart produce an electrical signal that stimulates rhythmic contractions of the ...
Lab 2: Blood Pressure
... increase blood pressure. When blood pressure is too high, the aortic arch and carotid artery baroreceptors signal the medulla’s cardiac center to respond by stimulating a parasympathetic decrease in heart rate, which decreases blood pressure. Blood pressure can decrease, momentarily, as a result of ...
... increase blood pressure. When blood pressure is too high, the aortic arch and carotid artery baroreceptors signal the medulla’s cardiac center to respond by stimulating a parasympathetic decrease in heart rate, which decreases blood pressure. Blood pressure can decrease, momentarily, as a result of ...
Chapter 12: The Circulatory System
... * Blood from the left ventricle is then directed into aorta by aortic valve (open during ventricular systole). The mitral valve is close at this time so that left atrium may collect blood from pulmonary veins. * The aorta has three parts: Ascending part, Arch, and Descending part. * The ascending pa ...
... * Blood from the left ventricle is then directed into aorta by aortic valve (open during ventricular systole). The mitral valve is close at this time so that left atrium may collect blood from pulmonary veins. * The aorta has three parts: Ascending part, Arch, and Descending part. * The ascending pa ...
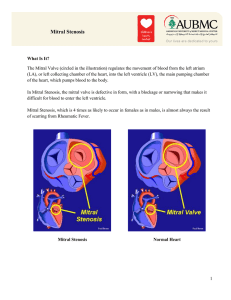
Mitral Stenosis
... The symptoms of Mitral Stenosis may be absent or very slight for long periods. However, they may gradually or suddenly worsen. If the blockage of the valve becomes severe, the left atrium will be unable to do its job adequately, blood will back up into the lungs and body tissues, and heart failure m ...
... The symptoms of Mitral Stenosis may be absent or very slight for long periods. However, they may gradually or suddenly worsen. If the blockage of the valve becomes severe, the left atrium will be unable to do its job adequately, blood will back up into the lungs and body tissues, and heart failure m ...
Circulatory System
... material (plaque) along the walls of arteries. – This fatty material thickens, hardens (forms calcium deposits), and may eventually block the arteries. – Slows down or stops blood flow; leads to chest pain (angina) or heart attack. – Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. The two terms are o ...
... material (plaque) along the walls of arteries. – This fatty material thickens, hardens (forms calcium deposits), and may eventually block the arteries. – Slows down or stops blood flow; leads to chest pain (angina) or heart attack. – Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. The two terms are o ...
Knepp, M.M. - University of Mount Union
... Higher Depression group students: had lower right frontal activity based on a neuropsychological assessment test reported more comparisons to others on their body shape, eating and exercise habits reported less moderate and strenuous exercise ...
... Higher Depression group students: had lower right frontal activity based on a neuropsychological assessment test reported more comparisons to others on their body shape, eating and exercise habits reported less moderate and strenuous exercise ...
association of hyperhomocystinemia with acute myocardial
... homocysteine induce sustained injury of arterial endothelial cells, proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells and enhance expression/activity of key participants in vascular inflammation, atherogenesis, and vulnerability of the established atherosclerotic plaque. In fact, the effect of elevated ...
... homocysteine induce sustained injury of arterial endothelial cells, proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells and enhance expression/activity of key participants in vascular inflammation, atherogenesis, and vulnerability of the established atherosclerotic plaque. In fact, the effect of elevated ...
Printer-Friendly Version
... in the chest, back, arms, and neck; nausea; an erratic pulse; and perspiration due to a lack of blood flow to the heart. When blood flow within any of the heart's coronary arteries (the vessels delivering fresh blood to the heart) is impeded, part of the tissue starts to die--a myocardial infarction ...
... in the chest, back, arms, and neck; nausea; an erratic pulse; and perspiration due to a lack of blood flow to the heart. When blood flow within any of the heart's coronary arteries (the vessels delivering fresh blood to the heart) is impeded, part of the tissue starts to die--a myocardial infarction ...
The Heart and Circulation Review
... 5. In the diagram below, color the oxygenated blood RED, and the deoxygenated blood BLUE. Be sure to label the three types of blood vessels: artery, vein, and capillary. Also, label the four chambers of the heart! ...
... 5. In the diagram below, color the oxygenated blood RED, and the deoxygenated blood BLUE. Be sure to label the three types of blood vessels: artery, vein, and capillary. Also, label the four chambers of the heart! ...
Hypertension - Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences
... remodelling of resistance arterioles, responsible for maintaining peripheral vascular tone. These changes, which precede in time the pressure elevation, produce specific organic lesions, some clinically defined. In 90% of cases the cause is unknown which has been called "essential hypertension", wit ...
... remodelling of resistance arterioles, responsible for maintaining peripheral vascular tone. These changes, which precede in time the pressure elevation, produce specific organic lesions, some clinically defined. In 90% of cases the cause is unknown which has been called "essential hypertension", wit ...
ATRIAL SYSTOLE
... Prior to atrial systole, blood has been flowing passively from the atrium into the ventricle through the open AV valve. During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins to ...
... Prior to atrial systole, blood has been flowing passively from the atrium into the ventricle through the open AV valve. During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins to ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... the instrument used to measure blood pressure. ...
... the instrument used to measure blood pressure. ...
hypertension - University of Western States
... continues to rise. Individuals who are normotensive at 55 years of age have a 90% lifetime risk for developing hypertension. The majority of persons with isolated systolic hypertension are not adequately controlling their blood pressure despite persuasive data from clinical trials documenting the be ...
... continues to rise. Individuals who are normotensive at 55 years of age have a 90% lifetime risk for developing hypertension. The majority of persons with isolated systolic hypertension are not adequately controlling their blood pressure despite persuasive data from clinical trials documenting the be ...
Body Temperature
... water freezes and 212˚F as the point at which it boils 2. Centigrade scale: uses 0˚C as the temperature at which water freezes and 100˚C as the point at which it boils ...
... water freezes and 212˚F as the point at which it boils 2. Centigrade scale: uses 0˚C as the temperature at which water freezes and 100˚C as the point at which it boils ...
Nursing Management of the Acute Congestive Heart Failure
... Hydralazine is an arteriolar dilator. It is used to treat severe mitral regurgitation. The drug is administered orally. The vasodilating effect occurs within 30 minutes to 1 hour and peaks in 3 hours. Nitroprusside is a potent veno and arteriolar dilator. It is reserved for severe fulminant heart fa ...
... Hydralazine is an arteriolar dilator. It is used to treat severe mitral regurgitation. The drug is administered orally. The vasodilating effect occurs within 30 minutes to 1 hour and peaks in 3 hours. Nitroprusside is a potent veno and arteriolar dilator. It is reserved for severe fulminant heart fa ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... thereby rid the body of extra salt and water (regulated also by ADH). In this way salt and water homeostasis can be efficiently regulated. However, about 20% of all adults in the United States have hypertension. High-salt intake along with perhaps an inability of the kidneys to properly eliminate sa ...
... thereby rid the body of extra salt and water (regulated also by ADH). In this way salt and water homeostasis can be efficiently regulated. However, about 20% of all adults in the United States have hypertension. High-salt intake along with perhaps an inability of the kidneys to properly eliminate sa ...
File - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... •Fusiform – dilation of entire circumference •Saccular – shaped like a sac, bulging on only one side •Dissecting – inner layer tear causes a cavity to form that fills with blood with each heartbeat) AneAneurysms ...
... •Fusiform – dilation of entire circumference •Saccular – shaped like a sac, bulging on only one side •Dissecting – inner layer tear causes a cavity to form that fills with blood with each heartbeat) AneAneurysms ...
Circulatory System
... Sudden loss of 1/3 of his blood can be fatal. However if the lose rate is slow (say: 24 hours) he can lose as much as 2/3 of the blood with much risk (well documented). ...
... Sudden loss of 1/3 of his blood can be fatal. However if the lose rate is slow (say: 24 hours) he can lose as much as 2/3 of the blood with much risk (well documented). ...
Instructor`s Answer Key Chapter 14: Cardiac Output, Blood Flow
... thereby rid the body of extra salt and water (regulated also by ADH). In this way salt and water homeostasis can be efficiently regulated. However, about 20% of all adults in the United States have hypertension. High-salt intake along with perhaps an inability of the kidneys to properly eliminate sa ...
... thereby rid the body of extra salt and water (regulated also by ADH). In this way salt and water homeostasis can be efficiently regulated. However, about 20% of all adults in the United States have hypertension. High-salt intake along with perhaps an inability of the kidneys to properly eliminate sa ...
Antihypertensive drug

Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used drugs are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental goal of treatment should be the prevention of the important endpoints of hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke and heart failure. Patient age, associated clinical conditions and end-organ damage also play a part in determining dosage and type of medication administered. The several classes of antihypertensives differ in side effect profiles, ability to prevent endpoints, and cost. The choice of more expensive agents, where cheaper ones would be equally effective, may have negative impacts on national healthcare budgets. As of 2009, the best available evidence favors the thiazide diuretics as the first-line treatment of choice for high blood pressure when drugs are necessary. Although clinical evidence shows calcium channel blockers and thiazide-type diuretics are preferred first-line treatments for most people (from both efficacy and cost points of view), an ACE inhibitor is recommended by NICE in the UK for those under 55 years old.