The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
... This device is a simplified version of a television tube that sends a beam of electrons (a cathode ray) from one end of the tube to another, striking a phosphorescent screen on the other end. In cross-section, the CRT appears as follows: ...
... This device is a simplified version of a television tube that sends a beam of electrons (a cathode ray) from one end of the tube to another, striking a phosphorescent screen on the other end. In cross-section, the CRT appears as follows: ...
Unit 15 Electrochemistry
... The more positive the Eored value for a half reaction, the greater the tendency for the reactant of the half reaction to be reduced and, therefore, to oxidize another species The half reaction with the smallest reduction potential is most easily reversed as an oxidation The Eored table acts as an a ...
... The more positive the Eored value for a half reaction, the greater the tendency for the reactant of the half reaction to be reduced and, therefore, to oxidize another species The half reaction with the smallest reduction potential is most easily reversed as an oxidation The Eored table acts as an a ...
Electrochemistry of Fuel Cell
... 2. Principle of Electricity Generation by Fuel Cells 3. Electricity Generation Characteristics of Fuel Cells 4. Fuel Cell Efficiency Glossary Bibliography Biographical Sketch Summary ...
... 2. Principle of Electricity Generation by Fuel Cells 3. Electricity Generation Characteristics of Fuel Cells 4. Fuel Cell Efficiency Glossary Bibliography Biographical Sketch Summary ...
Test Objectives for Unit 11: Oxidation/Reduction
... Use Table J to predict whether a particular redox reaction will occur or not. Use a table of standard electrode potentials to determine whether a particular redox reaction will occur or not. Relate chemical activity to oxidizing and reducing strength. Explain the concept of disproportionation. In an ...
... Use Table J to predict whether a particular redox reaction will occur or not. Use a table of standard electrode potentials to determine whether a particular redox reaction will occur or not. Relate chemical activity to oxidizing and reducing strength. Explain the concept of disproportionation. In an ...
Electrochemistry
... tube of an electrolyte that connects two voltaic half-cells allowing ions to move between compartments without mixing. ...
... tube of an electrolyte that connects two voltaic half-cells allowing ions to move between compartments without mixing. ...
Galvanic Cell Lab
... positive electrode. The positive electrode is called the cathode. Reduction reactions take place at the cathode. Ions in the electrolyte surrounding the cathode gain the electrons and form solids. The two electrolytes surrounding the cathode and the anode are connected with a salt bridge to allow ne ...
... positive electrode. The positive electrode is called the cathode. Reduction reactions take place at the cathode. Ions in the electrolyte surrounding the cathode gain the electrons and form solids. The two electrolytes surrounding the cathode and the anode are connected with a salt bridge to allow ne ...
HYDROGEN FUEL CELLS & ENERGY EFFICIENCY
... By: Claudio Bolzoni David Carlos Echeverria Andres Segura Dari Seo ...
... By: Claudio Bolzoni David Carlos Echeverria Andres Segura Dari Seo ...
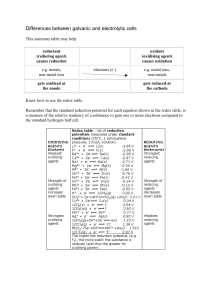
Differences between galvanic and electrolytic cells
... (reducing agent) causes reduction e.g. metals, non-metal ions gets oxidized at the anode ...
... (reducing agent) causes reduction e.g. metals, non-metal ions gets oxidized at the anode ...