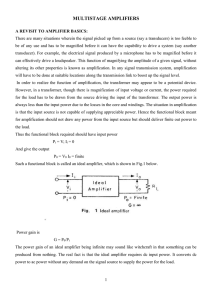
One of the first things you learn about operational amplifiers (op
... across it, from the output to the −input. When you put some input current into the −input (also known as the summing point), the gain is so high that all of the current must go through the feedback resistor. So, the output will be VOUT = −(IIN × RF). That's neat (Fig. 1). While we used to call this ...
... across it, from the output to the −input. When you put some input current into the −input (also known as the summing point), the gain is so high that all of the current must go through the feedback resistor. So, the output will be VOUT = −(IIN × RF). That's neat (Fig. 1). While we used to call this ...
Using Op Amps as Comparators INTRODUCTION by James Bryant
... A comparator has low offset, high gain, and high common-mode rejection. So does an op amp. So what is the difference? A comparator has a logic output that indicates which of the two inputs is at a higher potential. If its output is TTL or CMOS compatible (and many comparators are), it is always inte ...
... A comparator has low offset, high gain, and high common-mode rejection. So does an op amp. So what is the difference? A comparator has a logic output that indicates which of the two inputs is at a higher potential. If its output is TTL or CMOS compatible (and many comparators are), it is always inte ...
LF155/LF156/LF256 LF257 LF355 LF356
... The Temperature Coefficient of the adjusted input offset voltage changes only a small amount (0.5 μV/°C typically) for each mV of adjustment from its original unadjusted value. Common-mode rejection and open-loop voltage gain are also unaffected by offset adjustment. The input bias currents are junc ...
... The Temperature Coefficient of the adjusted input offset voltage changes only a small amount (0.5 μV/°C typically) for each mV of adjustment from its original unadjusted value. Common-mode rejection and open-loop voltage gain are also unaffected by offset adjustment. The input bias currents are junc ...
IN
... The gain of the transfer function between the plant output and an additive load disturbance input of frequency 2π Tu in closed loop with a P-controller designed according to the Ziegler-Nichols tuning rule as given above is (A) –1.0 ...
... The gain of the transfer function between the plant output and an additive load disturbance input of frequency 2π Tu in closed loop with a P-controller designed according to the Ziegler-Nichols tuning rule as given above is (A) –1.0 ...
FAN400A — Low-Power Green-Mode PWM Flyback Power Controller without Secondary Feedback
... The required startup current is only 8μA. This allows a high-resistance, low-wattage startup resistor to supply the controller’s startup power. A 1.5 MΩ/0.25W startup resistor can be used over a wide input range (100V240VAC) with very little power loss. ...
... The required startup current is only 8μA. This allows a high-resistance, low-wattage startup resistor to supply the controller’s startup power. A 1.5 MΩ/0.25W startup resistor can be used over a wide input range (100V240VAC) with very little power loss. ...
Making the Most of a Low-Power, High-Speed
... By comparing the OPA890 with the OPA683, we can see the clear advantage of using a current-feedback amplifier for high-gain applications. If we tried to use the OPA890 in a 100V/V application, we would achieve a 1.3MHz, –3dB bandwidth. This performance pales in comparison with the 35MHz bandwidth of ...
... By comparing the OPA890 with the OPA683, we can see the clear advantage of using a current-feedback amplifier for high-gain applications. If we tried to use the OPA890 in a 100V/V application, we would achieve a 1.3MHz, –3dB bandwidth. This performance pales in comparison with the 35MHz bandwidth of ...
ISSCC 2014 Digest of Technical Papers
... its column-driver ICs, ultra-low power and area circuit solutions are continuously urged to meet the market pressure on cost, image quality and display size. Multi-stage amplifiers have dominated those buffers due to their reliable DC gain, output swing, gain-bandwidth product (GBW) and slew rate (S ...
... its column-driver ICs, ultra-low power and area circuit solutions are continuously urged to meet the market pressure on cost, image quality and display size. Multi-stage amplifiers have dominated those buffers due to their reliable DC gain, output swing, gain-bandwidth product (GBW) and slew rate (S ...
a 250 MHz, 10 ns Switching Multiplexers w/Amplifier AD8170/AD8174
... mA of output current. They offer –3 dB signal bandwidth of 250 MHz and slew rate of greater than 1000 V/µs. Additionally, the AD8170 and AD8174 have excellent video specifications with low differential gain and differential phase error of 0.02% and 0.05° and 0.1 dB flatness out to 80 MHz. With a low ...
... mA of output current. They offer –3 dB signal bandwidth of 250 MHz and slew rate of greater than 1000 V/µs. Additionally, the AD8170 and AD8174 have excellent video specifications with low differential gain and differential phase error of 0.02% and 0.05° and 0.1 dB flatness out to 80 MHz. With a low ...
AN18 - Power Gain Stages for Monolithic Amplifiers
... feedback loop so that its offset voltage and gain errors are negligible. At higher frequencies, feedback is through Cf, so that phase shift from the load capacitance acting against the buffer output resistance does not cause loop instability. Small-signal bandwidth is reduced by Cf, but considerable ...
... feedback loop so that its offset voltage and gain errors are negligible. At higher frequencies, feedback is through Cf, so that phase shift from the load capacitance acting against the buffer output resistance does not cause loop instability. Small-signal bandwidth is reduced by Cf, but considerable ...
UC29431 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The UC39431 is an adjustable shunt voltage regulator with 100mA sink capability. The architecture, comprised of an error amplifier and transconductance amplifier, gives the user separate control of the small signal error voltage frequency response along with a fixed linear transconductance. A minimu ...
... The UC39431 is an adjustable shunt voltage regulator with 100mA sink capability. The architecture, comprised of an error amplifier and transconductance amplifier, gives the user separate control of the small signal error voltage frequency response along with a fixed linear transconductance. A minimu ...
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive.Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, but it also occurs naturally within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering.