chapter #4 - oscillator
... Duty cycles can be adjusted by values of R1 and R2. The duty cycle is limited to 50% with this arrangement. To have duty cycles less than 50%, a diode is placed across R2. The two formulas show the relationship. ...
... Duty cycles can be adjusted by values of R1 and R2. The duty cycle is limited to 50% with this arrangement. To have duty cycles less than 50%, a diode is placed across R2. The two formulas show the relationship. ...
Design Methodology for Common-Mode Stability of
... to regulate their output CM voltage. The input and output of the CMFB amplifier are the output of the main amplifier. This means that the CMFB amplifier is connected in unity feedback. As a result, its stabilization is usually troublesome since amplifiers are more prone to instability when they are ...
... to regulate their output CM voltage. The input and output of the CMFB amplifier are the output of the main amplifier. This means that the CMFB amplifier is connected in unity feedback. As a result, its stabilization is usually troublesome since amplifiers are more prone to instability when they are ...
9T Low Swing SRAM
... link. In the case of the SRAM register file a read will pull down the voltage on one of the two lines while pulling up the other in proportion to the pull-down strength of the SRAM and the pull-up strength of the line. If there is no read during the next cycle, the SRAM will automatically reset both ...
... link. In the case of the SRAM register file a read will pull down the voltage on one of the two lines while pulling up the other in proportion to the pull-down strength of the SRAM and the pull-up strength of the line. If there is no read during the next cycle, the SRAM will automatically reset both ...
RHK Technology Brief
... Early current-to-voltage converters used in STMs contained a simple design utilizing a single operational amplifier as shown in Figure 1. The gain is determined by the ratio of R1 and R2 and the bandwidth is determined by the product of R1 and the unavoidable stray capacitance of the tip along with ...
... Early current-to-voltage converters used in STMs contained a simple design utilizing a single operational amplifier as shown in Figure 1. The gain is determined by the ratio of R1 and R2 and the bandwidth is determined by the product of R1 and the unavoidable stray capacitance of the tip along with ...
AN1308: A Unique Coax Cable Driver Circuit with Common
... with a resistor RL equal to the impedance of the cable. This termination resistor is located between the output of the cable and the local ground (here called “point A”). The ground reference at point A differs in potential from the ground reference at the source. This difference is represented by t ...
... with a resistor RL equal to the impedance of the cable. This termination resistor is located between the output of the cable and the local ground (here called “point A”). The ground reference at point A differs in potential from the ground reference at the source. This difference is represented by t ...
AN-1718 Differential Amplifier Applications Up
... The LMH6515 is an open collector topology and has the option of two different output configurations. Each output has an on chip 200Ω pull-up resistor. In addition, there is an internal 400Ω resistor between the two outputs. This results in a 200Ω or a 400Ω differential load in parallel with the exte ...
... The LMH6515 is an open collector topology and has the option of two different output configurations. Each output has an on chip 200Ω pull-up resistor. In addition, there is an internal 400Ω resistor between the two outputs. This results in a 200Ω or a 400Ω differential load in parallel with the exte ...
Please click here for the LP7-4 instruction manual - Pac
... PAC L.O.C.PRO™ interfaces have been professionally designed for those who want the very best. ...
... PAC L.O.C.PRO™ interfaces have been professionally designed for those who want the very best. ...
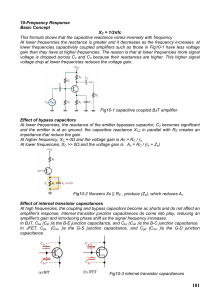
10-Frequency Response Basic Concept XC = 1/2πfc This formula
... voltage is lost due to a voltage-divider effect of the source resistance and the reactance of Cbe Fig10-4(a). When the reactance of Cbc (or Cgd ) becomes small enough, a significant amount of output signal voltage is fed back out of phase with the input (negative feedback), thus effectively reducing ...
... voltage is lost due to a voltage-divider effect of the source resistance and the reactance of Cbe Fig10-4(a). When the reactance of Cbc (or Cgd ) becomes small enough, a significant amount of output signal voltage is fed back out of phase with the input (negative feedback), thus effectively reducing ...
abstract - Engineering For Change
... components. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more AC or DC voltages. With the exception of passive shunt regulators, all modern electronic voltage regulators operate by comparing the actual output voltage to some internal fixed reference voltage. Any difference is amplified ...
... components. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more AC or DC voltages. With the exception of passive shunt regulators, all modern electronic voltage regulators operate by comparing the actual output voltage to some internal fixed reference voltage. Any difference is amplified ...
Getting the Full Potential from Your ADC (Rev. B)
... From these ratios the resistor values were chosen to be R1 = R3 = 100kΩ, R2 = R4 = 200kΩ. The pseudodifferential value, [+In – (–In)], corresponds to a 2.5Vp-p. A PGA setting of 2 maintains the full-scale range of this device. Without the PGA this circuit [(+In) – (–In)] would only make use of half ...
... From these ratios the resistor values were chosen to be R1 = R3 = 100kΩ, R2 = R4 = 200kΩ. The pseudodifferential value, [+In – (–In)], corresponds to a 2.5Vp-p. A PGA setting of 2 maintains the full-scale range of this device. Without the PGA this circuit [(+In) – (–In)] would only make use of half ...
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive.Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, but it also occurs naturally within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering.