The Human Body
... where it picks up oxygen (4). The now oxygen-rich blood is carried back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins (5). When the left atrium contracts, blood goes through a valve into the left ventricle (6). When the left ventricle contracts, blood is pumped through a valve and into the aorta (7 ...
... where it picks up oxygen (4). The now oxygen-rich blood is carried back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins (5). When the left atrium contracts, blood goes through a valve into the left ventricle (6). When the left ventricle contracts, blood is pumped through a valve and into the aorta (7 ...
Document
... In multicellular organisms specialized structures have been formed for different functions e.g., ingestion, egestion, exchange of gases. 7. Transportation:- In multicellular organisms, all the cells are not in direct contact with the environment. They have specific structures for exchange of gases, ...
... In multicellular organisms specialized structures have been formed for different functions e.g., ingestion, egestion, exchange of gases. 7. Transportation:- In multicellular organisms, all the cells are not in direct contact with the environment. They have specific structures for exchange of gases, ...
KCSE ONLINE REVISION BIOLOGY FORM 4 NOTES This
... a gradual change in living organisms from simple life forms to more complex forms over a long period of time. ii) Differentiate organic evolution from chemical evolution as theories of origin of life organic evolution refers to the emergence of present forms of organisms gradually from pre-exist ...
... a gradual change in living organisms from simple life forms to more complex forms over a long period of time. ii) Differentiate organic evolution from chemical evolution as theories of origin of life organic evolution refers to the emergence of present forms of organisms gradually from pre-exist ...
How Then Should We As Christians Respond?
... aberration, could have been formed by natural selection , seems, I freely confess, absurd in the highest possible degree. … The belief that an organ as perfect as the eye could have formed by natural selection is more than enough to stagger anyone.” Charles Darwin @ Dr. Heinz Lycklama ...
... aberration, could have been formed by natural selection , seems, I freely confess, absurd in the highest possible degree. … The belief that an organ as perfect as the eye could have formed by natural selection is more than enough to stagger anyone.” Charles Darwin @ Dr. Heinz Lycklama ...
File - Science with Mr. Davis
... laboratory is to introduce you to the microscopes that you will use to observe many biological structures and processes during this course. The familiarity that you gain with this exercise will allow you to spend your time in subsequent labs more effectively. The microscope used most frequently in t ...
... laboratory is to introduce you to the microscopes that you will use to observe many biological structures and processes during this course. The familiarity that you gain with this exercise will allow you to spend your time in subsequent labs more effectively. The microscope used most frequently in t ...
Sally Student O`Rourke Elementary Ms. O`Brien 2005-2006
... so it is able to float on top of it. If you were to add some other objects to this glass they would float or sink according to their densities. • Water in its liquid form is called ice. A unique property of water is that solid water is less dense than liquid water. This means that ice floats. You ha ...
... so it is able to float on top of it. If you were to add some other objects to this glass they would float or sink according to their densities. • Water in its liquid form is called ice. A unique property of water is that solid water is less dense than liquid water. This means that ice floats. You ha ...
2010
... organs. (ii) A plant with sunken stomata. (iii) A foreign body that induces the formation of antibodies in the body. (iv) The place where fertilization occurs in the female reproductive system. (v) An organization that looks after maternal and child welfare centres. [5] (b) State whether the followi ...
... organs. (ii) A plant with sunken stomata. (iii) A foreign body that induces the formation of antibodies in the body. (iv) The place where fertilization occurs in the female reproductive system. (v) An organization that looks after maternal and child welfare centres. [5] (b) State whether the followi ...
LABORATORY
... the eyepiece separation just like you do a pair of binoculars. Make sure that the substage condenser is in its highest position. Use the coarse adjustment knob to slowly move the slide and the objective lens apart. When the image becomes clear, switch to the fine adjustment know to make the image sh ...
... the eyepiece separation just like you do a pair of binoculars. Make sure that the substage condenser is in its highest position. Use the coarse adjustment knob to slowly move the slide and the objective lens apart. When the image becomes clear, switch to the fine adjustment know to make the image sh ...
C - bYTEBoss
... How can a student decide if a cell is from a plant or an animal? A If the cell has a cell wall, it must be from a plant. B If the cell has cytoplasm, it must be from a plant. C If the cell has a nucleus, it must be from an animal. D If the cell has a cell membrane, it must be from an animal. ...
... How can a student decide if a cell is from a plant or an animal? A If the cell has a cell wall, it must be from a plant. B If the cell has cytoplasm, it must be from a plant. C If the cell has a nucleus, it must be from an animal. D If the cell has a cell membrane, it must be from an animal. ...
3rd to 5th grade - The Health Museum
... much light is available, it gets bigger and smaller. Lens: Clear structure that focuses incoming light onto the back of the eye. Retina: Back surface of the eyeball. Light is focused onto the retina where special cells called rods and cones take information about the light and send it to the brain t ...
... much light is available, it gets bigger and smaller. Lens: Clear structure that focuses incoming light onto the back of the eye. Retina: Back surface of the eyeball. Light is focused onto the retina where special cells called rods and cones take information about the light and send it to the brain t ...
Bioluminescence
... • Fish such as the anglerfish use a light organ filled with bacteria that dangles from their forehead. • Prey are attracted to the light in the same way that a fisherman might use a glowing lure for night fishing. • Some fish use bioluminescence as a flashlight. They use light, produced by symbiotic ...
... • Fish such as the anglerfish use a light organ filled with bacteria that dangles from their forehead. • Prey are attracted to the light in the same way that a fisherman might use a glowing lure for night fishing. • Some fish use bioluminescence as a flashlight. They use light, produced by symbiotic ...
BIOL 202 LAB 10 Mollusca and Annelida
... bilaterally symmetrical, unsegmented organisms that have a true coelom and welldeveloped organ systems. Molluscs possess four major morphological features that distinguish them from other invertebrates: (1) a protective shell (reduced in some species), (2) a mantle, (3) a visceral mass which houses ...
... bilaterally symmetrical, unsegmented organisms that have a true coelom and welldeveloped organ systems. Molluscs possess four major morphological features that distinguish them from other invertebrates: (1) a protective shell (reduced in some species), (2) a mantle, (3) a visceral mass which houses ...
Ciliary Body
... aB-crystallin is a widely and constitutively expressed member of the small heat shock proteins family and is inducible by heat and other forms of stress. True g-crystallin tends to be concentrated in the nuclear region of the lens, as it is abundantly expressed early in development. True M ...
... aB-crystallin is a widely and constitutively expressed member of the small heat shock proteins family and is inducible by heat and other forms of stress. True g-crystallin tends to be concentrated in the nuclear region of the lens, as it is abundantly expressed early in development. True M ...
35 Arthropods and Echinoderms AP Biology
... the skin to try and reach each cell; is that is allows the animal to grow bigger (and therefore more complex). We also address two other very important concerns: (a.) the need to conserve water, (b.) the need to be more complex (i.e. isolate functions) so that it is more difficult to be killed. If w ...
... the skin to try and reach each cell; is that is allows the animal to grow bigger (and therefore more complex). We also address two other very important concerns: (a.) the need to conserve water, (b.) the need to be more complex (i.e. isolate functions) so that it is more difficult to be killed. If w ...
Science 8 - FR Haythorne Junior High
... A. red C. violet B. green D. orange 19. As frequency increases, this will happen to the wavelength. A. They get longer and less frequent C. They get shorter and less frequent B. They get longer and more frequent D. They get shorter and more frequent 20. Which of the following types of electromagneti ...
... A. red C. violet B. green D. orange 19. As frequency increases, this will happen to the wavelength. A. They get longer and less frequent C. They get shorter and less frequent B. They get longer and more frequent D. They get shorter and more frequent 20. Which of the following types of electromagneti ...
Light passes through transparent objects easily. Translucent objects
... convex lens ('kän·veks 'lenz) a lens that focuses light concave lens (kän·'k&v 'lenz) a lens that causes light to spread out ...
... convex lens ('kän·veks 'lenz) a lens that focuses light concave lens (kän·'k&v 'lenz) a lens that causes light to spread out ...
Hermansky Pudlak
... A curved window called the cornea first focuses the light. The light then passes through a hole called the pupil. A circle of muscle called the iris surrounds the pupil. The iris is the coloured part of the eye. The light is then focused onto the back of the eye by a lens. Tiny light sensitive patch ...
... A curved window called the cornea first focuses the light. The light then passes through a hole called the pupil. A circle of muscle called the iris surrounds the pupil. The iris is the coloured part of the eye. The light is then focused onto the back of the eye by a lens. Tiny light sensitive patch ...
1 - Quia
... b) catabolism- A complex, metabolic process in which energy is liberated for use in work, energy storage, or heat production by the destruction of complex substances by living cells to form simple compounds. Carbon dioxide and water are produced, as well as energy. c) metabolism- The aggregate of al ...
... b) catabolism- A complex, metabolic process in which energy is liberated for use in work, energy storage, or heat production by the destruction of complex substances by living cells to form simple compounds. Carbon dioxide and water are produced, as well as energy. c) metabolism- The aggregate of al ...
SensesHHAP
... ◦ Cones: blue, red, green cones, each sensitive to a different wavelength Cones are densest near the fovea centralis (center of macula):area of retina with only cones ...
... ◦ Cones: blue, red, green cones, each sensitive to a different wavelength Cones are densest near the fovea centralis (center of macula):area of retina with only cones ...
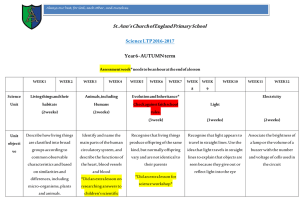
y6 science ltp autumn 2016-17 - St Ann`s Church of England Primary
... Assessment week* needs to be an hour at the end of a lesson ...
... Assessment week* needs to be an hour at the end of a lesson ...
Ch16.Special.Senses.Part1
... – Neural layer ends at the posterior margin of the ciliary body – Pigmented layer covers ciliary body & posterior surface of the iris ...
... – Neural layer ends at the posterior margin of the ciliary body – Pigmented layer covers ciliary body & posterior surface of the iris ...
Summative Assessment 4
... eight short answer questions, an opportunity for students to select the body systems, and one opportunity for written explanations of the selected systems. The language arts section, page two, contains a paragraph and four related questions. Teacher Directions: Distribute the assessments. Instruct s ...
... eight short answer questions, an opportunity for students to select the body systems, and one opportunity for written explanations of the selected systems. The language arts section, page two, contains a paragraph and four related questions. Teacher Directions: Distribute the assessments. Instruct s ...
Biology
... cells (multicellular - allows “specialization” of cells). Cell = basic unit of life and contains the “genetic code” Living things are organized at both the cellular level (organelles have specific tasks) and the multicellular level: cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems And they can maintain t ...
... cells (multicellular - allows “specialization” of cells). Cell = basic unit of life and contains the “genetic code” Living things are organized at both the cellular level (organelles have specific tasks) and the multicellular level: cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems And they can maintain t ...
creatures
... and for the correction of spherical and chromatic aberration, could have been formed by natural selection , seems, I freely confess, absurd in the highest possible degree. … The belief that an organ as perfect as the eye could have formed by natural selection is more than enough to stagger anyone.” ...
... and for the correction of spherical and chromatic aberration, could have been formed by natural selection , seems, I freely confess, absurd in the highest possible degree. … The belief that an organ as perfect as the eye could have formed by natural selection is more than enough to stagger anyone.” ...
Evolution of the eye
The evolution of the eye has been a subject of significant study, as a distinctive example of an analogous organ present in a wide variety of taxa. Complex, image-forming eyes evolved independently some 50 to 100 times.Complex eyes appear to have first evolved within a few million years, in the rapid burst of evolution known as the Cambrian explosion. There is no evidence of eyes before the Cambrian, but a wide range of diversity is evident in the Middle Cambrian Burgess shale, and the slightly older Emu Bay Shale. Eyes show a wide range of adaptations to meet the requirements of the organisms which bear them. Eyes vary in their visual acuity, the range of wavelengths they can detect, their sensitivity in low light levels, their ability to detect motion or resolve objects, and whether they can discriminate colours.